7 Alarming Signs of Sternum Cancer You Must Know
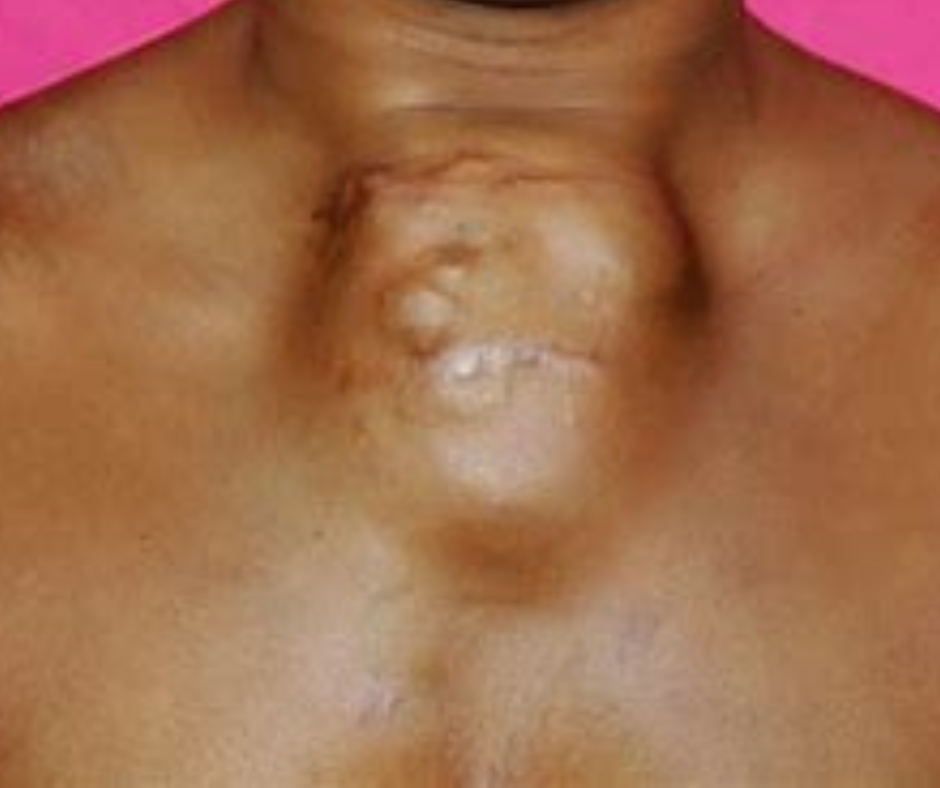
What is Sternum Cancer?
Sternum cancer, a rare and distinct type of malignancy, falls under the broader classification of chest wall cancers. The sternum, also known as the breastbone, is a flat bone located in the central part of the thoracic cavity, serving as an essential component of the rib cage. It connects to the ribs via costal cartilage, providing structural support and protection to vital organs such as the heart and lungs. The thoracic cavity, which houses these organs, is crucial for respiratory function and circulation, making the sternum’s integrity paramount.
While there are various forms of chest wall cancers, sternum cancer specifically pertains to tumors that originate in the sternum itself. This form of cancer is relatively uncommon compared to other malignancies, with fewer diagnosed cases each year. Most chest wall tumors can be categorized as either benign or malignant. The malignant tumors of the sternum may arise from different cell types, including bone, cartilage, or other tissues. Conditions such as chondrosarcoma and osteosarcoma are recognized types of malignancies that can affect the sternum, both resulting from the abnormal growth of cartilage and bone cells, respectively.
It is important to distinguish between different types of cancer affecting the thoracic region, especially since sternum cancer is less frequently encountered in clinical settings. Given its rarity, awareness and understanding of sternum cancer can be limited among both medical professionals and the general public. This blog post will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for cancers specifically originating in the sternum, shedding light on this overlooked area within oncology.
Causes and Risk Factors
Sternum cancer, while relatively rare, can arise due to a variety of factors that contribute to its development. One significant aspect is genetic predisposition, where individuals with a family history of cancer may have an increased risk of developing malignancies, including sternum cancer. Hereditary cancer syndromes such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome and Gorlin syndrome can increase the likelihood of developing various cancers, potentially including those affecting the sternum.
Another notable risk factor is exposure to radiation. Individuals who have undergone radiation therapy for previous cancers, particularly those targeting areas near the chest, may have an elevated risk of developing secondary malignancies in the sternum. This form of treatment, while effective for certain malignancies, can carry long-term risks, which necessitates careful monitoring by healthcare professionals post-treatment.
In addition to genetic and environmental factors, a history of other cancers can also play a crucial role in the incidence of sternum malignancies. For instance, patients previously diagnosed with cancers such as breast or lung cancer might find themselves at a higher risk due to the nature of their initial conditions and the treatments they received.
Lifestyle factors also significantly impact the chances of developing sternum cancer. Smoking has been widely recognized as a risk factor for various types of cancer, including those affecting the respiratory system and adjacent structures. The inhalation of carcinogenic substances may lead to the transformation of normal cells into abnormal ones, subsequently increasing the risk of malignancies. Furthermore, exposure to certain chemicals, such as asbestos or formaldehyde, has also been implicated in cancer development.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is essential for early detection and prevention strategies. While some factors may be beyond an individual’s control, awareness can empower proactive health management.
Symptoms of Sternum Cancer
Sternum cancer, although relatively rare, can present with a variety of symptoms that are crucial for early detection. Individuals experiencing any of the following symptoms should seek clinical evaluation promptly, as early intervention significantly enhances treatment outcomes. One of the most common symptoms associated with sternum cancer is chest pain, which may manifest as a persistent ache or sharp discomfort. This pain can sometimes be mistaken for musculoskeletal issues or other more benign conditions, potentially delaying diagnosis.
In addition to chest pain, patients may also encounter difficulty breathing. This symptom arises as the tumor increases in size, exerting pressure on surrounding structures and restricting airflow. Patients may notice this symptom worsening during physical activity or exertion, making it increasingly critical to consult a healthcare provider. Swelling in the chest area can be another alarming sign of sternum cancer. This may be localized around the sternum or more generalized throughout the chest, indicating potential lymphatic involvement.
Moreover, individuals may experience fatigue, a symptom that, while common to many health conditions, can be indicative of an underlying malignancy. Weight loss, often unexplained, is another symptom that may accompany sternum cancer, warranting further investigation. It’s essential to recognize that symptoms may vary widely among individuals; in some cases, there may be no symptoms at all in the early stages. This underlines the importance of being vigilant about changes in one’s health, especially for those with risk factors for chest cancers.
Overall, understanding these symptoms within the broader context of chest health can facilitate timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, enhancing the likelihood of better outcomes for individuals diagnosed with sternum cancer.

Diagnosis of Sternum Cancer
Diagnosing sternum cancer involves a multifaceted approach that incorporates various imaging techniques, biopsies, and blood tests. Initially, medical professionals usually begin with imaging studies to visualize the sternum and the surrounding structures. Commonly employed techniques include X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). X-rays can provide preliminary insights and highlight abnormal bony changes, but CT scans offer a more comprehensive view of the chest and can detect the presence of tumors while assessing their size and location. MRI is particularly beneficial for evaluating soft tissue involvement and helping to understand the extent of the disease.
Furthermore, if imaging results suggest the possibility of cancer, a biopsy is typically the next step. This procedure involves obtaining tissue samples from the sternum or nearby masses to determine the presence of malignant cells. There are several types of biopsies, including fine needle aspiration (FNA), core needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy. Each method varies in its invasiveness and accuracy, yet they all serve the essential purpose of confirming the diagnosis of sternum cancer by providing a definitive histological assessment.
In addition to these procedures, blood tests play a critical role in the diagnosis and management of sternum cancer. These tests may evaluate tumor markers, which are substances often produced by cancer cells or by the body in response to cancer. However, it is important to note that while tumor markers can aid in the detection and monitoring of cancer, they are not definitive on their own.
In summary, the diagnostic process for sternum cancer is intricate, utilizing a combination of imaging techniques, biopsies, and blood tests to confirm the disease and help stage it accurately. This effective diagnosis is vital for developing a targeted treatment strategy and improving patient outcomes.
Staging and Grading of Sternum Cancer
Sternum cancer, although relatively rare, necessitates a precise approach to staging and grading, which ultimately informs treatment strategies and prognostic assessments. The most widely utilized system for staging cancers, including sternum cancer, is the TNM classification. This system categorizes cancer based on three critical components: Tumor size (T), lymph Node involvement (N), and Metastasis (M).
The stages of sternum cancer range from Stage I to Stage IV, with Stage I indicating a localized tumor confined to the sternum, while Stage IV signifies an advanced disease with distant metastasis. In Stage I, the cancerous tissue is typically small and may not have spread to nearby lymph nodes. When the disease progresses to Stage II and Stage III, the tumor size increases, and there may be significant lymph node involvement. The transition to Stage IV, marked by the presence of metastases, suggests the cancer has advanced beyond the sternum and nearby tissues.
Grading of sternum cancer complements staging by examining the characteristics of tumor cells under a microscope. This process assesses how closely the cancer cells resemble normal cells. Grading usually ranges from low to high grade: low-grade tumors tend to grow slowly and resemble normal tissue, while high-grade tumors exhibit rapid growth and significant abnormalities. The grade of the tumor is a pivotal factor that affects treatment decisions, as high-grade cancers may necessitate more aggressive therapeutic approaches.
The comprehensive understanding of the staging and grading of sternum cancer plays a critical role in tailoring appropriate treatment modalities. It allows healthcare providers to predict the likely course of the disease, formulate treatment plans, and also provide insight into potential outcomes. Therefore, accurate staging and grading are essential components in the management of sternum cancer.
Treatment Options for Sternum Cancer
Treatment for sternum cancer typically involves a comprehensive approach that incorporates various modalities, aimed at ensuring the most effective management of the disease. The primary treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, each serving distinct purposes. The choice of treatment is largely determined by the type and stage of cancer, along with the overall health of the patient.
Surgery is often the first-line treatment for localized sternum cancer. This procedure may involve partial or complete removal of the sternum, alongside any surrounding tissues affected by the tumor. The main objective of surgical intervention is to eliminate cancerous cells, thereby reducing the risk of recurrence. However, surgery can be complex, and potential side effects include infection, bleeding, and prolonged recovery time.
Chemotherapy utilizes powerful drugs to target and kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. This treatment may be administered before surgery to shrink tumors (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) or after surgery to eradicate any remaining cancer cells (adjuvant chemotherapy). Administered through intravenous infusion or oral medications, chemotherapy can lead to side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and compromised immune function, which require careful management throughout the treatment process.
Radiation therapy is another common approach, often used in conjunction with surgery and chemotherapy. This treatment involves the targeted delivery of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors. Radiation may be applied externally or internally, depending on the cancer’s characteristics. Side effects can include skin irritation, fatigue, and localized swelling, which should be closely monitored by healthcare providers.
In addition to traditional treatment modalities, emerging strategies, such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and clinical trials, provide new avenues for managing sternum cancer. These innovative approaches are designed to improve efficacy and reduce side effects, illustrating the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in the treatment planning process.

Living with Sternum Cancer: Coping Strategies
Receiving a diagnosis of sternum cancer can evoke a range of emotions, from shock to fear, and can significantly impact both physical health and emotional well-being. Therefore, implementing effective coping strategies is crucial. One primary component of managing this condition is establishing a robust support network. Engaging with family, friends, and support groups can provide a sense of community and understanding, allowing patients to share experiences and strategies for navigating their journey. Emotional support from loved ones can be tremendously uplifting, as they often provide both reassurance and companionship during difficult times.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in coping with sternum cancer. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can enhance physical strength and bolster the immune system, enabling the body to better withstand treatments and manage side effects. Incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into one’s diet can help maintain energy levels and promote overall health. Consultation with a nutritionist specializing in cancer care can assist patients in creating a personalized eating plan, which could alleviate concerns about food choices relevant to their treatment regimen.
Regular exercise, adapted to one’s physical capabilities, has also been shown to benefit cancer patients. Gentle activities such as walking, yoga, or swimming can enhance physical stamina, improve mood, and alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression. Exercise releases endorphins, which serve as natural pain relievers and mood boosters. It’s important for patients to discuss their exercise plans with healthcare providers to tailor an appropriate program that accommodates their individual needs.
Lastly, prioritizing mental health resources is essential for those living with sternum cancer. Seeking professional counseling or therapy can provide an outlet for emotions and strategies for coping with the psychological strain of an illness. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and relaxation techniques, can also be beneficial. Patients are encouraged to actively engage in their treatment decisions, ensuring they understand their options and can voice their preferences. This level of involvement can lead to improved treatment outcomes and a greater sense of control during a challenging time.
Research and Future Directions
The realm of sternum cancer research is continually evolving, fueled by a commitment to uncover new insights and improve patient outcomes. Current trends indicate a robust focus on clinical trials that explore innovative treatment methodologies. These trials aim to evaluate the efficacy of targeted therapies and immunotherapies, which have shown promise in various cancer types. Specifically, research teams are investigating the role of checkpoint inhibitors, designed to enhance the body’s immune response against malignant cells residing within the sternum.
Moreover, advancements in diagnostic tools have significantly improved early detection rates. Techniques such as whole-genome sequencing are being employed to identify specific genetic mutations associated with sternum cancer. This focused approach not only aids in diagnosing the disease at an earlier stage but also helps in personalizing treatment plans tailored to an individual’s genetic profile. Furthermore, researchers are examining liquid biopsy methods, which allow for less invasive testing and monitoring of cancer progression by analyzing circulating tumor DNA.
A key aspect of ongoing research involves understanding the multifactorial causes of sternum cancer. By exploring the environmental, genetic, and lifestyle factors contributing to its onset, scientists aim to develop preventive strategies that could drastically reduce incidence rates. Collaborative efforts among research institutions worldwide have intensified, ensuring a shared pool of knowledge and resources that bolster the fight against this rare malignancy.
As the field progresses, the importance of continuous research efforts cannot be overstated. The development of novel therapies and diagnostic methods holds the promise of transforming sternum cancer treatment, ultimately improving survival rates and quality of life for those affected. By prioritizing research and embracing innovative practices, the medical community aims to pave the way for a future where the burden of sternum cancer is significantly alleviated.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Sternum cancer, while relatively rare, raises numerous questions for patients, families, and caregivers. Below, we address some commonly asked questions regarding this condition, based on the latest scientific insights and clinical guidelines.
What is the prognosis for someone diagnosed with sternum cancer?
The prognosis for individuals with sternum cancer largely depends on various factors such as the cancer type, stage at diagnosis, and overall health of the patient. Generally, cancers of the sternum can be categorized into primary and secondary types, with primary tumors, like chondrosarcoma, often exhibiting different behaviors compared to metastasized tumors. Early detection typically correlates with a better prognosis, emphasizing the importance of monitoring symptoms and seeking prompt medical advice.
What are the chances of recovery from sternum cancer?
The likelihood of recovery from sternum cancer depends on the tumor’s characteristics and the treatment response. Some patients may achieve remission, particularly with early intervention, while others may face more complex challenges. Treatment plans may involve surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy, tailored to the individual circumstances. Each case is unique, making a personalized approach crucial in evaluating recovery prospects.
How does sternum cancer affect life expectancy?
Life expectancy post-diagnosis can vary markedly among patients. Factors such as cancer type and stage, treatment efficacy, and patient health play integral roles in determining outcomes. Regular follow-up appointments and adherence to treatment plans significantly contribute to managing the disease and potentially improving life expectancy.
What side effects are associated with the treatment of sternum cancer?
Treatment for sternum cancer can lead to a range of side effects, which may include fatigue, nausea, changes in appetite, and localized discomfort. The severity and duration of these side effects can differ widely among patients. Oncologists often provide supportive care strategies to mitigate these effects and enhance the overall treatment experience.
What follow-up care is necessary after treatment?
Post-treatment follow-up care is essential in managing sternum cancer. This typically involves routine check-ups, imaging studies, and assessments to monitor for potential recurrences. Ensuring that patients remain informed about their condition and any new symptoms is vital for prompt intervention. Effective communication with healthcare providers can significantly improve long-term outcomes and quality of life.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

