7 Powerful Facts About Milk Ducts & Breastfeeding
Introduction to Milk Ducts
Milk ducts are an integral part of the female breast anatomy, playing a crucial role in the process of breastfeeding. These tubular structures serve as conduits for the transport of milk from the lobules, where it is produced, to the nipple, facilitating lactation. In a typically developed breast, there are several milk ducts, and each duct is lined with epithelial cells that assist in the secretion and movement of milk. The arrangement and number of ducts can vary among individuals, but their primary function remains consistent: to ensure that infants receive nourishment during breastfeeding.
During pregnancy and the lactation period, hormonal changes encourage the development of milk ducts as well as the surrounding glandular tissue, which is responsible for milk production. This transformation is essential for preparing the mother’s body to provide adequate milk supply to the newborn. Understanding the anatomy of milk ducts aids in comprehending their function and the overall mechanics of breastfeeding. Each duct leads to a nipple pore, allowing milk to flow freely when the infant suckles, highlighting the seamless integration of anatomy and function.
In addition to their primary role in lactation, milk ducts can also be susceptible to various issues, which can impact breastfeeding. Conditions such as ductal obstruction, infections, and inflammation can lead to complications that hinder the normal flow of milk. It is essential to be aware of these potential issues, as they may require medical attention to ensure the health of both the mother and child. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore these common issues and the implications for lactation, further emphasizing the importance of understanding milk ducts in the broader context of breastfeeding anatomy.
Anatomy of Milk Ducts
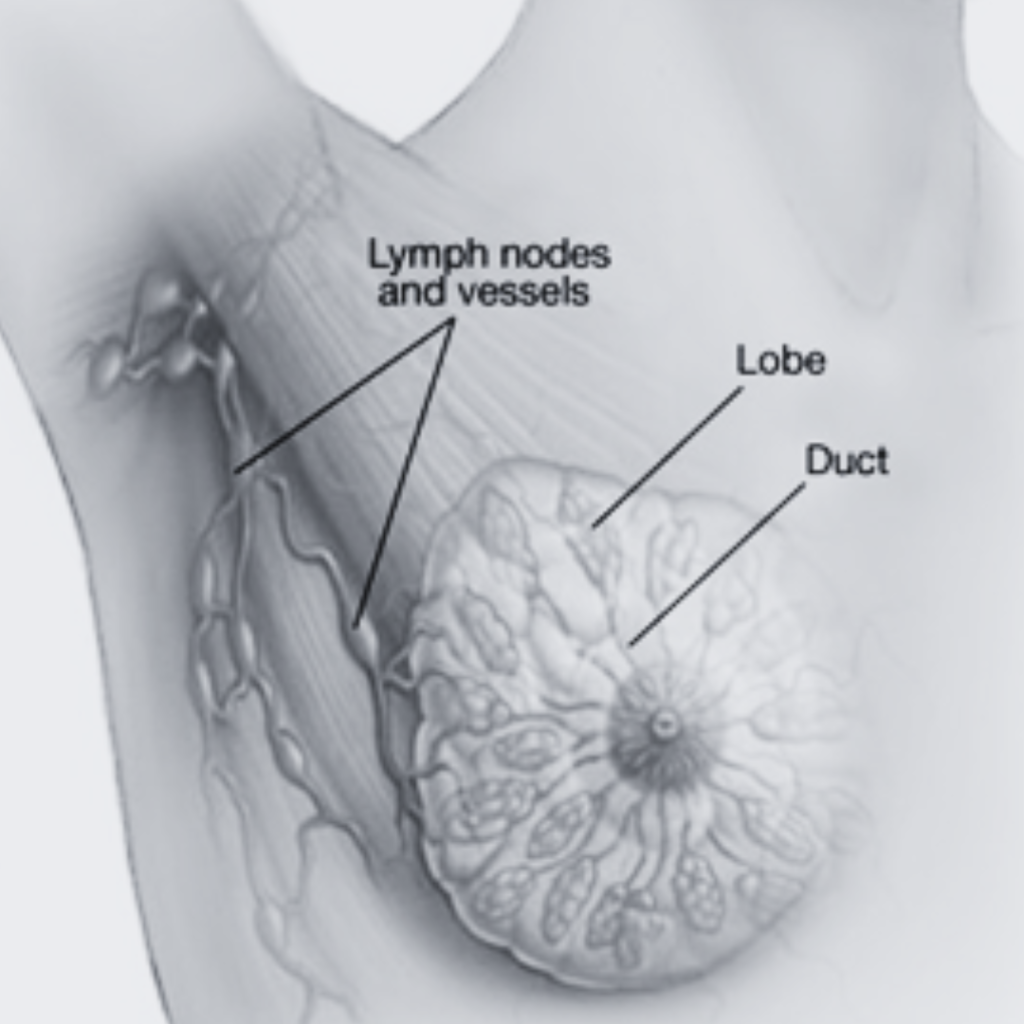
The anatomy of milk ducts is fundamental for understanding both their function and potential issues that may arise. Milk ducts are tubular structures that facilitate the transportation of milk from the lobules, which are cluster-like glandular structures, to the nipple. In women, milk ducts, alongside lobules and alveoli, form a crucial system within the breast, playing a central role in lactation.
Milk ducts are primarily located beneath the surface of the breast tissue, branching out in a configuration that resembles the structure of a tree. Each breast typically contains 15 to 20 milk ducts originating from the lobules. These ducts converge into larger ducts, which ultimately lead to the nipple. This intricate network not only serves the functional purpose of enabling breastfeeding but also connects the breast tissue to the surrounding lymphatic and vascular systems. Such a connection is vital, as it helps maintain the overall health and functionality of breast tissues.
The ducts are lined with epithelial cells that help in the regulation of milk flow. During lactation, hormonal signals trigger the expansion of the ducts, preparing them to transport milk efficiently. Surrounding the ducts, various connective tissues provide structural support and contribute to the overall shape and resilience of the breast.
Understanding the anatomy of milk ducts is essential, as it allows individuals to recognize the normal structure of breast tissue, thereby aiding in identifying any abnormalities. Common issues related to milk ducts, such as blockages or inflammation, can lead to discomfort and complications during breastfeeding. In subsequent sections, we will delve further into these issues and the importance of monitoring breast health to ensure optimal functioning of the milk ducts.
The Function of Milk Ducts
Milk ducts play a pivotal role in the process of lactation, serving as the conduits for milk produced by the mammary glands to travel from the lobules to the nipple. Each lobule contains clusters of alveoli, the structures responsible for the secretion of milk due to hormonal stimulation. During pregnancy, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes, particularly with the rise in levels of prolactin, which is essential for milk synthesis.
Once the baby begins to feed, oxytocin is released, leading to the contraction of myoepithelial cells surrounding the alveoli. This contraction pushes the milk into the milk ducts, initiating the transport process. Each milk duct opens at the nipple, allowing for the delivery of milk during breastfeeding. The system is remarkably efficient, designed to respond to the infant’s needs; the more the baby suckles, the more effectively the milk is produced and released.
The interplay of hormones is crucial in regulating the function of milk ducts. Prolactin promotes milk production, while oxytocin facilitates milk ejection. Additionally, estrogen and progesterone also play roles during pregnancy, preparing the milk ducts and lobules for lactation. After childbirth, the levels of these hormones shift, allowing for the full initiation of milk production and transportation through the ducts. This process is essential not only for feeding the infant but also for maintaining the overall health of the mother by stimulating breast tissue and promoting maternal-infant bonding.
Understanding the function of milk ducts is vital for recognizing and addressing common lactation issues. Anomalies in milk duct function can lead to problems such as engorgement, plugged ducts, or mastitis, which may be detrimental to both mother and child. Increased awareness of these functions can enhance breastfeeding experiences and inform health practices regarding lactation.

Common Issues Related to Milk Ducts
Milk ducts play a crucial role in lactation, facilitating the transport of breast milk from the lobules to the nipple. However, various issues can arise that may impede their function. One common concern is the blockage of milk ducts, which often occurs when milk remains in the ducts for an extended period, leading to engorgement. Symptoms of a blocked milk duct typically include localized tenderness, swelling, and a lump in the breast, often accompanied by discomfort during breastfeeding. If not addressed promptly, blockages can develop into infections, such as mastitis, characterized by fever, chills, and redness in the area surrounding the affected duct.
Infection of milk ducts is a significant concern for breastfeeding individuals. If bacteria enter the breast tissue through cracked nipples or clogged ducts, it can lead to mastitis, necessitating immediate medical attention. Treatment often involves antibiotics and may require frequent breastfeeding or pumping to maintain milk flow and alleviate pressure.
Another serious issue is the potential for ductal carcinoma, a type of breast cancer that can originate in the milk ducts. Symptoms may include discharge from the nipple, changes in breast shape or texture, and persistent lumps. Regular breast self-exams and clinical evaluations are essential for early detection. Women must be vigilant about any unusual changes, as timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Ultimately, understanding these common milk duct issues is vital for maintaining optimal breast health and ensuring successful breastfeeding. Regular monitoring and prompt action upon noticing signs of complications can prevent the escalation of problems, facilitating a smoother breastfeeding experience while safeguarding overall breast health.
Impact of Blocked Milk Ducts
Blocked milk ducts can significantly affect a breastfeeding mother’s experience, leading to both physical discomfort and emotional distress. These ducts, which transport milk from the lobules to the nipple, can become obstructed for various reasons. One common cause is inadequate emptying of the breast during feeding or pumping. When milk is not fully removed, it can accumulate and create a blockage. Additionally, factors such as tight-fitting bras, sudden changes in breastfeeding routine, or stress can contribute to this condition.
Symptoms of blocked milk ducts typically include localized pain or discomfort in the breast, swelling, and the presence of a hard lump. Mothers may also experience redness in the affected area and, in some cases, flu-like symptoms if the blockage progresses to infection, known as mastitis. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective management and maintaining a healthy breastfeeding journey.
To relieve a blocked milk duct, several evidence-based methods can be employed. Encouraging frequent breastfeeding is paramount, as this aids in relieving the blockage by facilitating adequate milk drainage. Additionally, applying warm compresses to the affected area before feeding can help soften the duct and ease milk flow. Massage can also be beneficial; gently massaging the area towards the nipple during breastfeeding promotes the release of trapped milk.
Preventive care is essential for minimizing the risk of future blockages. Mothers should prioritize emptying their breasts completely during each feeding session and consider adjusting their breastfeeding positions to ensure the complete evacuation of milk. Furthermore, maintaining proper fitting of nursing bras and managing stress through relaxation techniques can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing blocked ducts. By adopting these strategies, mothers can improve their breastfeeding experience and reduce complications associated with blocked milk ducts.
Milk Ducts and Breastfeeding
Milk ducts play a critical role in the breastfeeding process, serving as the channels through which milk is transported from the mammary glands to the nipple. During nursing, the infant’s sucking stimulates the mother’s body to release oxytocin, a hormone that causes the milk ducts to contract and deliver milk to the baby. This natural reflex is essential for successful breastfeeding, affecting not only the infant’s nourishment but also the overall bonding experience between mother and child.
To ensure a successful breastfeeding experience, proper positioning of the infant is paramount. Mothers should aim for a comfortable hold that allows the baby to latch deeply onto the nipple, ensuring effective suckling. A good latch helps to effectively empty the breast, which in turn keeps the milk ducts healthy and functioning optimally. Additionally, mothers should be mindful of their own comfort and alignment, as this can impede or enhance milk flow.
However, breastfeeding can sometimes lead to challenges related to milk ducts. Blocked milk ducts are a common issue that can arise when milk is not adequately removed. Symptoms may include localized pain, engorgement, and redness in the affected area. To manage these challenges, it is advisable for mothers to frequently nurse or express milk to relieve pressure and encourage drainage. Gentle massage, warm compresses, and changing nursing positions can also help alleviate discomfort and clear any blockages. In more severe cases, consulting a healthcare professional may be necessary to address persistent issues.
Understanding the anatomy and function of milk ducts is crucial for nursing mothers. By implementing effective breastfeeding techniques and addressing any issues that arise, mothers can support both their own health and their baby’s nutritional needs. Ensuring that milk ducts remain clear and functional is key to a successful breastfeeding journey.

Diagnostic Techniques for Milk Duct Concerns
When it comes to assessing the health of milk ducts, several diagnostic techniques have been developed to provide clarity and understanding of potential issues. Milk ducts, which play a crucial role in the breastfeeding process, can sometimes encounter various concerns that require medical attention. Appropriate diagnostic methods allow healthcare providers to monitor and evaluate the condition of these ducts effectively.
One of the primary imaging techniques used for evaluating milk duct health is the mammogram. This method utilizes low-dose X-rays to create detailed images of the breast tissue, allowing radiologists to identify abnormalities such as blockages or cysts within the ducts. It is recommended as a routine screening tool for women, especially those over the age of 40, or if they present with specific symptoms. During this procedure, patients typically experience some pressure against their breasts as the images are taken, but the process usually lasts only a few moments.
Ultrasounds are another essential diagnostic tool used to examine milk ducts. This technique employs sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, and it can be particularly beneficial for assessing solid masses or fluid-filled cysts. An ultrasound is non-invasive, painless, and does not require exposure to radiation, making it a preferable option in many cases, especially for younger women or during pregnancy.
In addition to imaging methods, physical examinations performed by healthcare professionals are imperative for identifying any palpable issues associated with milk ducts. Healthcare providers may check for signs of infections, pain, or discharge. Patients can expect to discuss their medical history and any symptoms they are experiencing, which will help in formulating a comprehensive diagnostic approach. By employing these varied techniques, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions regarding treatment and management of milk duct concerns.
Treatment Options for Milk Duct Problems
Milk duct issues can manifest in various forms, including blockages, infections, or cysts, leading to discomfort, pain, or other complications. Treatment options can vary based on the severity and type of the problem. Non-medical interventions can often be effective for minor issues. For instance, warm compresses applied to the affected area can help alleviate pain and may assist in unclogging a blocked duct. Gentle massage of the breast tissue can also encourage milk flow, particularly in cases of engorgement or mild clogging. Women are encouraged to frequently nurse or pump milk to aid in resolving these issues, as this can help clear any obstructions in the ducts. Staying hydrated and ensuring a balanced diet can further support breast health.
However, medical interventions might be necessary for more severe or persistent problems. If a blockage does not resolve with conservative measures after a reasonable period, or if there are signs of infection such as fever or increasing pain, it is crucial to seek professional help. A healthcare provider may recommend antibiotics if an infection is present. In cases where a milk duct is chronically blocked, a procedure known as ductal lavage may be performed, which involves flushing out the duct to clear any obstructions.
For women experiencing recurrent issues, imaging tests may be recommended to identify underlying problems such as fibrocystic changes or other anatomical abnormalities. In rare situations, surgical intervention may be indicated to remove obstructive lesions or resolve significant blockages. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before proceeding with any treatment to ensure appropriate management tailored to individual needs. Recognizing when to seek help is crucial in maintaining breast health and alleviating discomfort.
FAQs about Milk Ducts
Understanding milk ducts is essential for both breastfeeding individuals and those experiencing breast-related concerns. Below are some frequently asked questions regarding milk ducts, providing clear answers to common issues.
What are milk ducts and what is their role?
Milk ducts are tubular structures in the breast tissue that transport milk from the lobules, where it is produced, to the nipple. During breastfeeding, the baby suckles, stimulating the release of hormones that cause milk to flow through these ducts. This vital anatomy allows for efficient nursing and is critical to infant nutrition.
Is pain in the milk ducts normal?
While some discomfort during breastfeeding is common, significant pain in the milk ducts can indicate an issue such as a blockage or infection, known as mastitis. Blocked milk ducts can cause swelling, tenderness, and even localized lumps in the breast. If pain persists, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How can hormonal changes affect milk ducts?
Hormones play a pivotal role in the health of the breast and milk production. Hormonal fluctuations during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or postpartum can cause alterations in milk duct function. Such changes may lead to issues like engorgement or increased sensitivity. Understanding these hormonal influences can help individuals recognize typical versus concerning symptoms.
Can milk duct problems impact breastfeeding?
Yes, issues with milk ducts can significantly affect breastfeeding. Conditions such as blocked ducts may lead to decreased milk supply and can complicate nursing efforts. It is essential to address these problems early to ensure both maternal comfort and adequate infant feeding. Strategies like frequent breastfeeding or manual expression can help alleviate symptoms.
For those experiencing difficulties, seeking support from lactation consultants or healthcare providers can be invaluable in navigating the challenges associated with milk ducts.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

