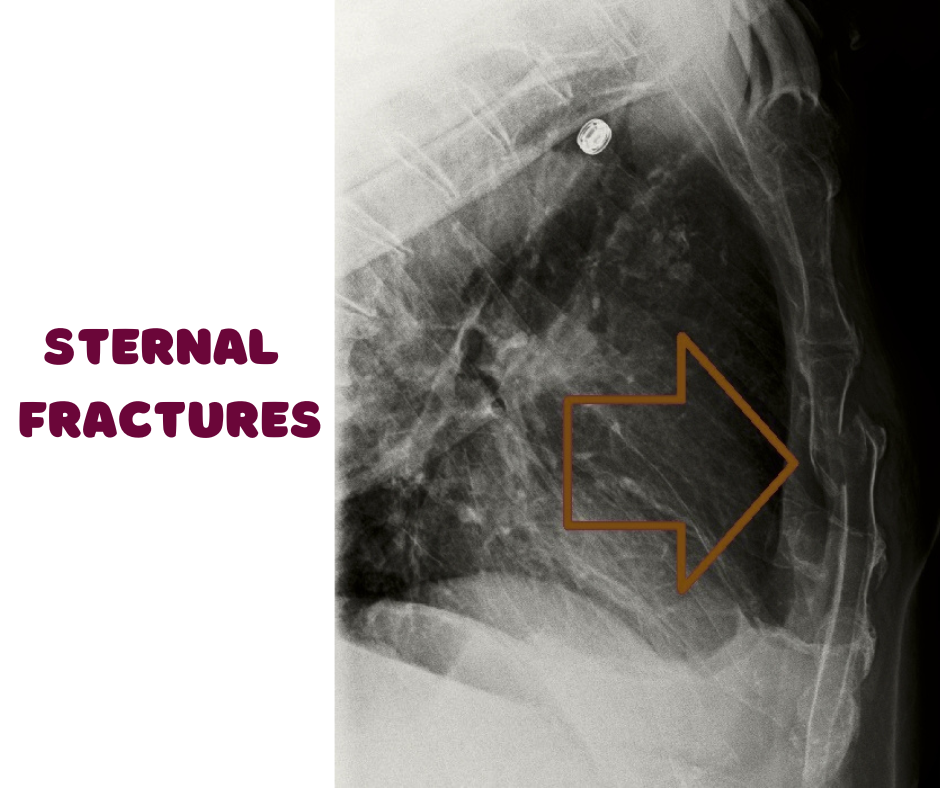
What is a Sternal Fracture?
A sternal fracture refers to a break in the sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, which is a flat bone located at the center of the thoracic cage. This anatomical structure plays a critical role in protecting vital organs such as the heart and lungs while also serving as an attachment point for several ribs via costal cartilage. Due to its position, the sternum is susceptible to injury, particularly during high-impact scenarios such as vehicular accidents and contact sports like football or rugby.
Sternal fractures primarily occur when a significant amount of force is applied to the chest, resulting in a crack or complete break of the bone. The most frequent cause of such fractures is blunt trauma, where force is directly transmitted to the thoracic region. Other potential causes include cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) maneuvers, falls from heights, or any incident that subjects the torso to sudden, intense pressure.
Demographically, sternal fractures can affect individuals across all age groups; however, older adults, especially those with weaker bones due to osteoporosis, may be more vulnerable. The injury is also more prevalent among athletes engaged in contact sports or individuals who frequently experience trauma. Despite its severity, a sternal fracture can sometimes go unnoticed initially, as the symptoms may resemble those of other chest injuries, including rib fractures. Regardless of the cause or demographic factors, recognizing a sternal fracture’s occurrence is critical as it can have implications on the respiratory system and overall chest stability.
Causes of Sternal Fractures
Sternal fractures are frequently the result of significant trauma to the chest area. Understanding the causes of these injuries is essential for both prevention and proper treatment. One of the most common causes is the impact sustained during car accidents. In such incidents, the forces involved can exert substantial pressure on the sternum, leading to fractures. Motor vehicle collisions, particularly those involving high speeds or direct impacts, often result in serious thoracic injuries, including fractures of the sternum.
Another prevalent cause of sternal fractures is falls, especially among the elderly or individuals engaged in recreational activities. When a person falls onto a hard surface, their body can experience a sudden and severe jolt, causing the sternum to fracture upon impact. In sports, certain high-contact games like football, rugby, and hockey pose a higher risk for sternal injuries. During collisions or falls in these sports, the athlete may land heavily on the chest, resulting in a fracture.
Additionally, sternal fractures can occur in occupational settings where individuals may experience significant chest trauma. For example, construction workers or individuals involved in heavy manual labor may be at risk if they are exposed to falling objects or accidents related to the equipment they handle. Furthermore, certain medical procedures, such as CPR or invasive treatments involving the chest, can inadvertently lead to sternal fractures in already vulnerable individuals.
Overall, the mechanics behind these injuries highlight the importance of safety measures in various environments. Awareness of the circumstances that typically lead to sternal fractures can guide preventative strategies and reduce the incidence of such injuries.
Signs and Symptoms of Sternal Fractures
Sternal fractures, which involve a break in the breastbone, frequently result from trauma, typically in vehicular accidents or during contact sports. Recognizing the signs and symptoms associated with these fractures is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. One of the primary symptoms of a sternal fracture is acute chest pain, often exacerbated by deep breathing, coughing, or movement. This pain may range from mild discomfort to severe anguish, substantially impacting the individual’s quality of life and ability to perform daily activities.
In addition to chest pain, individuals with a sternal fracture may experience difficulty in breathing. This symptom may arise due to the pain associated with breathing or because of potential complications arising from the fracture itself, such as injury to surrounding structures, including the lungs or heart. Thus, monitoring respiratory function is essential following trauma to the chest area.
Visible signs, such as swelling or bruising over the sternum, may also manifest, indicating a localized injury. The presence of these symptoms can vary in intensity depending on the severity of the fracture. In some cases, individuals might also experience tenderness when palpating the area over the sternum, further confirming the injury. It is worth noting that symptoms may not always immediately present following the trauma, and they might develop over time, making timely recognition challenging.
Immediate medical attention is warranted when experiencing these symptoms, as early identification of a sternal fracture can facilitate appropriate evaluation and treatment. Timely intervention is critical to minimizing complications, reducing pain, and enhancing the overall recovery process. A thorough assessment, often including imaging studies, is needed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the best course of action for management.

Diagnosis of Sternal Fractures
Diagnosing sternal fractures is a critical aspect of appropriate medical care, as these injuries can frequently accompany more severe damage to surrounding structures, including the ribs and vital organs. The initial step in diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination conducted by a healthcare professional. During this examination, the physician will assess for typical signs and symptoms associated with sternal fractures, which may include localized tenderness, swelling, and palpable deformities in the sternum area. Additionally, the clinician may inquire about the patient’s recent trauma history, which could provide valuable context for the suspicion of a fracture.
In order to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the injury, healthcare professionals often utilize imaging tests. X-rays are commonly employed as the first line of investigation; they are effective in identifying obvious sternal fractures and any associated rib fractures. However, due to the limitations of X-rays in assessing soft tissues and potential internal injuries, computed tomography (CT) scans may be recommended, particularly in cases where the trauma was severe or when there is a suspicion of internal organ damage. CT imaging offers a more detailed view, enabling clinicians to assess the extent of the fracture and the condition of surrounding organs comprehensively.
Accurate diagnosis of sternal fractures is paramount, as failing to recognize these injuries could lead to inadequate treatment and serious complications. Furthermore, misdiagnosing sternal fractures could lead to overlooking critical injuries that require urgent intervention. Consequently, a combination of careful clinical evaluation, appropriate imaging studies, and awareness of potential associated injuries plays a crucial role in the management of patients presenting with thoracic trauma. With this comprehensive approach, healthcare providers can ensure optimal outcomes for individuals suffering from sternal fractures and related injuries.
Treatment Options for Sternal Fractures
Treatment methods for sternal fractures vary depending on the severity of the injury and the patient’s overall health. In most cases, conservative management is the first line of defense. This approach focuses on alleviating pain, allowing the body to heal naturally. Healthcare professionals typically recommend rest, combined with over-the-counter or prescription pain medications to mitigate discomfort. Ice application at the injury site can also help reduce swelling and provide additional pain relief. Patients are generally advised to avoid strenuous activities that could exacerbate the fracture during the initial healing phase.
In cases where the fracture is severe, or if there is associated damage to surrounding structures such as blood vessels or organs, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options may include procedures to stabilize the sternum, such as internal fixation, where metal plates or screws are utilized to secure the fractured pieces together. This method is significant for ensuring proper alignment and facilitating optimal healing.
Following surgical treatment or conservative management, a structured rehabilitation program is essential for a full recovery. Physiotherapy usually begins with passive movements to maintain mobility, gradually progressing to active exercises as pain decreases and healing progresses. Patients can expect to engage in rehabilitation focused on strengthening the chest muscles and improving overall physical functionality. The recovery timeline can vary, but most individuals with a sternal fracture can expect to resume normal activities within six to eight weeks, conditional on the fracture’s severity and the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
While most patients recover well with appropriate management, it is crucial to follow healthcare professionals’ guidelines throughout the healing process to prevent complications and ensure complete recovery.
Potential Complications of Sternal Fractures
Sternal fractures, while often manageable, can lead to a range of complications that necessitate careful monitoring. One of the most serious risks associated with this type of injury is pneumothorax, a condition where air leaks into the pleural space, leading to lung collapse. The proximity of the sternum to critical structures such as the lungs and heart means that a fracture can disrupt these areas, causing significant respiratory distress. Symptoms of pneumothorax may include sudden chest pain and shortness of breath, making timely intervention crucial.
Another potential complication is cardiac injury. Given the sternum’s location shielding the heart, fractures can sometimes result in direct trauma to the cardiac tissue or major blood vessels. This may present as arrhythmias, pericardial effusion, or even cardiac contusion. Detection of such complications often requires diagnostic imaging and close observation by healthcare professionals, as they can significantly influence treatment outcomes.
Additionally, patients recovering from sternal fractures might experience chronic pain or discomfort in the chest area that could persist long after the initial injury has healed. Chronic pain management can become a challenging aspect of post-fracture care, impacting a person’s quality of life and ability to perform daily activities. Techniques such as physical therapy, pain management therapies, and possibly psychological support may be required to address these ongoing issues.
Given these potential complications, follow-up care is paramount for individuals with sternal fractures. Regular monitoring through clinical evaluations and appropriate imaging can help detect any delayed complications early, ensuring the right interventions are applied. Engaging in open communication with healthcare providers about any new or worsening symptoms can facilitate a more favorable recovery trajectory, ultimately reducing the risks associated with this injury.

Preventing Sternal Fractures
Sternal fractures, while often associated with high-impact injuries, can occur due to various circumstances. Therefore, adopting a proactive approach to injury prevention is paramount. One of the primary strategies is the implementation of safety measures in vehicles. Wearing seat belts is essential; they significantly reduce the risk of sustaining chest injuries during collisions. Modern vehicles are equipped with additional safety features, such as airbags, which can further mitigate the impact of an accident. Ensuring that these safety devices are functioning correctly can provide an extra layer of protection against potential injuries, including sternal fractures.
In the realm of sports, the use of protective gear is highly recommended. Athletes engaging in contact sports, such as football, rugby, or martial arts, can benefit greatly from wearing chest protectors and padded vests. These types of protective equipment are designed to distribute the force of impacts, thereby reducing the risk of fractures, including those affecting the sternum. Coaches and organizations should emphasize the importance of such gear to participants and ensure it is a routine part of practice and competition.
Moreover, individuals should maintain heightened awareness in potentially hazardous situations. Activities like climbing, biking, or any high-risk pastime require a cautious approach. Basic precautions, like assessing the environment and using appropriate safety harnesses or helmets, are vital. Developing safe habits not only protects against sternal fractures but also contributes to overall well-being. Regular physical fitness also strengthens the musculoskeletal system, thereby making it more resilient to injuries.
In conclusion, by ensuring safety measures in vehicles, utilizing protective gear during sports, and being mindful of one’s surroundings, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of sternal fractures. Taking these preventive steps is a crucial aspect of a comprehensive injury prevention strategy.
FAQs about Sternal Fractures
Sternal fractures, while relatively uncommon, often raise numerous questions among those affected or concerned. Here, we address some frequent inquiries to provide clarity and understanding.
What is the typical recovery time for a sternal fracture?
The recovery time for a sternal fracture can vary based on the severity of the injury. Generally, patients can expect to heal in approximately six to eight weeks. During this period, it’s crucial to follow physician recommendations and allow sufficient time for the chest area to heal without undue strain.
When should I seek medical help if I suspect a sternal fracture?
Immediate medical attention is essential if you experience severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, or any signs of a heart condition, such as palpitations. Swelling, bruising, or limited mobility in the chest area post-injury can also warrant prompt consultation with a healthcare provider to ensure proper diagnosis and management.
How can I manage pain related to a sternal fracture at home?
Effective pain management is vital in facilitating recovery. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate discomfort. It is advisable to avoid activities that may worsen the pain, including heavy lifting or strenuous exercise. Cold packs applied to the affected area may also provide relief. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any pain management regimen.
Are there any long-term complications associated with sternal fractures?
While most individuals recover without complications, some may experience chronic pain or changes in chest mobility. It is essential to follow up with healthcare providers periodically to monitor healing progress and address any emerging concerns during recovery.
Can a sternal fracture lead to other injuries?
While sternal fractures themselves are localized to the chest, the force that causes them may also result in additional injuries. These could include rib fractures, damage to the lungs, or heart contusions, depending on the severity of the trauma. It’s important to have a thorough medical evaluation following any chest injury to rule out other potentially serious conditions or complications.
This section serves to clarify common concerns regarding sternal fractures, aiding in understanding the injury’s implications and management strategies. By staying informed and proactive, patients can navigate their recovery effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, sternal fractures, while often associated with significant trauma, require a comprehensive understanding for effective management and recovery. These injuries typically arise from high-impact events such as automobile accidents, falls, or even severe blunt force impacts. Awareness of the potential causes is crucial since early detection can significantly affect treatment outcomes and prevent complications.
Furthermore, recognizing the symptoms associated with a sternal fracture is essential. Common indicators include localized chest pain, tenderness, and difficulty breathing, often exacerbated by movement or deep breaths. A thorough clinical evaluation, including imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans, aids in confirming the diagnosis and determining the extent of the injury.
Treatment for sternal fractures primarily focuses on pain management and ensuring proper healing. In most cases, conservative measures such as rest, analgesics, and gradual return to normal activities are sufficient. However, more severe cases may necessitate surgical intervention. This highlights the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for tailored advice and monitoring recovery progress.
The implications of an untreated or incorrectly managed sternal fracture can be serious, leading to complications such as respiratory issues or persistent pain. Thus, maintaining an informed approach and proactively seeking medical guidance can aid in achieving a successful recovery. Staying educated about sternal fractures promotes awareness and preparedness for anyone who may encounter such an injury in themselves or others, ultimately fostering a healthier, more informed community.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

