What is The Eustachian Tube?
The Eustachian tube is a critical structure within the auditory system, serving as a conduit between the middle ear and the nasopharynx. This tube is typically about 3.5 centimeters long in adults and is composed of both bony and cartilaginous segments. Its anatomical location allows it to play a vital role in maintaining ear health and function. The Eustachian tube helps to equalize air pressure in the middle ear, which is essential for proper hearing. Effective ventilation occurs through this tube, enabling sound waves to travel efficiently from the outer ear to the inner ear.
One of the primary functions of the Eustachian tube is to regulate air pressure. When the pressure in the external environment changes, such as during altitude shifts or underwater activities, the Eustachian tube opens to equalize the pressure on both sides of the eardrum. This mechanism is crucial for preventing discomfort or pain, often referred to as ear barotrauma. The tube’s opening is facilitated by the contraction of muscles surrounding the tube, which occurs during actions such as swallowing or yawning.
Additionally, the Eustachian tube aids in the drainage of fluids from the middle ear. It allows secretions and mucus that accumulate in the ear to flow into the nasopharynx, thereby preventing infections and maintaining an optimal environment for the ear’s structures. Dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can lead to a range of disorders, including otitis media, which is characterized by fluid buildup in the middle ear. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the Eustachian tube is essential, as its proper function is crucial for ear health and overall auditory performance.
How the Eustachian Tube Functions
The Eustachian tube plays a pivotal role in maintaining ear health by regulating air pressure and drainage within the middle ear. This narrow tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, the upper part of the throat behind the nose, and it primarily functions to equalize air pressure on both sides of the eardrum. When there is a change in altitude, such as during flying or driving in mountainous regions, the Eustachian tube opens, allowing air to enter or exit the middle ear. This action helps in preventing discomfort and preserving auditory function.
Two key muscles are involved in the mechanism of the Eustachian tube: the tensor veli palatini and the levator veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini assists in the opening of the tube during swallowing or yawning, a movement crucial for equalizing pressure. The levator veli palatini also contributes but primarily aids in maintaining patency of the tube. The coordination of these muscles is essential for its proper functioning, and any disruption in muscle activity can lead to dysfunction of the Eustachian tube.
Normal physiological processes involve the tube opening approximately 5 to 7 times per minute during relaxed states, allowing for continuous pressure equalization. In cases where the Eustachian tube fails to open effectively, conditions such as Eustachian tube dysfunction may arise. Symptoms can include ear fullness, discomfort, and impaired hearing, often exacerbated by respiratory infections, allergies, or irritants. Understanding how the Eustachian tube functions contributes to better awareness of conditions that disrupt its operation, which is critical for maintaining overall ear health.
Common Disorders of the Eustachian Tube
The Eustachian tube plays a crucial role in maintaining ear health by regulating air pressure in the middle ear and draining fluids. However, when this tube malfunctions, various disorders can arise. Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is the most prevalent issue, occurring when the tube fails to open appropriately, leading to pressure imbalances and associated discomfort. This condition may arise from allergies, respiratory infections, or anatomical anomalies. Symptoms often include a feeling of fullness in the ears, muffled hearing, and occasional pain.
Another notable disorder is otitis media, an infection or inflammation of the middle ear. This condition is frequently linked to Eustachian tube dysfunction, as blocked tubes can lead to fluid buildup, creating a breeding ground for bacteria or viruses. Otitis media is especially common in children and can present with symptoms such as ear pain, fever, and irritability. In severe cases, it can result in complications like hearing loss or the formation of tympanic membrane perforation.
Barotrauma is another disorder associated with the Eustachian tube, arising from sudden changes in atmospheric pressure, such as during air travel or diving. This pressure change can cause significant discomfort if the Eustachian tube cannot equalize the pressure effectively. Symptoms often include sharp pain in the ear, dizziness, and potential hearing changes. Long-term effects of untreated barotrauma may include potential damage to the middle ear structures and hearing difficulties. Overall, understanding these disorders is essential for recognizing their impact on health and for seeking appropriate treatment options.

Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Symptoms and Diagnosis
The Eustachian tube is a crucial structure that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. When functioning properly, it helps equalize pressure and drain fluids from the middle ear. However, dysfunction of the Eustachian tube can lead to various symptoms that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. One of the primary symptoms is a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear, which can occur when the tube becomes blocked or fails to open as needed. This sensation can be particularly pronounced during altitude changes, such as during a flight or diving.
In addition to ear fullness, discomfort may accompany Eustachian tube dysfunction. This discomfort can manifest as pain or heaviness in the ear, often leading patients to seek medical evaluation. Hearing loss is another common symptom, which can vary from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the dysfunction. Individuals may experience this as a sensation of muffled sounds or an inability to hear clearly. Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, can also arise, presenting an additional challenge for those affected.
Diagnosing Eustachian tube dysfunction typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. The process generally begins with a thorough physical examination, during which the medical provider will assess symptoms and inspect the ear canal and eardrum. In some cases, diagnostic imaging techniques such as tympanometry or endoscopy might be utilized to evaluate the functionality of the Eustachian tube more closely. These methods allow for a detailed assessment of the tube’s patency and any possible structural abnormalities that may contribute to the dysfunction. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical for managing symptoms effectively and preventing potential complications.
Treatment Options for Eustachian Tube Disorders
Eustachian tube disorders can lead to discomfort and hearing issues, necessitating a range of treatment options to alleviate symptoms and restore function. The approach to management often depends on the severity of the disorder and the underlying causes. Initially, conservative management methods are typically employed and can be effective for many patients. Nasal decongestants and corticosteroid nasal sprays are frequently recommended to relieve congestion. These options help reduce inflammation and promote drainage from the ear. While generally effective, they may come with side effects, including nasal irritation, headaches, and potential rebound congestion if used for extended periods. Thus, patients are advised to follow usage guidelines closely.
Another commonly suggested conservative option is nasal irrigation, which can help clear mucus and allergens from the nasal passages, further assisting Eustachian tube function. Additionally, autoinflation techniques, such as yawning or swallowing, can facilitate Eustachian tube opening and may be advised as simple yet effective methods for symptom relief.
For individuals who do not respond to non-invasive treatments, surgical interventions may be considered. One such procedure is balloon Eustachian tuboplasty, which involves the inflation of a small balloon within the Eustachian tube to physically widen it. This method has gained popularity due to its minimally invasive nature and the potential for long-lasting results. Patients typically report an improvement in their symptoms following the procedure. Nevertheless, like any surgical intervention, it carries risks, including infection, anesthetic complications, and the potential for recurrent Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Ultimately, the choice of treatment for Eustachian tube disorders should be made collaboratively between the patient and their healthcare provider, considering individual circumstances and the potential benefits and risks associated with each option.
Preventing Eustachian Tube Problems
The health of the Eustachian tube is crucial for maintaining proper ear function and overall ear health. Preventing Eustachian tube issues can be approached through various lifestyle changes and preventive measures that target common risk factors. One key strategy is to avoid allergens and irritants that can lead to inflammation of the nasal passages and, consequently, the Eustachian tube. Regular cleaning of the living environment, using air purifiers, and minimizing exposure to smoke can significantly reduce such risks.
Traveling, particularly by air, can pose unique challenges for the Eustachian tubes due to changes in air pressure. To mitigate this, individuals should consider chewing gum or swallowing during takeoff and landing to help equalize pressure. Additionally, using a saline nasal spray before flights can keep the nasal passages moist and reduce congestion, allowing for better Eustachian tube function. Staying hydrated is vital during travel as well, since dehydration can lead to thickened mucus and potential blockage of the tubes.
Furthermore, practicing good hand hygiene is essential for preventing infections that can affect the Eustachian tubes. Regular hand washing, especially during cold and flu season, can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing upper respiratory infections that could lead to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Engaging in a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, bolsters the immune system and aids in combating infections.
Self-care techniques also play a vital role in maintaining ear health. Regularly performing gentle Valsalva maneuvers can help open up the Eustachian tubes when one feels sensation of fullness or pressure. Avoiding excessive use of decongestant nasal sprays is crucial, as overuse can lead to rebound congestion, further complicating Eustachian tube function. By integrating these preventive measures into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of Eustachian tube problems and maintain optimal ear health.

The Eustachian Tube and the Impact of Allergies and Infections
The Eustachian tube plays a crucial role in maintaining ear health by equalizing pressure in the middle ear and draining mucus. However, it can be significantly affected by allergies and infections, often leading to dysfunction and various complications. Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, mold, and dust mites can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and surrounding areas. This inflammation commonly leads to congestion, which may hinder the proper functioning of the Eustachian tube. When allergens are encountered, the body responds by producing histamines, which can cause further swelling of the mucous membranes, resulting in impaired drainage and pressure equalization.
Infections, particularly upper respiratory tract infections like the common cold and sinus infections, also have a profound impact on the Eustachian tube. Viral infections can lead to nasal congestion, which subsequently affects Eustachian tube function. Bacterial infections may follow, complicating the situation further. When mucus accumulates and becomes trapped in the middle ear, it creates a suitable environment for bacterial growth, potentially resulting in otitis media, or middle ear infection. Symptoms of this condition can include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss, which is often attributed to the dysfunction of the Eustachian tube.
The relationship between allergens, infections, and Eustachian tube dysfunction is often cyclical. For instance, an initial allergic reaction may lead to a cold, and the resultant congestion further exacerbates Eustachian tube problems. Therefore, managing allergies through avoidance strategies or medication can play a vital role in preventing subsequent infections and preserving ear health. In light of this interconnectivity, a comprehensive understanding of how allergies and infections influence the Eustachian tube is essential for developing effective treatment strategies and alleviating related complications.
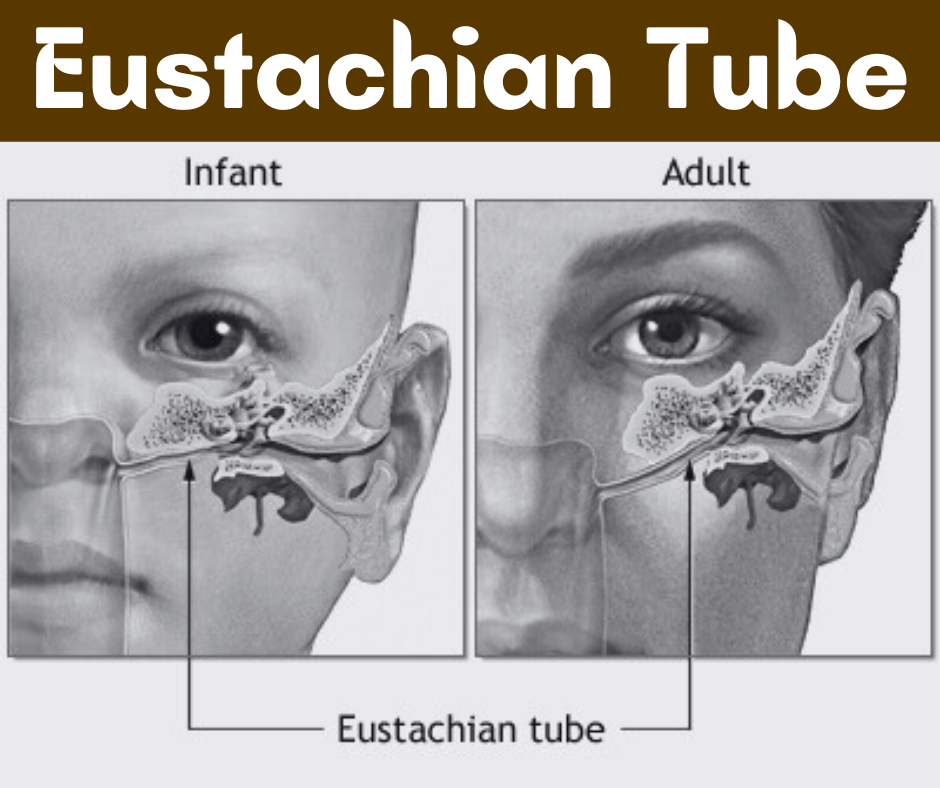
Eustachian Tube in Children vs. Adults
The Eustachian tube, a critical structure connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx, plays an integral role in equalizing ear pressure and maintaining ear health. However, significant anatomical and functional differences exist between the Eustachian tubes in children and adults. These disparities contribute to varying susceptibility to ear-related disorders, particularly middle ear infections, also known as otitis media.
In children, the Eustachian tube is shorter, more horizontal, and more flexible compared to that of adults. This anatomical configuration affects its ability to ventilate the middle ear adequately. As a result, children face more significant challenges when it comes to equalizing pressure or draining fluid. The horizontal orientation makes it easier for pathogens from the nasopharynx to enter the middle ear, increasing the likelihood of infections. Furthermore, children’s immune systems are still developing, which makes it more difficult for them to fight off the bacteria or viruses that can lead to these infections.
In contrast, an adult’s Eustachian tube is typically longer, more angled, and firmer, which allows better drainage and ventilation of the middle ear. While adults can also experience Eustachian tube dysfunction and middle ear infections, the incidence is lower due to these anatomical advantages. Parents should, therefore, be particularly vigilant regarding signs of ear infections in children, such as ear pain, irritability, or fever. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help spot potential issues early, facilitating timely intervention.
Awareness of these differences between children’s and adults’ Eustachian tubes can empower parents to take preventive measures. By understanding the predisposition of children to ear disorders, parents can implement strategies to mitigate risks, thus promoting better ear health during critical developmental years.
FAQ about the Eustachian Tube
The Eustachian tube plays a crucial role in maintaining ear health by equalizing pressure in the middle ear. Understanding common questions about this structure can illuminate various concerns related to ear health.
What causes Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Eustachian tube dysfunction typically arises from a blockage, which can be caused by allergies, sinus infections, colds, or changes in altitude. In some cases, structural issues such as a deviation of the septum can lead to persistent dysfunction. When the Eustachian tube cannot open correctly, it can result in discomfort, a feeling of fullness, or hearing issues. Individuals with frequent respiratory infections or seasonal allergies are particularly at risk as these conditions can lead to inflammation and congestion affecting the Eustachian tube’s function.
Can Eustachian tube problems affect hearing permanently?
Generally, issues related to the Eustachian tube can lead to temporary hearing loss due to fluid retention or pressure imbalances in the ear. However, if left untreated, especially in cases of chronic dysfunction, some individuals might experience more prolonged effects. Updated research suggests that while complete hearing loss is rare, ongoing Eustachian tube problems may contribute to long-term complications such as chronic otitis media, which can affect overall hearing health. It is essential to address any ongoing symptoms to prevent possible complications.
When should you see a doctor?
Consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable if symptoms persist, particularly if experiencing significant pain, hearing loss, or recurrent ear infections. Early intervention can help mitigate potential complications and provide targeted treatment to restore the function of the Eustachian tube. Regular check-ups are also encouraged for individuals prone to Eustachian tube dysfunction, ensuring any underlying issues are promptly addressed.
What are the symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction?
Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction can vary in severity but commonly include a feeling of fullness in the ears, muffled hearing, ear pain, dizziness, and occasional ringing in the ears (tinnitus). Some individuals may also experience popping or crackling sounds when swallowing or yawning. Symptoms often worsen with altitude changes, such as during air travel or driving through mountainous regions. If these symptoms persist for an extended period, medical evaluation may be necessary to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
How is Eustachian tube dysfunction treated?
Treatment for Eustachian tube dysfunction depends on the severity and underlying cause. Mild cases often resolve on their own or with simple techniques such as swallowing, yawning, or chewing gum to help open the tube. Nasal decongestants, antihistamines, or corticosteroid sprays may be recommended if the dysfunction is linked to allergies or sinus congestion. In more persistent or severe cases, medical interventions such as Eustachian tube balloon dilation or pressure equalization tubes (ear tubes) may be considered. Consulting an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can help determine the most effective treatment plan.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

