7 Shocking Sternal Deformities & How to Fix Them
Understanding Sternal Deformities
Sternal deformities, often classified as abnormalities of the sternum, are structural irregularities that can occur in this critical bone of the thoracic skeleton. The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat bone situated in the center of the chest, connecting the rib bones and serving as an essential component of the ribcage. It plays an integral role in protecting vital organs such as the heart and lungs while also providing support to the shoulder girdle. Sternal deformities can manifest in various forms, including pectus excavatum (sunken sternum) and pectus carinatum (protruding sternum), each presenting unique anatomical challenges.
The occurrence of sternal deformities can stem from a range of causes, including genetic conditions, congenital malformations, or developmental anomalies. The complexity of these deformities warrants considerable attention, particularly as they may significantly impact an individual’s respiratory function and overall health. Patients with sternal deformities frequently experience limitations in lung capacity, leading to respiratory issues. Furthermore, these skeletal abnormalities can affect self-esteem and psychological well-being due to the observable physical changes.
Prevalence studies indicate that sternal deformities occur in a notable subset of the population. For example, pectus excavatum is estimated to affect approximately 1 in every 400 to 1000 individuals, with a higher incidence reported in males. This prevalence highlights the importance of understanding sternal deformities; early diagnosis and intervention can ameliorate the associated health implications. As a subject of ongoing research in medical literature, sternal deformities deserve comprehensive exploration, encompassing their types, diagnostic methods, as well as treatment options available for affected individuals.
Types of Sternal Deformities
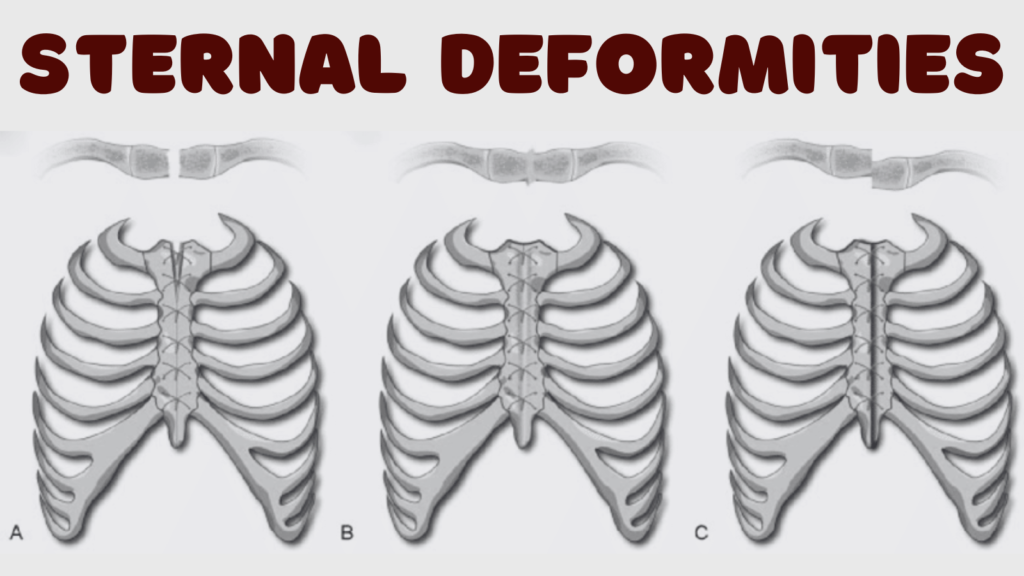
Sternal deformities are categorized primarily into two major types: pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum. Each of these conditions presents unique characteristics that distinguish them from one another, contributing to varying levels of impact on an individual’s health and appearance.
Pectus excavatum, often referred to as “sunken chest,” is characterized by a noticeable indentation in the sternum, where the breastbone appears to be recessed. This condition typically becomes more prominent during adolescence and can lead to psychological distress as well as physical complications, such as reduced lung capacity and heart function. Individuals with pectus excavatum may experience shortness of breath, particularly during physical activities. The severity of this condition is often classified based on the depth of the indentation, with significant cases often requiring surgical intervention.
On the other hand, pectus carinatum, also known as “pigeon chest,” is characterized by a protruding sternum. In contrast to pectus excavatum, this condition results in an outward bulging of the breastbone and is often observable at birth or develops during childhood. Pectus carinatum can sometimes be associated with other musculoskeletal abnormalities. Although it is generally less likely to have significant physical effects compared to pectus excavatum, it can still lead to cosmetic concerns and, to some extent, respiratory issues during growth spurts.
In addition to these primary types, there are other less common forms of sternal deformities, including mixed and composite deformities, where features of both pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum are present. Understanding these types is essential for early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, which may include physical therapy, bracing, or surgical correction based on individual cases.
Causes of Sternal Deformities
Sternal deformities, which result in abnormal shapes of the sternum, can arise from various genetic and environmental factors. One significant contributor is heredity. Many sternal deformities may be inherited within families, indicating a genetic predisposition that affects the development of the sternum. Various gene mutations are thought to play a role in the formation of these anomalies, affecting cartilage growth and bone structure.
Another critical factor linked to sternal deformities is connective tissue disorders. Conditions such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and Osteogenesis imperfecta can disrupt normal connective tissue formation, leading to irregularities in sternum shape and structure. These disorders can affect the integrity and pliability of the cartilage that forms the sternum, contributing to conditions such as pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum, known colloquially as funnel chest and pigeon chest, respectively. Due to the matrix of collagenous tissues that connect bones and support various bodily structures, any alteration can profoundly influence sternal morphology.
In addition to hereditary factors and connective tissue disorders, prenatal factors may also impact sternum development. Abnormalities during fetal development, such as inadequate space in the thoracic cavity, improper positioning, and external pressures, can lead to congenital sternal deformities. Moreover, maternal health, including nutrition and exposure to teratogens during pregnancy, may further complicate the normal development of the fetal sternum and surrounding thoracic structures.
Biomechanical factors are also relevant when considering the development of these deformities. Whether due to underlying health issues or aspects of posture, the resultant abnormal growth patterns in cartilage or bone can lead to sternal deviations. Understanding these contributing factors is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment planning of sternal deformities.

Symptoms and Clinical Features
Sternal deformities encompass a range of conditions that can manifest with various symptoms and clinical features. The presentation often varies significantly depending on the specific type of deformity present, with the most common being pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum. In general, individuals with these conditions may exhibit noticeable physical signs, particularly changes in the visual appearance of the chest. For instance, pectus excavatum leads to a concave chest that can appear sunken inwards, while pectus carinatum results in a protruding chest, giving it a bird-like appearance.
Aside from the aesthetic concerns, these deformities can have functional implications. Patients may experience breathlessness or reduced exercise capacity, particularly in cases where severe deformity impacts lung function or the mechanics of respiration. Some individuals report difficulty in performing physical activities, which can range from everyday tasks to competitive sports. This exercise intolerance can lead to a reduced quality of life, triggering feelings of frustration or embarrassment.
Moreover, it is crucial to consider the emotional effects of sternal deformities. Adolescents and children, in particular, may face social challenges stemming from the visual aspects of their condition, leading to issues related to self-esteem and body image. The psychological impact can be profound, potentially resulting in anxiety or depression for some patients.
Given the variety of symptoms and associated complications, proper diagnosis is essential. Healthcare professionals must conduct thorough physical examinations and may utilize imaging techniques to assess the degree of the deformity and its impact on respiratory function. By understanding the clinical significance of these symptoms, medical practitioners can better guide patients toward appropriate treatment options, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Diagnosis of Sternal Deformities
The diagnosis of sternal deformities is a multi-faceted process that often begins with a comprehensive physical examination performed by a healthcare professional. During this examination, the clinician assesses the patient’s chest shape and symmetry, palpates the sternum for any unusual protrusions or depressions, and checks for any associated respiratory difficulties or cardiovascular issues. This physical assessment is crucial because it helps in identifying the presence and type of deformity, such as pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum, and provides a preliminary understanding of its severity.
Following the initial examination, various imaging techniques are employed to gain a clearer understanding of the underlying anatomical structures and to evaluate the extent of the deformity. X-rays are commonly used as the first-line imaging modality to visualize the chest and identify any structural abnormalities in the sternum and surrounding ribcage. However, X-rays have limitations in providing comprehensive details about cartilage and soft tissue involvement.
For a more detailed assessment, computed tomography (CT) scans are often utilized. These scans provide cross-sectional imaging, allowing for a three-dimensional view of the thoracic cavity. This level of detail is particularly valuable in pre-surgical planning, as it helps in assessing the relationship between the sternum and vital thoracic structures, including the heart and lungs. Additionally, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended in specific cases to evaluate the soft tissues surrounding the sternum without exposing the patient to ionizing radiation.
Ultimately, early diagnosis of sternal deformities is critical, as it enables timely intervention and monitoring of potential complications that may arise. Proper imaging and assessment facilitate an effective treatment plan, which can significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Treatment Options for Sternal Deformities
Sternal deformities, which can manifest as conditions such as pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum, require careful consideration of treatment options based on severity, symptoms, and the patient’s age. Initially, non-surgical approaches may be recommended, particularly for less severe cases or in younger patients. These methods include physical therapy and brace therapy, aimed at improving posture and promoting thoracic expansion. Physical therapy may involve targeted exercises to strengthen the chest and surrounding muscles, potentially alleviating discomfort and enhancing physical function.
Brace therapy, meanwhile, utilizes custom-fitted orthotic braces designed to gradually reshape the sternum over time. This method has shown effectiveness particularly in growing children, as their thoracic structures are still malleable. Nevertheless, adherence to the prescribed regimen is critical for success, and parents often play an essential role in ensuring consistency in treatment.
For more severe sternal deformities that significantly impact respiratory function or psychosocial well-being, surgical interventions may be indicated. The Nuss procedure is one of the most frequently employed techniques, particularly for pectus excavatum. This minimally invasive surgery involves the placement of a curved metal bar beneath the sternum, which is then flipped to correct the depression. Typically, recovery is swift, yet the potential risks such as infection and bar displacement must be considered.
Another prominent surgical option is the Ravitch technique, which entails a more traditional open surgery. This approach involves the removal of deformed cartilage and repositioning of the sternum. While it is effective, it is associated with a longer recovery time compared to the Nuss procedure. Each patient’s case must be evaluated carefully by a specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment, taking into account the individual’s medical history, the nature of the deformity, and overall health status. Collaboration between the patient, family, and healthcare team is crucial in the journey toward correction of sternal deformities.

Living with Sternal Deformities
Individuals living with sternal deformities often face unique challenges that can affect their everyday lives, self-image, and psychological well-being. The visible nature of these deformities may lead to feelings of self-consciousness and insecurity, particularly during social interactions or while wearing clothing that exposes the chest area. As a result, many individuals report experiencing anxiety or depression stemming from their appearance, which can impact their quality of life.
Adjustments to daily activities may be necessary for those with sternal deformities. For instance, certain physical activities, including competitive sports or rigorous exercise, might need to be modified or avoided altogether. Individuals may also need to pay closer attention to their posture and body mechanics to minimize discomfort or complications associated with their condition. Additionally, the management of any associated respiratory issues could require lifestyle changes to promote optimal lung function and overall health.
Support systems play a crucial role in the lives of patients and their families. Connecting with medical professionals who specialize in sternal deformities can provide invaluable guidance on managing the condition. Support groups, whether online or in-person, offer opportunities for individuals to share their experiences and learn from one another. Families also benefit from educational resources and counseling services that help them better understand the condition and its implications. Engaging with community programs can foster a sense of belonging, which is essential for emotional and psychological support.
In fostering an environment of understanding and acceptance, individuals with sternal deformities can develop more confidence in their self-image. This process may involve embracing one’s unique physical traits while also seeking proactive medical and psychological support. Ultimately, recognizing the importance of community and professional assistance plays a vital role in coping with sternal deformities and the manifesting challenges.
Research and Future Directions
The field of sternal deformities has seen significant advancements in recent years, particularly in the realms of surgical techniques and genetic studies. Ongoing research is vital for enhancing our understanding of these conditions, which can substantially affect an individual’s quality of life. One promising area is the refinement of surgical approaches aimed at correcting sternal deformities, such as pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum. These conditions can impose not only physical but also psychological burdens on patients. Innovative minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as the Nuss procedure, have shown increased success in achieving favorable aesthetic and functional outcomes while minimizing recovery times.
In addition to surgical innovations, the exploration of genetic factors contributing to sternal deformities is gaining traction. Studies investigating the hereditary patterns and molecular mechanisms behind these conditions could lead to early identification and intervention strategies. By understanding the genetic basis, researchers may one day develop targeted therapies that could prevent the development of sternal deformities or mitigate their severity. Furthermore, advancements in imaging technologies, such as 3D modeling and personalized simulations, are assisting in creating tailored treatment plans that account for the unique anatomical variations of each patient.
Looking ahead, the potential for gene therapy offers a novel avenue for research that could alter the trajectory of treatment options available for sternal deformities. As investigators continue to delve deeper into the complexities of these conditions, it is highly plausible that we will see innovative therapies that will complement existing surgical methods. The anticipation of long-term outcomes from these enhanced treatment modalities will also inform best practices and improve patient care in the future. Continuous research is critical in the journey towards understanding and effectively managing sternal deformities, emphasizing a commitment to improving patient outcomes across various domains.
FAQs About Sternal Deformities
Sternal deformities present a range of concerns for individuals and their families. Below are frequently asked questions that address common inquiries regarding this condition.
What are sternal deformities?
Sternal deformities refer to structural anomalies of the sternum, which can manifest in various forms, including pectus excavatum (sunken chest) and pectus carinatum (protruding chest). These deformities can be classified based on their severity and the specific anatomical changes involved. Many individuals with sternal deformities are born with them, but some may develop these conditions over time.
How do sternal deformities affect overall health?
The impact of sternal deformities on an individual’s health can vary. In many cases, minor deformities may not lead to significant health issues. However, more severe cases can potentially lead to difficulties in breathing or exercise tolerance, cardiovascular complications, and psychosocial effects due to appearance. It is essential for individuals with noticeable deformities to consult with healthcare professionals for tailored advice.
What treatment options are available for sternal deformities?
Treatment for sternal deformities generally depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases, observation and regular monitoring may suffice. In contrast, more severe cases often require surgical intervention, such as the Nuss procedure or the Ravitch procedure, to correct the underlying structural issues. Non-surgical methods, including physical therapy and bracing, may also be employed as appropriate.
What is the prognosis following treatment?
The prognosis for individuals undergoing treatment for sternal deformities is generally favorable. Surgical interventions can effectively correct the deformity, enhance physical function, and improve aesthetic appearance. Most patients experience a positive change in their quality of life, leading to increased confidence and physical capability.
Understanding the complexities surrounding sternal deformities is vital for those affected. Seeking medical advice can clarify individual circumstances and lead to appropriate interventions.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

