Jungle Profits: 7 Powerful Tactics for Success
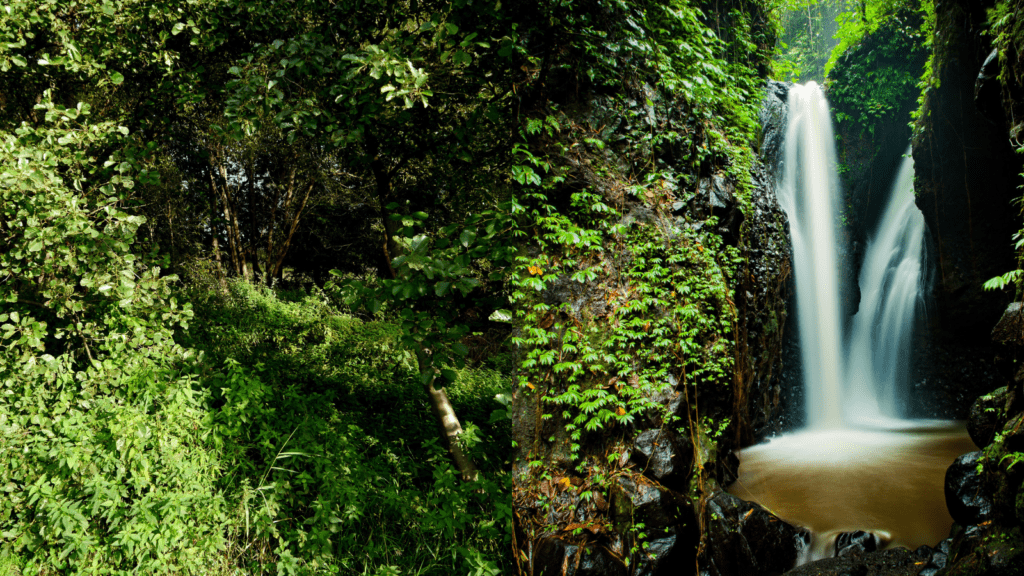
Jungle Ecosystem
The jungle, often characterized by its dense vegetation and towering trees, is one of the most diverse ecosystems on Earth. These vibrant environments are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where the climate is warm and moisture levels are high. The lush greenery and towering canopies create an intricate habitat that supports an astounding array of flora and fauna, surpassing all other ecosystems in terms of biodiversity. This incredible richness enables the jungle to play a pivotal role in global ecological balance.
One distinct feature of jungle ecosystems is their stratification. This is the division of the forest into different layers, each hosting unique species adapted to varying light conditions. The emergent layer consists of the tallest trees reaching for the sun, while the canopy layer is a bustling community of life comprised of birds, insects, and mammals. Below these levels lies the understory, characterized by smaller plants and young trees, and finally, the forest floor, which is dense with decomposing organic material, vital for nutrient recycling. This multi-layered structure not only enhances biodiversity but also fosters complex interdependencies among species.
Globally, jungles can be categorized into different types such as tropical rainforests, dry forests, and subtropical forests, each possessing its unique characteristics. For instance, the Amazon Rainforest is renowned for its immense size and rich biodiversity, while the Southeast Asian jungles are known for their unique plant species and distinct wildlife. The ecological importance of jungles extends beyond their physical dimensions; they contribute significantly to carbon storage, climate regulation, and oxygen production, underscoring their role in maintaining Earth’s health. As such, understanding the jungle ecosystem is crucial for developing conservation strategies and ensuring the preservation of these extraordinary habitats for future generations.
Flora of the Jungle: A Rich Plant Kingdom
The jungle represents one of the most diverse ecosystems on Earth, characterized by a rich tapestry of plant species that thrive within its various layers. These layers are typically categorized into four distinct zones: the emergent layer, the canopy, the understory, and the forest floor. Each of these habitats supports a unique assemblage of flora, contributing to the jungle’s overall biodiversity.
The emergent layer is home to towering trees that can reach heights of up to 60 meters. These giants are often crowned with broad, umbrella-like leaves, allowing them to capture sunlight that permeates the dense foliage below. Species such as the kapok tree and the Brazil nut tree flourish in this layer, demonstrating remarkable adaptations to survive the harsh conditions of wind and rain.
Below the emergent layer lies the canopy, which serves as a bustling habitat for countless life forms. This layer, roughly 30 meters high, is primarily composed of interconnected branches and leaves that form a thick, green blanket. It is rich in biodiversity, hosting iconic plants like orchids, bromeliads, and various ferns. These plants not only display remarkable adaptations to collect sunlight but also provide crucial resources for the myriad of organisms inhabiting the canopy.
Moving deeper, the understory is dominated by smaller trees and shrubs. This layer receives significantly less light, prompting many plants to develop larger leaves to maximize photosynthesis. Notable species found here include the cacao tree, from which chocolate is derived, and the rubber tree, vital for the production of natural rubber. These plants are often equipped with unique features that enable them to thrive in low-light conditions.
Finally, the forest floor, which is shaded and often damp, is crucial for nutrient recycling. Here, decay plays a vital role, as fallen leaves and organic matter decompose, enriching the soil. It is in this layer that one can find various ferns, fungi, and saplings, all playing an integral part in sustaining the jungle ecosystem. In conclusion, the jungles serve as a remarkable showcase of global plant diversity, illustrating nature’s extraordinary ability to adapt and flourish in various environmental layers.
Fauna of the Jungle: Wildlife Diversity
The jungle is renowned for its incredible wildlife diversity, hosting a myriad of animal species that have uniquely adapted to this complex ecosystem. Among the most prominent inhabitants are mammals such as jaguars, sloths, and capuchin monkeys. Jaguars, for instance, exhibit incredible strength and agility, allowing them to navigate the dense foliage of the jungle. Their role as apex predators ensures the balance of the ecosystem, as they help regulate the populations of various prey animals.
Birds also play a significant role in the jungle’s biodiversity. Colorful species such as toucans, macaws, and various types of parrots not only add vibrancy to the jungle but also contribute to seed dispersal through their feeding habits. Toucans, with their distinctively large bills, can reach fruits that many other animals cannot, ensuring a wider distribution of plant species. Moreover, the melodious calls of these birds contribute to the vibrant soundscape of the jungle, which is essential for communication within and between species.
Reptiles, including snakes, lizards, and iguanas, exhibit remarkable adaptations that allow them to thrive in the humid environment of the jungle. For example, the green tree python demonstrates exceptional camouflage, allowing it to blend seamlessly with the foliage, facilitating both hunting and protection from predators. Insects comprise another essential component of jungle fauna, with diverse species such as ants, butterflies, and beetles playing critical roles in pollination and decomposition. The interconnectedness of these various species underscores the essential balance of jungle ecosystems.
Each of these animal groups, from mammals to reptiles and insects, contributes to the intricate web of life in the jungle. Their diverse adaptations not only enable them to survive but also enrich the overall biodiversity of this vibrant and complex habitat. Understanding these species and their interactions deepens our appreciation of the wonders of the jungle.

The Role of Jungles in Climate Regulation
Jungles play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate through various ecological functions, primarily carbon sequestration and oxygen production. These densely forested areas serve as significant carbon sinks, absorbing substantial amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during the process of photosynthesis. It is estimated that tropical rainforests, which include a sizable portion of jungles, absorb approximately 1.1 billion tons of carbon dioxide annually. This process not only mitigates the effects of climate change but also contributes to maintaining a stable atmosphere. The preservation of these ecosystems is vital, as their potential for carbon sequestration directly correlates with the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions globally.
Oxygen production is another critical function of jungles, with forests contributing around 28% of the world’s oxygen supply. This relies heavily on the photosynthetic processes carried out by the abundant flora in these regions. As trees and plants convert carbon dioxide into oxygen, they are essential for sustaining life on Earth, making jungles invaluable to ecological stability. The loss of these habitats, primarily through deforestation and land conversion for agriculture or urbanization, significantly impacts not only local biodiversity but also global climate patterns.
Deforestation exacerbates climate change by releasing previously stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, creating a feedback loop that accelerates global warming. Current scientific data indicates that the conversion of jungles to agricultural land leads to a rise in atmospheric carbon levels, thus intensifying temperature fluctuations and altering precipitation patterns. Protecting jungles is therefore indispensable for climate regulation, as they play an integral role in both local and global ecosystems. Continued research and policy efforts are necessary to safeguard these vital environments, promoting sustainable practices that benefit both our climate and biodiversity.
Threats to Jungle Ecosystems: An Urgent Concern
The jungle, with its rich biodiversity and intricate ecosystems, faces numerous threats that jeopardize its health and sustainability. One of the most pressing issues is deforestation, driven largely by agricultural expansion, logging, and infrastructure development. According to recent research, areas of tropical rainforest are being cleared at an alarming rate, often leading to habitat loss for countless species. This reduction in available habitat can trigger a decline in biodiversity, as many animals and plants are unable to adapt to fragmented environments. Deforestation not only disrupts local ecosystems but also contributes significantly to global climate change due to the release of stored carbon dioxide from trees.
Climate change itself poses a formidable threat to jungle ecosystems. Altered weather patterns, including increased temperatures and irregular precipitation, can lead to drought conditions or excessive rainfall, both of which can have detrimental effects on flora and fauna. For example, many plant species are sensitive to temperature changes, impacting their ability to reproduce. Additionally, wildlife may be forced to migrate to cooler areas, leading to further disruption of established ecological relationships.
Urbanization presents another significant challenge as cities expand into previously untouched jungle areas. The encroachment of urban development not only fragments habitats but also affects the availability of resources such as food and water for native species. Furthermore, urban areas often lead to increased pollution, heightening the risk of exposure for wildlife and degrading their natural habitats.
Finally, the illegal wildlife trade has devastating effects on jungle biodiversity. Species are often poached for their exotic appeal, leading to dramatic decreases in population numbers for vulnerable species. This trade threatens not only individual species but also entire ecosystems due to the loss of key species that maintain ecological balance. The combination of these threats creates an urgent need for concerted efforts aimed at preserving and restoring jungle ecosystems, ensuring their vitality for future generations.
Conservation Efforts: Protecting Our Jungles
The preservation of jungle ecosystems is critical, given their role in maintaining biodiversity and regulating the Earth’s climate. Conservation efforts are increasingly essential due to the rapid depletion of these habitats driven by deforestation, illegal wildlife trade, and climate change. To address these issues, various approaches are being implemented globally, focusing on sustainable practices and community involvement.
Sustainable practices are at the forefront of conservation strategies, aiming to balance ecological health with human economic needs. Initiatives such as agroforestry and ecotourism allow local communities to benefit economically while preserving their natural surroundings. These methods promote land use that does not involve destructive practices, thereby safeguarding flora and fauna. By integrating sustainable agriculture within jungle environments, it is possible to reduce pressure on these ecosystems and encourage biodiversity.
Community-led conservation has proven to be a highly effective approach to safeguarding jungle habitats. Engaging local populations in the stewardship of their environment fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment. Various organizations have recognized the importance of indigenous knowledge in conservation practices and have incorporated local expertise into their programs. These initiatives often yield positive outcomes, as communities become active participants in the protection of their regions. Education and awareness are also key components, enabling locals to understand the value of their biodiversity.
International organizations play a crucial role in conservation efforts worldwide. Initiatives such as the United Nations’ REDD+ program provide financial incentives to countries that reduce greenhouse gas emissions through forest conservation. Collaborations between governments, NGOs, and private sector partners have also led to significant efforts to create protected areas and reserves, ensuring that remaining jungle ecosystems receive the necessary protections.
Overall, the combination of sustainable practices, community involvement, and international cooperation forms a robust strategy to combat the threats faced by jungle ecosystems. These efforts underline the importance of preserving these vital habitats for future generations, highlighting the intricate balance we must maintain to ensure the health of our planet.

The Relationship Between Humans and Jungles
Jungles, often referred to as tropical rainforests, are rich ecosystems that have sustained human populations for millennia. Historically, indigenous communities have forged harmonious relationships with these environments, relying on their dense flora and fauna for sustenance, shelter, and cultural practices. The abundance of resources such as fruits, nuts, and medicinal plants provided crucial support for survival while also fostering a deep appreciation for biodiversity and ecological balance.
Moreover, jungles play a vital role in the spiritual and cultural lives of many indigenous groups. Rituals and traditions are often intertwined with the landscapes, as certain species of trees, plants, or animals are viewed as sacred. This connection emphasizes the importance of preserving these ecosystems, not only for their ecological benefits but also for maintaining cultural heritage. The knowledge passed down through generations about survival techniques, sustainable harvesting, and biodiversity illustrates a profound understanding of the complex interrelations between humans and their environments.
Contemporary times, however, have seen a significant shift in the dynamics between human activity and jungle ecosystems. With the advancement of agriculture, urbanization, and deforestation, many jungles face threats that have resulted in habitat loss and biodiversity decline. Activities such as logging and land conversion for farming pose substantial risks to these ecosystems, fundamentally altering the delicate balance that has existed for years. The displacement of indigenous populations due to encroachment on their lands further complicates this relationship, causing social upheaval and loss of cultural identity.
Nevertheless, there are ongoing efforts to promote sustainable practices and conservation initiatives aimed at educating both local populations and outsiders about the importance of jungles. These endeavors seek to reunite human communities with the natural world, encouraging a sense of stewardship over these invaluable ecosystems. Consequently, recognizing the historical and contemporary interplay between humans and jungles is crucial for fostering an equitable and sustainable future for both.
Exploring the Jungle: Eco-Tourism and Adventure
The concept of eco-tourism has gained significant traction in recent years, particularly in jungle regions where biodiversity thrives. Eco-tourism and adventure tourism not only offer thrilling experiences but also promote a deeper understanding of the vital ecosystems that the jungles represent. Responsible eco-tourism can lead to numerous benefits for local communities, ensuring that they receive economic support while fostering conservation efforts.
Travelers engaging in eco-tourism are increasingly interested in activities that align with sustainable practices. By participating in guided nature walks, wildlife observation, and local cultural experiences, tourists help create job opportunities for residents, which can reduce reliance on harmful environmental practices. Such responsible tourism also encourages communities to protect their natural resources, thus conserving habitats and endemic species found within this rich ecosystem.
However, the rapid rise in tourism can present challenges if not managed properly. Unregulated or mass tourism poses a significant threat to wildlife and their habitats. Overcrowding can lead to soil erosion, pollution, and disturbance to local fauna, potentially resulting in the degradation of delicate ecosystems. Moreover, the introduction of foreign species through tourism activities might disrupt existing ecological networks, presenting further danger to the local biodiversity. It is vital for both tourists and operators to prioritize sustainability and respect natural habitats.
Regulations, such as visitor limits and eco-friendly guidelines, are essential in safeguarding the unique environments of jungles. By promoting educational initiatives and encouraging environmental stewardship among travelers, eco-tourism can successfully thrive while preserving the remarkable biological and cultural heritage of these areas. As explorers continue to unveil the wonders of the jungle, a collective commitment to responsible practices can ensure that both local communities and their environments benefit from the adventure that eco-tourism offers.
FAQs About Jungles: Understanding the Ecosystem
Jungles, often synonymous with tropical rainforests, are rich ecosystems home to an astounding variety of flora and fauna. This section will address some frequently asked questions that illuminate the complexities of jungles and their significance in our world.
What defines the geographical distribution of jungles?
Jungles primarily thrive in equatorial regions, specifically between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. Countries such as Brazil, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Indonesia are renowned for their extensive jungle coverage. The climate in these areas is characterized by high temperatures and substantial rainfall, creating a perfect environment for diverse plant and animal life.
How do species adapt to jungle environments?
The adaptation of species within jungles is remarkably unique. Many animals and plants have evolved specific traits that enable survival in the dense canopies and rich understories. For instance, certain birds are equipped with strong beaks to crack open tough fruits, while reptiles may possess vibrant colors that provide camouflage among colorful flowers. The layer of the jungle ecosystem also facilitates specialization; organisms often occupy different niches, from the forest floor to the canopy, contributing to incredible biodiversity.
What conservation measures are being taken to protect jungles?
With the increasing threat of deforestation and climate change, various conservation initiatives are being implemented to protect jungles. Organizations around the world are working to establish protected areas, promote sustainable agricultural practices, and raise awareness about the importance of these ecosystems. Reforestation efforts are also crucial, as they aim to restore degraded areas, enhance biodiversity, and mitigate the impacts of habitat loss.
What safety considerations should visitors keep in mind when exploring jungles?
Safety is paramount when visiting jungle environments. Individuals are advised to stay on marked paths to avoid getting lost and to be cautious of wildlife encounters. It is also essential to utilize appropriate gear, such as sturdy footwear and insect repellent, to protect against bites and stings from insects or plants. Engaging a knowledgeable guide can enhance both safety and the experience of understanding the complex ecosystem.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

