Costochondritis Relief: 7 Proven Ways to Ease Pain
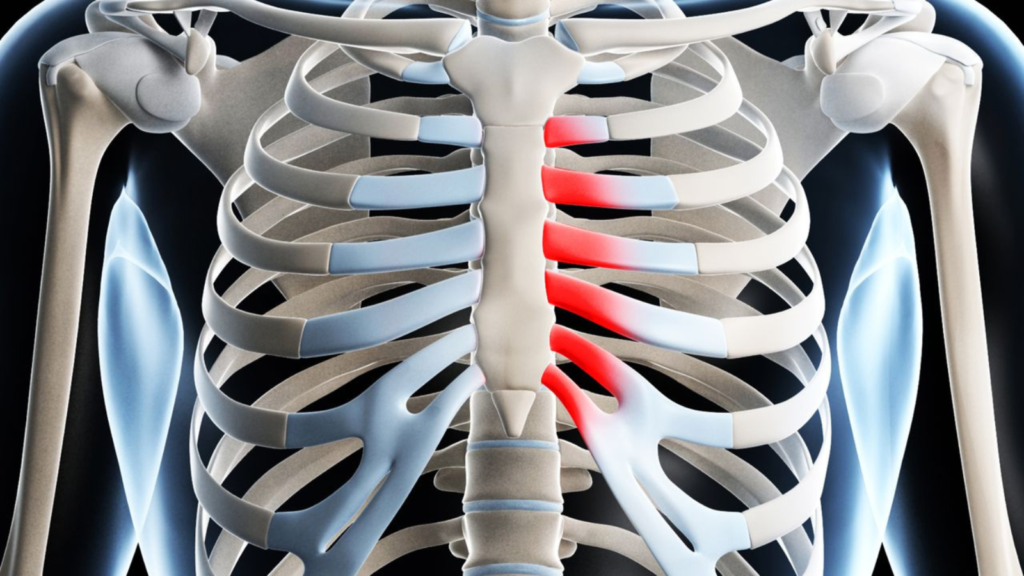
What is Costochondritis?
Costochondritis is defined as an inflammation of the cartilage that connects a rib to the sternum, an area known as the costosternal junction. This inflammation can lead to localized pain and tenderness in the chest wall. Anatomically, the ribs articulate with the sternum via costal cartilages, which serve as a flexible connection, allowing for the expansion and contraction of the chest during respiration. In instances of costochondritis, these cartilages may become irritated and inflamed due to various factors, resulting in discomfort that can mimic cardiac-related issues.
This condition primarily affects adults, particularly those between the ages of 20 and 40, although it can occur at any age. Women are statistically more likely to experience costochondritis, although the reasons for this disparity are not entirely understood. The onset of symptoms may follow trauma or overexertion, although sometimes the exact cause remains elusive. Additionally, individuals with conditions such as fibromyalgia or certain respiratory disorders may be at an increased risk of developing costochondritis due to the interaction between chronic pain and inflammation.
Understanding costochondritis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment, as misinterpretation of the symptoms can lead to unnecessary anxiety about potential cardiac conditions. The pain associated with costochondritis is typically sharp and intensified by certain movements, deep breathing, or palpation of the costosternal area. Therefore, recognizing the specific characteristics of this inflammation can aid in differentiating it from more serious ailments. By identifying costochondritis early and understanding its implications, patients can pursue appropriate treatment options to alleviate symptoms and return to regular activities.
Causes of Costochondritis
Costochondritis is an inflammatory condition that affects the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum, known as the costal cartilage. The precise causes of costochondritis are not entirely understood, but several factors have been identified as common triggers. A primary contributor to this condition is physical strain or trauma. Activities that involve repetitive movements or heavy lifting can exacerbate the chest area, leading to inflammation and pain. Additionally, a sudden injury or trauma from accidents, sports, or falls can result in costochondritis, especially if there is direct impact on the chest.
Infections also play a role in the development of costochondritis. Viral infections, particularly those that lead to respiratory issues, can result in inflammation of the costal cartilage. Moreover, certain bacterial infections can lead to costochondritis as a secondary complication. It is noteworthy that in some instances, fungi or other pathogens can contribute to the inflammation, although these cases are rarer. Research has shown that conditions such as respiratory infections may increase the likelihood of chest pain related to costochondritis.
Other potential factors contributing to the onset of costochondritis include age-related changes, autoimmune disorders, and certain underlying medical conditions. Studies suggest that individuals with inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may be more susceptible to developing this condition due to the generalized inflammation that affects joint structures. Obesity has also been identified as a potential risk factor, as excess weight can place additional strain on the ribcage dynamics, leading to discomfort and pain.
In summary, the causes of costochondritis are multifaceted, involving physical strain, trauma, infections, and other contributing factors, such as age and underlying health conditions. Understanding these causes can aid in both prevention and management of the condition.
Symptoms of Costochondritis
Costochondritis primarily presents with chest pain, a hallmark symptom that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. This pain typically arises in the area where the ribs attach to the sternum, known as the costosternal junction. Patients often describe the pain as sharp, aching, or pressure-like and it may intensify with certain movements, such as twisting or deep breathing. The intensity of the pain can vary widely among individuals, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain that may mimic the symptoms of a heart attack, which can understandably cause anxiety and concern.
Another characteristic feature of costochondritis is that the chest pain often worsens with physical activity and may be alleviated by rest. Some individuals might also experience increased sensitivity in the affected area, characterized by tenderness when pressure is applied. It is important to note that symptoms can occur on both sides of the chest, although they are typically localized to one side. In some cases, the pain may radiate to nearby areas, such as the back or abdomen, which could mislead individuals to think they may be experiencing more serious conditions.
Due to the potential overlap of symptoms with other medical conditions, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to differentiate costochondritis from similar issues, such as cardiac problems or gastrointestinal disorders. Each person’s experience of symptoms can be unique, often leading to a range of severity and duration. Consequently, understanding the signs of costochondritis is essential for adequate diagnosis and to prevent unnecessary interventions. Collectively, this nuanced understanding of symptoms allows for better management and treatment options for those affected by this painful condition.

Risk Factors and Demographics
Costochondritis, an inflammation of the cartilage that connects the rib to the sternum, can manifest due to various risk factors and demographic influences. Research indicates that age plays a significant role in the onset of this condition. Individuals between the ages of 20 and 40 are often more susceptible to developing costochondritis, although it can occur in individuals of any age. As this demographic typically engages in active physical pursuits, the risk of injury or repetitive strain may increase instances of this painful ailment.
Physical activity levels are also critical in assessing risk. Those who engage in high-impact sports or activities that require repetitive upper body movements may experience greater stress on the chest wall, leading to inflammation. Moreover, individuals who have physical occupations, such as construction or manual labor, may find themselves at an elevated risk due to the nature of their work, which often necessitates lifting and strenuous movements. Conversely, sedentary lifestyles may also contribute to musculoskeletal issues, including costochondritis, as reduced physical conditioning can render the thoracic muscles more vulnerable to strain.
Genetic predispositions may also factor into the likelihood of developing costochondritis. Some families may exhibit a higher prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders, suggesting that hereditary tendencies could influence susceptibility. In terms of gender, while costochondritis can affect both males and females, some studies suggest that females may report symptoms more frequently, possibly due to hormonal changes or different pain sensitivity experiences.
In summary, the interplay between age, physical activity, hereditary factors, and gender manifests in a complex risk landscape for costochondritis, emphasizing the importance of recognizing these elements in both prevention and treatment strategies.
Diagnosis of Costochondritis
The diagnosis of costochondritis begins with a thorough assessment of the patient’s medical history. Healthcare professionals will typically inquire about the onset and duration of chest pain, any recent injuries, physical activities, and relevant medical conditions. A detailed account of symptoms assists in determining whether the pain is localized or generalized, as well as identifying factors that may exacerbate or alleviate the discomfort.
Following the medical history review, a physical examination is conducted. During this examination, the physician applies pressure to the areas around the ribs and sternum to locate the precise source of pain. Costochondritis is characterized by tenderness at the costosternal, costochondral, or costovertebral joints, and this tenderness is a key indicator during the examination process. The physician also assesses for any signs of swelling or inflammation in the chest area.
To rule out other potential causes of chest pain, which may include conditions such as rib fractures, heart issues, or gastrointestinal problems, diagnostic imaging may be employed. X-rays are commonly used to exclude structural abnormalities or any signs of injury within the chest. While X-rays do not directly show costochondritis, they are vital in confirming that no other conditions are present that might require immediate attention. In certain cases, advanced imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans can be utilized, particularly if the pain persists or other concerning symptoms arise.
Ultimately, the diagnosis of costochondritis relies on a combination of clinical evaluation, physical examination findings, and exclusion of other possible conditions that may manifest with chest pain. This diagnostic approach ensures that patients receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of their symptoms.
Treatment Options for Costochondritis
Costochondritis is an inflammatory condition that affects the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone. Managing this condition effectively requires a comprehensive understanding of various treatment options available. The approach to treatment can vary based on the severity of the condition and individual patient needs.
Home remedies often serve as the initial line of treatment for costochondritis. Patients are encouraged to apply heat or cold packs to the affected area, which can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Additionally, practicing gentle stretching exercises can improve flexibility and strengthen muscles around the ribs. Rest is also essential to prevent further irritation of the affected cartilage.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms associated with costochondritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can provide relief from pain and decrease inflammation. Patients should follow recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist despite medication use.
Physical therapy may also be beneficial in the management of costochondritis. A physical therapist can create a customized exercise program aimed at strengthening the chest and back muscles, improving posture, and promoting overall flexibility. Techniques such as manual therapy and ultrasound may be employed to alleviate pain and enhance mobility.
In more severe cases where conservative measures fail to provide relief, corticosteroid injections may be considered. These injections deliver steroids directly to the inflamed area, offering significant pain relief and reduced inflammation. However, this treatment is typically reserved for instances where other options have not proven effective, as repeated injections may carry risks.
In conclusion, managing costochondritis involves a multifaceted approach that utilizes home remedies, OTC medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, corticosteroid injections. Understanding these treatment options is essential for those affected by this painful condition and can greatly improve their quality of life.
Living with Costochondritis
Living with costochondritis can be challenging, as the inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum often leads to discomfort and pain, particularly during physical activities or certain movements. To effectively manage this condition and maintain a reasonable quality of life, some lifestyle modifications and pain management strategies can be beneficial.
First and foremost, it is essential to recognize and avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms. Engaging in repetitive movements or heavy lifting can lead to increased discomfort. Individuals with costochondritis might benefit from implementing a balanced exercise routine that focuses on gentle activities such as swimming, cycling, or stretching exercises. These can help maintain physical fitness without putting excessive strain on the rib area.
Additionally, practicing good posture is key in minimizing discomfort. Poor posture can increase tension in the rib cage and surrounding muscles, potentially intensifying pain. Adopting an ergonomic workspace arrangement, using supportive seating, and being conscious of body alignment can provide relief. Furthermore, when sitting or standing for prolonged periods, taking frequent breaks to stretch and reposition can be advantageous.
Pain management strategies are also critical in dealing with costochondritis. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort. Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area may also provide relief by soothing muscle tension and diminishing pain. In more persistent cases, consulting a healthcare professional for alternative therapies, such as physical therapy or chiropractic care, may offer additional support.
Finally, adopting a supportive network can make a significant difference. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges, whether through support groups or online forums, can provide emotional assurance and practical tips for coping with costochondritis. Understanding the condition and implementing these management strategies will empower individuals to live more comfortably with costochondritis, ultimately enhancing their overall quality of life.

FAQs about Costochondritis
Costochondritis is a condition that frequently raises many questions among those experiencing its symptoms. Below are some common inquiries and their corresponding answers that can help clarify the understanding of this ailment.
How long do symptoms of costochondritis last?
The duration of symptoms related to costochondritis can vary significantly from person to person. Some individuals may experience discomfort for a few weeks, while others may endure symptoms for several months. In many cases, the pain may diminish with time, particularly with appropriate rest and treatment. However, some may find that symptoms can recur over time, particularly if they engage in activities that strain the chest area.
Can costochondritis be mistaken for heart problems?
Yes, the chest pain associated with costochondritis can sometimes be misinterpreted as a heart issue, given that both can present with similar symptoms. It is critical to recognize that costochondritis specifically involves inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the breastbone. When experiencing unexplained chest pain, it is advisable to seek medical attention to rule out cardiovascular issues and attain a definitive diagnosis.
What steps can be taken to prevent recurrence of costochondritis?
Prevention strategies primarily focus on avoiding activities that may exacerbate the condition. Engaging in gentle stretches, maintaining good posture, and using proper techniques during physical activities can help minimize strain on the chest area. Furthermore, individuals should listen to their bodies and rest when needed. Regular physical therapy sessions may also offer valuable guidance in managing symptoms and reducing the likelihood of future flare-ups.
Is costochondritis a chronic condition?
While costochondritis is generally considered a temporary condition, some individuals may experience chronic or recurrent episodes. Chronic costochondritis can occur when inflammation persists or if repeated strain is placed on the affected area. In such cases, long-term management strategies, including physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and lifestyle modifications, may be necessary to alleviate discomfort and prevent flare-ups.
Are there any specific dietary changes that can help with costochondritis?
Although there is no specific diet for costochondritis, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet may help manage symptoms. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, as well as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can support overall joint and cartilage health. Additionally, reducing the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine may help minimize inflammation and discomfort. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can contribute to overall recovery and well-being.
As awareness of costochondritis continues to grow, individuals experiencing related discomfort are encouraged to remain informed and consult healthcare professionals to navigate their symptoms effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Costochondritis is often characterized by localized chest pain that can mimic serious conditions such as a heart attack. However, there are specific circumstances under which individuals experiencing symptoms related to costochondritis should consult a healthcare provider. Recognizing these warning signs is crucial for ensuring adequate medical attention and preventing potential complications.
Individuals should seek immediate medical attention if they experience severe chest pain that radiates to the arm, shoulder, jaw, or back. This type of symptom could indicate more serious underlying conditions such as myocardial infarction or pulmonary embolism, which require urgent care. Additionally, if chest pain is accompanied by shortness of breath, dizziness, or sweating, these may signify a medical emergency that necessitates prompt evaluation.
In cases where the pain associated with costochondritis persists or progressively worsens over time, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Chronic or escalating pain may suggest there is more to the condition than simple inflammation, warranting further investigation to rule out other potential issues such as infections, tumors, or inflammatory diseases.
Furthermore, individuals should be vigilant for accompanying symptoms such as fever, chills, or unintentional weight loss, which could indicate an underlying illness requiring attention. If the pain is affecting daily activities, sleep, or quality of life, it is prudent to seek medical advice for effective management strategies.
In summary, while costochondritis may often be self-limiting, remaining aware of evolving symptoms and potential warning signs can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their health and well-being. Timely consultation with a healthcare provider is key to receiving appropriate care and intervention.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

