Bursae Pain Relief: 7 Powerful Ways to Heal Fast
What Are Bursae?
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that play a crucial role in the musculoskeletal system, serving primarily as cushioning structures that minimize friction between moving tissues. These sacs are lined with synovial membrane and contain synovial fluid, which aids in lubrication. Bursae are strategically positioned throughout the body, particularly in areas where bones, tendons, and muscles are in close proximity, and they help to facilitate smooth movements during physical activities.
Anatomically, bursae can be classified into different types depending on their location and the specific functions they serve. The most common types of bursae include subcutaneous bursae, which are found just beneath the skin; subfascial bursae, located under the fascia; and subtendinous bursae, situated between tendons and bones. Each type of bursa is designed to accommodate specific movements and loads, thereby protecting adjacent tissues from stress or injury.
Important examples of bursae include the subacromial bursa in the shoulder, which alleviates friction between the rotator cuff and the acromion, and the olecranon bursa located at the elbow, which serves to decrease pressure during flexion and extension of the arm. The prepatellar bursa at the knee helps reduce friction between the kneecap and the skin. In sum, bursae are integral components that support joint function and mobility, contributing significantly to the overall health of the musculoskeletal system.
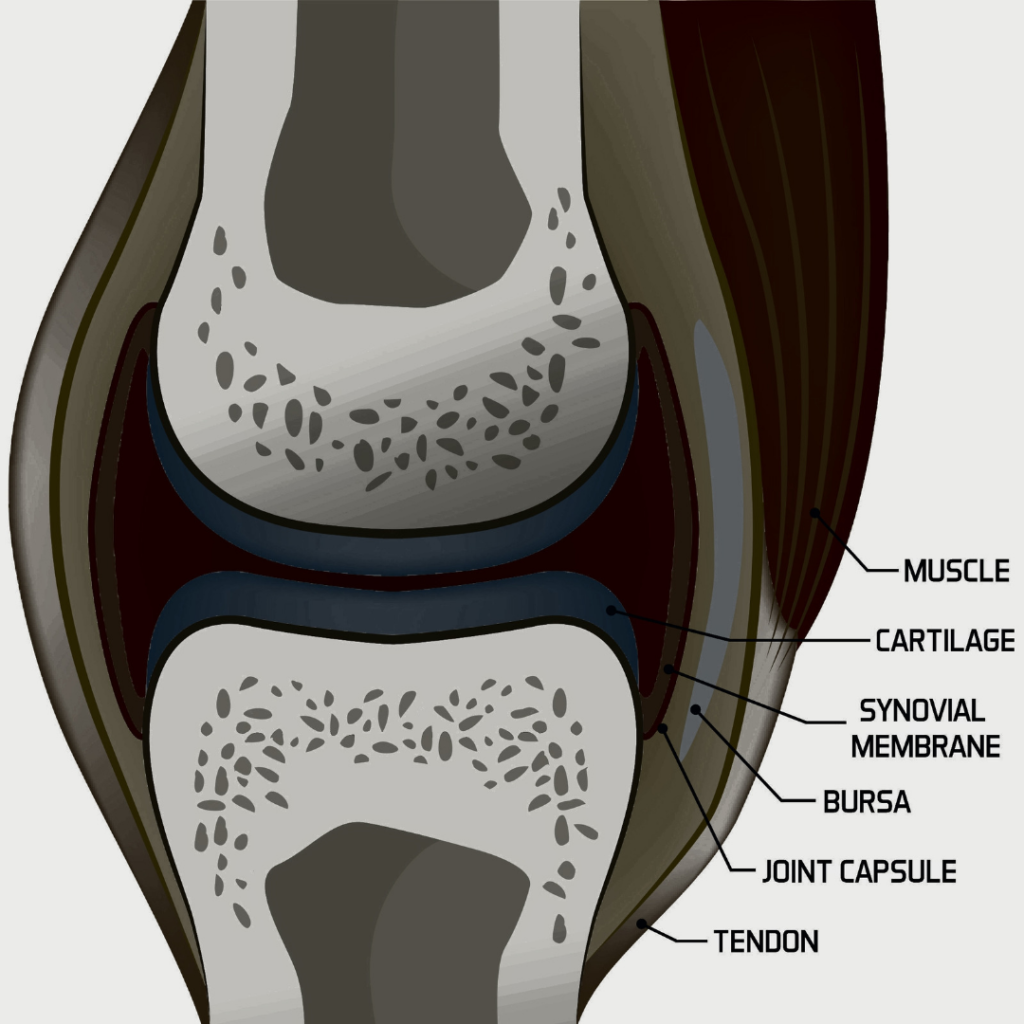
The Anatomy of Bursae
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs situated in various locations throughout the human body, primarily at points where muscles and tendons slide over bones. These structures serve a crucial function in reducing friction, thereby promoting smooth movement and minimizing wear and tear on the joints. Anatomically, a typical bursa is composed of a synovial membrane that surrounds a capsular composition of fibrous tissues. This specialized membrane is filled with synovial fluid, a viscous liquid that acts as a lubricant and shock absorber.
In terms of size and shape, bursae can vary significantly depending on their location and the specific anatomical demands of an area. For example, larger bursae can be found near the shoulder, known as the subacromial bursa, which plays a significant role in shoulder mechanics. Similarly, the prepatellar bursa is located in front of the kneecap and acts to cushion the joint during movement. Understanding these anatomical variations is essential, as they can help explain how bursae interact with nearby muscles and tendons.
Furthermore, bursae are strategically placed in locations where mechanical stress is prevalent, such as over bony prominences or where tendons pivot. Each bursa is designed to accommodate the movement of adjacent structures, allowing for efficient locomotion with minimal friction. Diagrams and images depicting the anatomy of bursae illustrate their connection to muscles and tendons, stressing the importance of these structures in maintaining joint health and function.
Overall, the anatomy of bursae highlights their indispensable role in the musculoskeletal system. By understanding their composition and function, one can appreciate the significance of these small yet vital sacs in supporting our daily movements.
Functions of Bursae
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs located throughout the body, primarily in areas where friction between bones, tendons, and muscles occurs. Their primary role is to reduce friction, allowing for smoother movements at the joints. When an individual engages in activities that require repetitive motion, these sacs serve as a critical buffer that prevents excessive wear and tear on surrounding tissues. The synovial fluid within bursae aids in lubricating the joint spaces, significantly contributing to the overall functionality of the musculoskeletal system.
In addition to reducing friction, bursae play an essential role in shock absorption. For example, during physical activities such as running or jumping, the impact generated can put considerable strain on adjacent structures. Bursae act as cushions, dissipating the force and thereby protecting bones, tendons, and muscles from potential injuries. This shock-absorbing feature not only preserves the structural integrity of the joints but also promotes optimal performance during dynamic movements.
Furthermore, bursae facilitate the smooth gliding of muscles and tendons over bony surfaces. This action ensures that joints can move freely without restriction, which is vital for maintaining a full range of motion. When bursae are functioning properly, they contribute to the overall balance and coordination of physical activities. In contrast, inflammation or damage to these structures can lead to conditions such as bursitis, impacting joint health and functionality. Therefore, understanding the multifaceted roles of bursae in reducing friction, absorbing shock, and ensuring smooth joint movement is crucial for recognizing their importance in maintaining optimal joint health.

Common Disorders of Bursae
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs located throughout the body that help reduce friction between tissues, particularly around joints. Despite their protective role, bursae can become inflamed or damaged, leading to various conditions, with bursitis being one of the most prevalent disorders associated with bursae. Bursitis is characterized by the inflammation of the bursae, often resulting from repetitive movements or prolonged pressure on the joints.
The causes of bursitis can vary widely. Frequently, it is linked to repetitive motions or positions that stress the bursa, such as kneeling, leaning on elbows, or participating in sports. It can also develop from sudden trauma, infection, or underlying health conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Symptoms typically include localized swelling, tenderness, and pain around the affected joint, which may worsen during movement or pressure. The intensity of these symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, leading to decreased mobility and discomfort.
Risk factors for developing bursitis include age, with older individuals being more susceptible due to natural wear and tear on the joints. Occupational activities that involve repetitive motion, such as construction work or gardening, also heighten the risk. Additionally, individuals with certain health conditions, obesity, or those who engage in high-impact sports may experience a higher incidence of bursitis.
Recognizing the signs of bursitis is crucial for timely intervention. If one experiences persistent pain, swelling, or fever in conjunction with joint discomfort, it is advisable to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis can facilitate appropriate treatment and recovery, preventing further complications associated with bursitis and ensuring a more comfortable return to regular activities.
Diagnosing Bursae-Related Issues
The diagnosis of bursae-related issues, such as bursitis, begins with a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional. This initial step usually involves a detailed medical history and physical examination. During the medical history assessment, the practitioner will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, onset, duration, and any activities that may have aggravated the condition. This information is crucial for understanding the underlying cause of the pain and inflammation associated with the bursa.
Next, a physical examination is performed. The healthcare provider will inspect the affected area for signs of swelling, redness, or warmth, which are common indicators of inflammation. Additionally, the practitioner may test the range of motion in the joint adjacent to the bursa to determine if movement is restricted or painful. Palpation may also be employed to identify tenderness or localized sensitivity, helping to identify the specific bursa that may be inflamed.
To confirm a diagnosis of bursitis or other bursae-related conditions, imaging tests are often utilized. Common imaging modalities include X-rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). X-rays can help rule out other potential sources of joint pain, such as fractures or arthritis, while ultrasound can provide real-time visualization of the bursa, allowing for the evaluation of swelling or fluid accumulation. MRI is a more detailed imaging technique that can offer insights into the condition of surrounding tissues and help assess the severity of the inflammation.
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend additional assessments, such as blood tests or aspiration of the bursa fluid, to check for infection or other abnormalities. By employing these diagnostic techniques, medical practitioners can accurately identify the source of a patient’s discomfort, formulate an effective treatment plan, and monitor the progression of bursae-related issues.
Treatment Options for Bursitis
Bursitis, characterized by inflammation of the bursae, can significantly affect mobility and quality of life. The treatment of bursitis varies, starting with conservative approaches aimed at alleviating symptoms and restoring function. Initially, rest is essential to allow the inflamed bursa to heal. Reducing activities that exacerbate symptoms is crucial; this may include avoiding repetitive motions or heavy lifting.
Ice therapy plays a pivotal role in managing swelling and pain. Applying ice packs to the affected area for intervals of 15 to 20 minutes can reduce inflammation, especially in the early stages following the onset of symptoms. Additionally, over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide relief from pain and reduce inflammation.
Physical therapy is often recommended as a non-invasive treatment option. A physical therapist can guide individuals through exercises that enhance strength and flexibility, targeting both the affected area and surrounding muscles to prevent future occurrences of bursitis. Stretching and strengthening exercises are tailored to the individual’s specific needs, addressing muscle imbalances or weaknesses contributing to the condition.
For cases that do not respond to conservative treatment, more invasive interventions may be necessary. Corticosteroid injections are commonly used to provide fast relief from severe inflammation. These injections deliver medication directly into the bursa to decrease swelling and pain. Another option is aspiration, which involves removing fluid from the swollen bursa, providing immediate relief and allowing for a more effective assessment of the underlying issue.
In rare and severe instances, surgical intervention may be required, particularly when bursitis is chronic or recurrent. Surgery typically involves removing the affected bursa and is reserved for cases where traditional treatments fail to provide relief. Advances in minimally invasive techniques have made this option more accessible.
Preventing Bursitis and Supporting Joint Health
Bursitis, characterized by inflammation of the bursae, can significantly impact joint mobility and quality of life. Preventing this condition involves a multi-faceted approach that emphasizes lifestyle modifications, proper exercise techniques, and ergonomic practices. By incorporating these strategies, individuals can promote optimal joint health and minimize the risk of bursitis.
First and foremost, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in preventing bursitis. Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate unnecessary stress on the joints, particularly those that are commonly affected by bursitis, such as the hips and knees. Employing a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables, may also support joint health. Hydration is equally important, as it keeps the synovial fluid within the joints adequately lubricated.
In terms of exercise, engaging in regular, low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, or walking can strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints, providing better support for the bursae. It is equally important to incorporate stretching exercises to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness. When participating in physical activities, it is vital to engage in proper techniques to avoid placing excess strain on the joints, which could lead to inflammation.
Additionally, ergonomic practices in daily activities can significantly reduce stress on bursae. For instance, when lifting objects, bending the knees rather than the waist can help protect the hip bursae. Using cushioning supports such as knee pads or ergonomic chairs can also aid in minimizing pressure on sensitive bursae during prolonged periods of sitting or kneeling.
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can take proactive steps toward supporting joint health and reducing the risk of developing bursitis. Prioritizing joint care through lifestyle choices, appropriate exercise methods, and ergonomic awareness remains essential for long-term mobility and comfort.

FAQs About Bursae
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that provide cushioning between bones and soft tissues, playing a crucial role in reducing friction during joint movements. Despite their importance, many individuals have questions regarding their function, related conditions such as bursitis, and how to manage potential issues. Here are some frequently asked questions about bursae.
What are the common signs of bursitis?
Symptoms of bursitis typically include localized pain, swelling, and tenderness near a joint, alongside stiffness that exacerbates with movement. Over time, individuals may notice limited range of motion in the affected area. It is essential to recognize these signs early to prevent further complications.
How can bursitis be prevented?
Prevention strategies primarily focus on reducing repetitive motions and overuse injuries. For instance, incorporating proper warm-up routines and utilizing ergonomic tools at work can minimize the risk. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular, low-impact exercise helps support joint health and alleviate excessive pressure on bursae.
What are the treatment options for bursitis?
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition. Initial management typically includes rest, ice application to reduce swelling, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain. In more persistent cases, corticosteroid injections may be necessary, while physical therapy can strengthen surrounding muscles and improve joint function.
When should one consult a healthcare provider?
It is advisable to seek medical attention if symptoms persist despite home treatment, or if there is persistent swelling, significant pain, or fever accompanying the discomfort. A healthcare provider can recommend further evaluation and more advanced treatment strategies if needed.
Can bursitis become a chronic condition?
Yes, if left untreated or if repetitive stress continues, bursitis can become a chronic issue. Chronic bursitis may lead to persistent swelling, pain, and reduced mobility in the affected joint. Long-term management, including physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and anti-inflammatory treatments, can help prevent flare-ups.
Are there any home remedies for managing bursitis?
Yes, in addition to rest and ice application, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve joint function. Compression bandages may reduce swelling, while elevating the affected area can alleviate discomfort. Some individuals find relief through warm compresses or Epsom salt baths, but these should complement, not replace, medical advice.
Understanding bursae and their associated conditions allows for better management of joint health, encouraging proactive measures to maintain mobility and quality of life.
Conclusion: The Importance of Bursae in Joint Health
Bursae play a critical role in maintaining joint health and functionality. These small, synovial fluid-filled sacs serve as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles, effectively reducing friction and facilitating smooth movements. Understanding the structure and function of bursae is essential for recognizing their significance in preventing joint issues. When these protective sacs become inflamed—a condition known as bursitis—it can lead to pain, limited mobility, and overall discomfort, significantly affecting one’s quality of life.
As discussed, bursae are strategically located around key joints such as the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees. This strategic positioning underscores their importance in providing not only support but also protection to the surrounding tissues. Thus, taking proactive steps to ensure the health of these structures is paramount. Simple practices such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in stretching and strengthening exercises, and using proper techniques during physical activities can help support bursae function and prevent inflammation.
Moreover, recognizing the early signs of bursitis can lead to timely intervention, often preventing chronic conditions from developing. Awareness of factors that may contribute to the degeneration of bursae is equally essential—such as repetitive movements, prolonged pressure on joints, and age-related changes. By implementing thoughtful approaches to joint care, individuals can preserve their bursae and promote better overall joint health.
In conclusion, understanding bursae is vital for appreciating their role in joint functionality and health. This knowledge can empower individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles, reduce the risk of bursitis, and maintain joint integrity throughout their lives. Prioritizing the health of bursae not only enhances movement but also contributes to long-term well-being and active living.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

