7 Warning Signs of Sternal Infections (Must-Read)
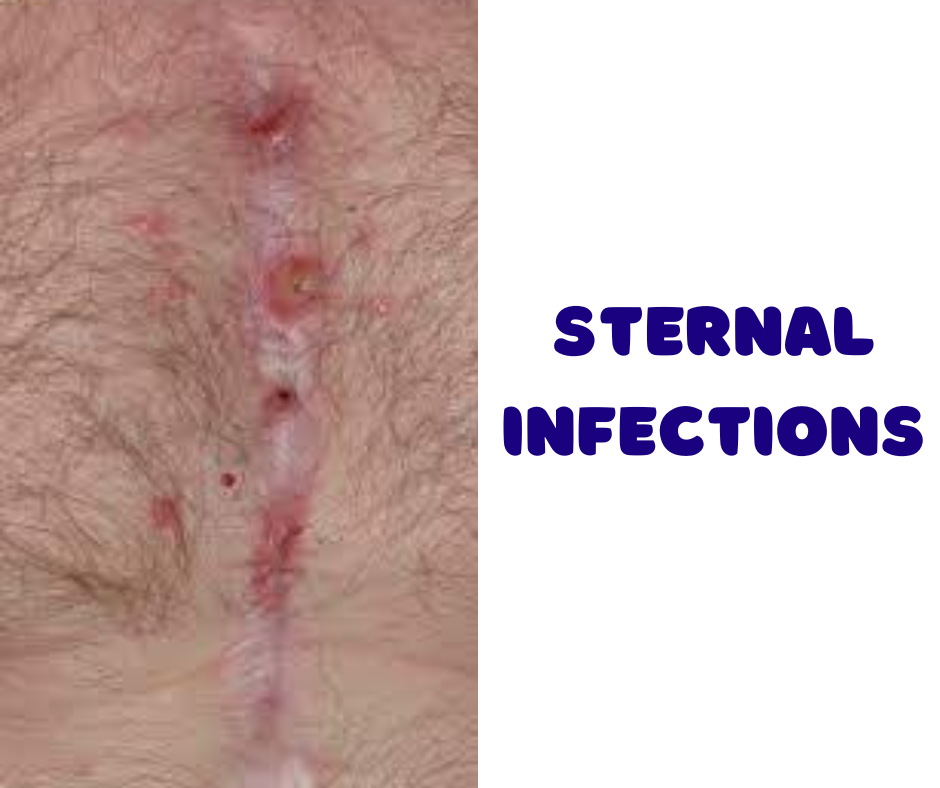
What are Sternal Infections?
Sternal infections refer to an array of infectious conditions affecting the sternum, which is a flat bone located in the central part of the chest, connecting to the ribs via cartilage. It plays a crucial role in protecting the heart, lungs, and larger blood vessels from damage, however, it is also susceptible to various types of infections. These infections can arise due to several mechanisms, including postoperative complications, hematogenous spread, or direct inoculation from trauma.
Postoperative infections are among the most common types of sternal infections, particularly in patients who have undergone cardiac surgery, such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Following such procedures, bacteria can enter the sternal area through surgical incisions, leading to potential infection. Symptoms associated with these infections may include localized pain, swelling, and fever, ultimately necessitating evaluation and treatment.
Hematogenous infections, on the other hand, occur when pathogens spread through the bloodstream, taking root in the sternal area. Conditions such as bacteremia, where bacteria circulate in the blood, can contribute to this form of infection. The anatomy of the sternum provides a conducive environment for these infections, as it contains a rich vascular supply that can transport bacteria from distant sites of infection.
Direct inoculation can result from trauma to the sternal area, including fractures or surgical procedures. Open wounds or exposed bone can provide a direct pathway for microbes to infiltrate the sternum, leading to acute infections characterized by intense pain and inflammation.
Understanding the various types of sternal infections is essential for early diagnosis and treatment, particularly in patients with risk factors associated with surgical or traumatic interventions. Early intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent complications associated with these infections.
Causes of Sternal Infections
Sternal infections, medically known as sternal osteomyelitis, can arise from a variety of underlying causes, necessitating a comprehensive understanding to ensure effective treatment and prevention. One prominent cause is surgical complications, particularly following median sternotomy which is commonly performed during cardiac surgery. Infections may develop if the surgical site is contaminated or if there is a delay in wound healing. Underlying mechanical stress on the sternum due to chest wall movements could further exacerbate the risk of infection.
Another significant factor contributing to sternal infections is the presence of invasive devices, such as pacemakers or central venous catheters. These devices, while essential for monitoring and treatment, can serve as foreign bodies that introduce pathogens into the bloodstream or the surrounding tissue, ultimately leading to infection. Bacterial colonization around these devices can initiate localized sternal infections, emphasizing the importance of meticulous care during insertion and maintenance.
Preexisting medical conditions also play a crucial role in predisposing individuals to sternal infections. For instance, diabetes is known to impair wound healing and weaken the immune response, making affected individuals more susceptible to infections. Likewise, patients with immune deficiencies or chronic illnesses, such as those receiving immunosuppressive therapy, are at an elevated risk. Their bodies may struggle to combat infections effectively, permitting pathogens to proliferate and infect the sternum.
Common pathogens involved in sternal infections include Staphylococcus aureus, particularly Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which is notorious for its resistance to standard antibiotics. Other bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus species, may also be implicated. Understanding these causative factors is essential for clinicians to implement appropriate preventive measures and treatment strategies, thereby improving patient outcomes.
Symptoms of Sternal Infections
Sternal infections, often stemming from surgical procedures or injuries, can present with a range of symptoms that are critical for timely diagnosis and management. One of the primary indicators of a sternal infection is localized pain near the sternum, which may be sharp or throbbing in nature. This discomfort often intensifies with movement or pressure, making it imperative for patients to seek medical evaluation.
Accompanying the pain, swelling around the sternum can occur as the body responds to the infection. This swelling may be accompanied by tenderness, indicating inflammation in the affected area. Additionally, redness over the sternum is commonly observed, which signifies an immune response to the infection.
Fever is another prevalent symptom associated with sternal infections. The body typically raises its temperature as part of the immune response, which can manifest as chills or excessive sweating. Patients may experience systemic symptoms, such as fatigue and malaise, as the infection progresses, impacting overall well-being and activity levels.
The severity and type of sternal infection can greatly influence the symptoms experienced. For instance, a superficial infection might lead to minor localized symptoms, while a deeper, more severe infection may result in significant systemic effects, including elevated white blood cell counts and prolonged fever. In cases of osteomyelitis, where the bone is affected, symptoms may become more pronounced, necessitating urgent treatment.
As such, it is critical to recognize variations in symptoms based on individual cases. Early identification of sternal infection symptoms can lead to prompt medical intervention, significantly enhancing recovery outcomes and preventing complications. Monitoring for these signs and communicating them effectively to healthcare providers can be pivotal in managing this condition.

Diagnosis of Sternal Infections
Diagnosing sternal infections requires a systematic approach that integrates clinical evaluation, imaging techniques, and laboratory tests. A thorough physical examination is often the first step in identifying signs of a sternal infection. Clinicians will look for symptoms such as localized tenderness, swelling, erythema (redness), and warmth over the sternum, which may indicate the presence of infection. Additionally, the history of surgery or trauma to the sternum can play a significant role in guiding the diagnostic process.
To further assess the condition, imaging studies are frequently employed. Radiographs, or X-rays, are typically the initial imaging modality used to visualize the sternal area. They can reveal bone abnormalities, localized osteomyelitis, or fluid collections that may suggest an infection. In cases where the diagnosis remains unclear or if there is a need for more detailed visualization, computed tomography (CT) scans may be utilized. CT imaging provides cross-sectional views of the sternal region and can detect deep tissue involvement and other complications associated with infections.
Laboratory tests are crucial for confirming the diagnosis of sternal infections. Blood cultures are commonly conducted to isolate and identify pathogens responsible for the infection. Elevated inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and leukocyte count, may also assist in indicating the presence of an infectious process. In cases of wound infections, obtaining tissue samples or swabs for culture can yield precise information regarding the causative organisms.
Early diagnosis of sternal infections is imperative for optimizing treatment outcomes. Prompt identification allows for the timely initiation of appropriate antibiotic therapy and aids in determining whether surgical intervention is necessary to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue. Overall, integrating various diagnostic methods ensures a comprehensive evaluation of sternal infections, thereby enhancing patient management strategies.
Treatment Options for Sternal Infections
Sternal infections can arise from various sources, including surgical procedures, trauma, or underlying health conditions. As such, their treatment must be tailored to the specific cause and severity of the infection. The primary treatment modalities for sternal infections encompass antibiotic therapy, potential surgical interventions, and effective wound care management.
Antibiotic therapy plays a crucial role in managing sternal infections. The choice of antibiotics depends on the suspected or confirmed pathogens involved. Typically, physicians utilize culture and sensitivity tests to identify the responsible microorganisms, ensuring that the selected antibiotics will effectively target the infection. In cases where the infection is caused by resistant bacteria, broad-spectrum antibiotics may be necessary until specific sensitivity results are available. It is imperative to commence antibiotic treatment as early as possible to mitigate the risks of complications.
In addition to pharmacological treatment, surgical intervention may be required, especially in severe or deep infections. Surgical options can range from debridement—removing necrotic tissue and foreign materials—to more extensive procedures, such as reconstructive surgery, in cases of significant structural damage. The goal of surgical management is to remove infected material and promote healing, often leading to improved patient outcomes.
Wound care management constitutes another fundamental aspect of treating sternal infections. Proper care of the surgical site or wound is vital to prevent further complications. This may include regular cleaning, dressing changes, and monitoring for signs of worsening infection. Additionally, patient education regarding hygiene and self-care practices can significantly enhance recovery and prevent the recurrence of sternal infections.
In conclusion, effectively managing sternal infections requires a comprehensive approach, integrating antibiotic therapy, surgical options when necessary, and diligent wound care management tailored to the patient’s unique needs. Each treatment plan should consider the infection’s etiology and individual patient factors to optimize healing and ensure timely recovery.
Complications of Sternal Infections
Sternal infections, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to a range of serious complications that may significantly impact a patient’s health and quality of life. One of the most common complications is the development of chronic wounds. These wounds can be particularly challenging to heal and may persist for extended periods, causing discomfort and necessitating ongoing medical care. Chronic sternal wounds can also increase the risk of further infections, thereby compounding the initial issue.
Another potential complication stemming from sternal infections is osteomyelitis, which is an infection of the bone. The sternum, being a central structure of the chest, can become infected following sternal surgery, such as that performed during cardiac procedures. The presence of osteomyelitis can lead to severe pain and may require prolonged antibiotic therapy, potentially alongside surgical interventions to remove infected tissue or parts of the bone. This condition not only prolongs recovery periods but can also lead to significant morbidity.
Moreover, sternal infections can escalate to systemic sepsis, a life-threatening reaction to infection characterized by widespread inflammation throughout the body. This condition poses a significant risk, as it can lead to multiple organ failure and requires immediate medical attention. The systemic effects of sepsis can have lasting repercussions, impacting overall health long after the initial infection is treated, including prolonged hospitalization or rehabilitation.
The long-term implications of these complications can be profound, affecting not only physical health but also mental well-being and the overall quality of life for patients. It is, therefore, imperative that sternal infections are promptly recognized and adequately managed to minimize the risk of these serious complications.
Preventing Sternal Infections
Preventing sternal infections is a multifaceted approach that requires vigilance and adherence to established medical protocols. One primary method to mitigate the risk of these infections is the strict implementation of aseptic techniques during surgical procedures. This involves ensuring that all surgical instruments and environment are sterilized properly before any operation occurs. Surgical teams should follow rigorous protocols to minimize the risk of contamination, including proper hand hygiene and the use of sterile equipment. Such practices are essential in maintaining a clean operating environment and reducing the likelihood of postoperative infections.
Another significant factor in the prevention of sternal infections is the timely management of comorbid conditions that may predispose patients to infections. Conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease can impair healing and directly increase the risk of infections. Healthcare providers should work closely with patients to optimize the management of these underlying conditions before, during, and after surgical intervention. Regular monitoring and adjustment of medications or therapies can play a crucial role in promoting healing and preventing complications.
Patient education also serves as a vital component in the prevention strategy for sternal infections. Individuals undergoing sternotomy should be informed about the potential signs and symptoms of infection, including increased redness, swelling, or discharge at the surgical site, as well as systemic symptoms such as fever. This awareness empowers patients to seek prompt medical attention if these symptoms arise, facilitating early intervention and reducing the severity of complications.
Finally, maintaining good hygiene practices is fundamental to preventing sternal infections. Patients should be instructed on how to care for their surgical wounds, emphasizing the importance of keeping the area clean and dry. Regular handwashing and avoiding contact with potentially infected surfaces are also essential measures in safeguarding against infections. When combined, these strategies form a robust framework for significantly reducing the risk of sternal infections and promoting optimal surgical recovery.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Sternal infections, medically known as deep sternal wound infections (DSWIs), often raise various queries among patients and their families. Understanding these questions can greatly alleviate concerns and provide clarity regarding the condition. Below are some common questions related to sternal infections.
How long does recovery from a sternal infection typically take?
The recovery period for a sternal infection can vary widely based on several factors, including the patient’s overall health, age, and the severity of the infection. Generally, patients may begin to see improvements within a few weeks, but full recovery can take several months. It is crucial to follow the healthcare provider’s advice and attend follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process.
Can sternal infections recur?
Yes, sternal infections can recur, particularly in individuals who have risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, or those with compromised immune systems. Patients who have previously experienced a sternal infection should be vigilant and report any unusual symptoms promptly to their healthcare provider to facilitate early intervention.
What can patients do to support their healing after a sternal infection?
Patients can take several steps to support their healing process. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can enhance the immune response, while staying well-hydrated plays a key role in recovery. Following the doctor’s instructions regarding wound care is vital, as is avoiding physical strain during the healing phases. Regular check-ups and adhering to prescribed medications are essential in preventing complications and reinforcing the recovery process.
Are sternal infections life-threatening?
While sternal infections can be serious, they are typically treatable with prompt medical attention. If left untreated, they can lead to complications such as sepsis or mediastinitis, which can be life-threatening. Early diagnosis, appropriate antibiotic therapy, and sometimes surgical intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent severe complications.
What are the early signs of a sternal infection?
Early signs of a sternal infection may include redness, swelling, or warmth around the surgical site, increased pain, drainage of pus or fluid, fever, and a feeling of general weakness. If any of these symptoms appear, it is essential to contact a healthcare provider immediately to prevent the infection from worsening.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, patients and caregivers can better understand sternal infections, leading to improved outcomes. It is always advisable to maintain an open line of communication with healthcare professionals to address any further concerns or queries that may arise during the healing journey.
Conclusion
Sternal infections represent a serious complication that can arise, particularly in patients who have undergone cardiac surgery or experienced trauma to the chest. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these infections is crucial not only for healthcare providers but also for patients and their families. Key factors contributing to sternal infections include improper wound care, the presence of infections in other parts of the body, and insufficient blood supply to the sternum area. Recognizing the early signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and fever, is essential for timely intervention.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are paramount in managing sternal infections effectively. This often involves a combination of antibiotics and, in some cases, surgical debridement to remove infected tissue. Patients must be vigilant in monitoring their recovery and report any concerning symptoms to their healthcare team immediately. The significance of awareness cannot be overstated, as proactive measures can lead to better outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Furthermore, ongoing research into sternal infections is vital for improving treatment protocols and prevention strategies. As our understanding of these infections evolves, new methodologies may emerge, offering hope for enhanced patient care. It is imperative for individuals who suspect they may have a sternal infection to seek medical advice without delay. The collaborative efforts of researchers, healthcare professionals, and patients alike play a crucial role in tackling the challenges presented by sternal infections. By fostering a strong awareness and understanding of these infections, we can work towards better prevention and treatment techniques in the future.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

