Injury Scars: 7 Effective Ways to Heal Faster
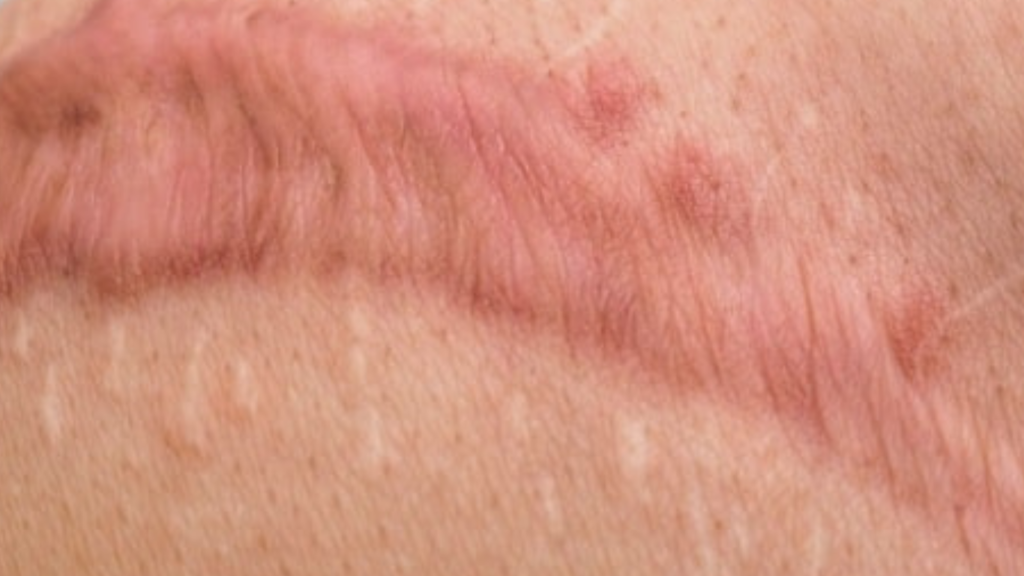
What Are Injury Scars?
Injury scars are a natural outcome of the body’s healing process following skin damage, such as cuts, burns, or surgical wounds. When skin is injured, the body initiates a complex biological response to repair the damaged tissue. This involves a series of phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Initially, blood vessels constrict to prevent excessive bleeding, followed by inflammation where white blood cells remove debris and pathogens. The proliferation phase sees new tissue, including collagen, formed to provide support, while the remodeling phase gradually reorganizes this tissue over time.
Scars can be categorized into several types, each defined by specific characteristics. Hypertrophic scars are raised, red, and typically confined to the boundaries of the original injury. They often improve with time but can be itchy or uncomfortable. On the other hand, keloid scars extend beyond the original wound site, appearing thick, rubbery, and often darker than the surrounding skin. These scars can be more persistent and may require medical intervention, such as corticosteroid injections or surgical removal, if they cause discomfort or aesthetic concerns.
Finally, atrophic scars present as depressions in the skin, commonly resulting from conditions like acne or chickenpox. The lack of collagen during the healing process leads to this sunken appearance, which can also necessitate treatment solutions like dermal fillers or laser therapy.
Understanding the types of injury scars and the mechanisms behind their formation is crucial for those seeking effective management strategies. The healing process is influenced by various factors, including the severity of the original injury, individual skin type, and overall health. By comprehensively understanding scar biology, individuals can make informed decisions regarding their treatment options and approaches to care.
The Science Behind Scarring: How the Body Heals
Understanding the physiological mechanisms underlying wound healing is essential for comprehending the formation and maturation of injury scars. Wound healing occurs through a series of distinct yet overlapping stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Each phase plays a crucial role in restoring the integrity of the skin and surrounding tissues, ultimately influencing the characteristics of any resulting scar.
The first phase, hemostasis, begins immediately after an injury occurs. Blood vessels constrict to minimize blood loss, and platelets aggregate at the site to form a clot. This clot not only serves as a physical barrier against pathogens but also releases growth factors that play a significant role in the subsequent healing processes. The inflammatory phase follows, lasting a few days. During this time, the body activates immune responses to remove debris and bacteria. Inflammatory cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, infiltrate the wound site to facilitate cleaning and prepare for healing.
Following inflammation, the proliferation phase begins and lasts several days to weeks. In this stage, fibroblasts are activated, proliferating and synthesizing collagen, a key protein essential for tissue repair. Collagen forms the structural framework for new tissue, promoting strength and integrity. Additionally, angiogenesis occurs, leading to the formation of new blood vessels, allowing for improved nutrient delivery to the area. This process is critical, as the newly formed tissue, referred to as granulation tissue, is vital for the healing process.
Lastly, the remodeling phase can last for months to years. During this time, the collagen matrix undergoes continuous restructuring, which helps the scar mature and become more like normal tissue. The role of fibroblasts remains significant as they help reorganize collagen fibers, facilitating better tensile strength of the scar. Understanding these physiological processes highlights the complexity of scar formation and the importance of proper care during each healing stage.
Factors Influencing Scar Formation
Scar formation is a complex biological process influenced by a myriad of factors, including age, genetics, skin type, and the nature of the injury. Understanding these factors is essential for both effective management of existing scars and prevention of new ones.
Age plays a significant role in how the body responds to injury and heals. Children’s skin typically heals faster and may result in softer scars due to the higher cellular turnover rates compared to older adults. As individuals age, their skin loses elasticity and collagen production decreases, which can lead to more pronounced and rigid scars. This age-related change is vital in determining the appearance and texture of scars.
Genetics is another critical aspect that significantly influences scar formation. Individuals may inherit certain traits that predispose them to thicker or more noticeable scars, such as keloids or hypertrophic scars. Understanding one’s family history concerning scar formation can provide insight into how one might heal from injuries and what preventive measures could be effective.
The type of skin also contributes to scar characteristics. For instance, fairer skin may develop less noticeable scars, while darker skin types may be at an increased risk for hyperpigmented or keloid scars. Moreover, the location of the injury and the tension in the surrounding skin can affect scar development as well; areas subject to high movement or pressure are more likely to create distinctive scars.
Finally, the nature of the injury itself—whether it is a surgical incision, burn, or laceration—directly impacts the healing process. More severe injuries or those involving deeper layers of skin often lead to more substantial scarring. Thus, a multifactorial approach is essential in comprehensively understanding how different elements contribute to scar formation and outcomes.

Preventing Scarring: Best Practices for Injury Care
Effective management of injuries not only promotes healing but also plays a crucial role in minimizing the potential for scarring. The first step in preventing scarring is ensuring proper wound care from the moment of injury. This includes cleaning the wound with mild soap and water to remove debris and bacteria, followed by applying an appropriate antiseptic. Keeping the wound covered with a sterile bandage can help to protect it from infection and further injury.
Hydration is an essential aspect of both overall health and skin recovery. Proper hydration helps to maintain skin elasticity and aids in the healing process. Consuming adequate fluids can positively influence the appearance of scars, as well-hydrated skin tends to repair more efficiently. Alongside hydration, nutrition plays a vital role. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins promotes cellular repair and supports skin health. Nutrients such as vitamins C and E, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial for wound healing.
In addition to hydration and nutrition, utilizing silicone sheets or gels can be an effective strategy for minimizing scarring. These products work by providing a protective barrier over the wound, which can help to regulate moisture and promote an optimal healing environment. Clinical studies have shown that silicone treatments can significantly reduce scar formation when applied consistently to healing wounds.
While many injuries can be managed at home, certain situations warrant medical attention. It is advisable to seek professional help for deeper wounds, those that show signs of infection, or injuries that do not exhibit healing progress. Timely medical intervention can prevent excessive scarring and ensure a comprehensive approach to injury care.
Scar Treatment Options: From Home Remedies to Medical Procedures
Scar treatment options encompass a wide array of choices, ranging from simple home remedies to advanced medical procedures. It is essential to evaluate the effectiveness and suitability of each option based on the scar type, location, and individual skin characteristics.
Topical treatments, such as silicone gel sheets and creams, are popular for their accessibility and ease of use. Silicone has been extensively studied and found to improve the appearance of hypertrophic scars and keloids. These products work by hydrating the scar and creating an optimal healing environment. While they are non-invasive with minimal side effects, results can vary, and a consistent application over several months is usually necessary to see visible improvements.
Another common home remedy includes natural oils like aloe vera and vitamin E, which some people use for their presumed healing properties. Although these remedies can offer some moisturizing benefits, scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness in scar reduction is limited.
For those seeking more significant results, advanced medical procedures are available. Laser therapy is one such option, utilizing focused light technology to diminish scar tissue. It can stimulate collagen production and improve texture and pigmentation. However, multiple sessions may be required, and patients might experience discomfort or temporary skin irritation.
Dermabrasion is another effective technique that involves mechanically exfoliating the top layers of skin to promote new skin growth. Though this can produce significant improvements for certain scars, it may not be suitable for all skin types and requires an adequate recovery period.
Surgical scar revision is considered for more severe or prominent scars. This procedure entails removing the existing scar and realigning the skin to heal more aesthetically. While this option can provide dramatic results, it also carries risks such as infection and the potential for new scarring.
In summation, when considering scar treatment options, it is crucial to weigh the pros and cons of each method, tailoring the choice to individual needs for optimal results.
Psychological Impact of Scars: Coping Mechanisms
The presence of scars, whether a result of injury, surgery, or trauma, often extends beyond the physical realm, embedding profound psychological effects in those affected. Living with visible scars can significantly influence self-esteem and body image. Individuals may experience embarrassment, self-consciousness, or even feelings of diminished identity, particularly if the scars are prominent or located on visible areas of the body. This psychological burden manifests in various ways, including social withdrawal, anxiety, or depression, which may compound the emotional aspect of recovery.
To effectively manage these psychological impacts, it is essential for individuals to develop coping mechanisms that can facilitate emotional healing alongside physical recovery. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one such approach, which focuses on changing negative thought patterns and improving self-perception. This therapeutic modality often helps individuals refrain from internalizing negative societal messages about scars, thereby fostering a healthier self-image.
In addition to professional help, support groups represent a valuable resource for those coping with the psychological effects of scars. Sharing experiences with others who face similar challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation and enhance feelings of community. Moreover, individuals can utilize mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, to manage anxiety and improve emotional resilience.
Furthermore, engaging in creative therapies, such as art or music therapy, can provide an outlet for self-expression. These practices encourage individuals to articulate their feelings regarding their scars and may ultimately lead to a more positive relationship with their bodies. Emphasizing the importance of mental health support during the healing process is paramount, as addressing psychological distress can play a critical role in recovering from both the emotional and physical aspects of living with scars.

Innovative Research and Future Directions in Scar Management
The field of scar management is evolving rapidly, with innovative research exploring various advanced therapeutic strategies designed to mitigate the appearance and impact of scars. Recent advancements have focused on treatments such as stem cell therapy, bioengineered skin substitutes, and emerging technologies that have the potential to revolutionize scar management. Stem cell therapy, in particular, has garnered significant attention for its ability to promote skin regeneration and healing. Research indicates that stem cells can enhance the body’s natural repair mechanisms, potentially leading to improved outcomes in scar reduction.
Another promising development in scar management is the use of bioengineered skin substitutes. These substitutes are designed to mimic the properties of natural skin, providing a supportive environment for healing and tissue regeneration. Clinical trials have shown that these advanced materials can reduce scar formation and improve aesthetic results post-injury or surgery. As technology continues to improve, the integration of bioengineering techniques in scar treatment is likely to become more prevalent.
Additionally, advancements in medical technology are paving the way for new and more effective modalities in scar treatment. Techniques such as laser therapy, radiofrequency treatments, and microneedling are being refined to enhance their specificity and efficacy in targeting scar tissue. Furthermore, researchers are investigating the role of anti-inflammatory agents and growth factors in preventing scar formation or improving the texture of existing scars. These treatments hold great promise for enhancing patient outcomes and minimizing the psychological impact of scars.
As the understanding of scar biology deepens, continued research will probably uncover additional innovative approaches for effective scar management. These advancements not only offer hope for patients seeking aesthetic improvement but also emphasize the importance of scientific inquiry in developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions about Injury Scars
Injury scars can be a concern for many individuals, leading to various questions about their appearance, healing process, and potential treatment options. Here, we address some of the most frequently asked questions regarding injury scars to provide clarity and understanding.
What are the different types of injury scars?
Injury scars are classified into several types, including atrophic, hypertrophic, and keloid scars. Atrophic scars appear depressed due to loss of underlying tissue, while hypertrophic scars are raised but remain confined to the injury site. Keloid scars, on the other hand, extend beyond the original wound and can be itchy or painful. Each type requires a different approach for management and treatment.
How long does it usually take for injury scars to heal?
The healing process for injury scars varies significantly based on factors such as the type and severity of the injury, individual skin type, and location on the body. Generally, initial healing may take a few weeks, but complete maturation of the scar could take several months to years. Throughout this time, the scar often changes in color and texture, gradually becoming less noticeable.
Are there cosmetic procedures available for scar treatment?
Yes, there are numerous cosmetic procedures to improve the appearance of injury scars. Options include laser therapy, microdermabrasion, chemical peels, and surgical revision. These procedures aim to remove or minimize scarring, as well as restore skin texture and tone. Consultation with a qualified dermatologist or plastic surgeon is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment based on individual circumstances.
What potential complications should I be aware of?
Injury scars can sometimes lead to complications, such as infection, abnormal healing, or emotional distress. In some cases, scars can cause discomfort or restricted movement, particularly if located near joints. It is vital to monitor the healing process and consult a healthcare professional if any unusual symptoms arise.
Can injury scars completely disappear over time?
While some injury scars may fade significantly over time, they rarely disappear completely. The extent of fading depends on factors like the type of scar, individual healing ability, and treatment methods used. Consistent use of scar creams, sun protection, and appropriate treatments can enhance the fading process and improve overall appearance.
How can I prevent a scar from becoming more prominent?
To minimize scar prominence, it is essential to care for the wound properly during the healing process. Keep the wound clean, hydrated, and protected from the sun. Silicone sheets or gels and pressure therapy can also help flatten raised scars. Avoid picking at scabs or stretching the healing skin, as this can worsen scarring.
Do over-the-counter products help in reducing scars?
Over-the-counter products, such as silicone gels, scar creams containing onion extract or Vitamin E, and moisturizing lotions, can help reduce the appearance of scars. These products work best on new or mild scars and require consistent use over time. For more significant scars, consulting a dermatologist for specialized treatments may be necessary.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

