The Marvels of Milk Ducts: Nourishing Life from Within
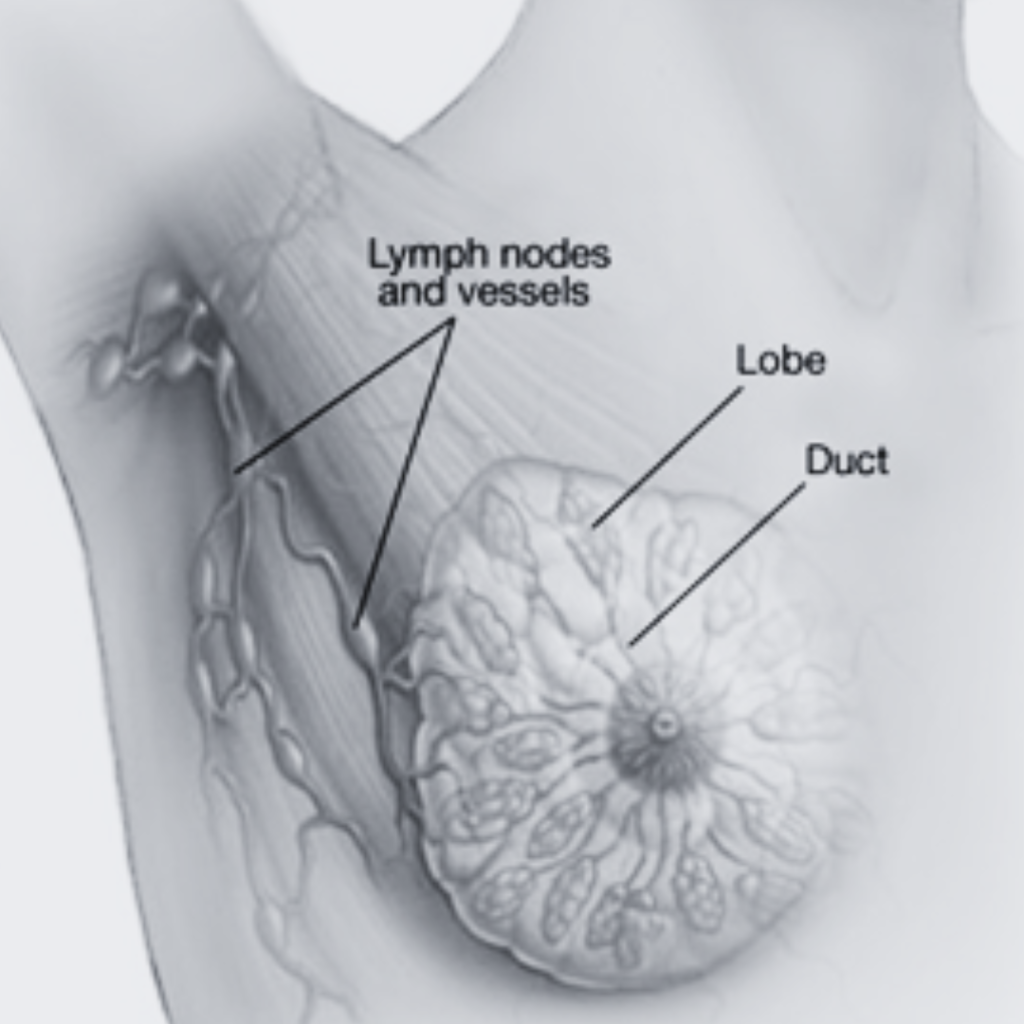
Milk ducts, often an underappreciated part of the human body, play a crucial role in the nourishment and sustenance of life. These intricate structures, found primarily in the female breast, are responsible for the production, storage, and transportation of milk. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of milk ducts, exploring their anatomy, function, and significance in the miracle of motherhood.
The Anatomy of Milk Ducts
Milk ducts are slender, tube-like structures that make up a complex network within the breast. They start as tiny, hollow sacs called alveoli, which are distributed throughout the breast tissue. These alveoli are lined with milk-producing cells and are connected to one another through a network of ever-branching ducts. As these ducts merge and converge, they eventually form larger ducts that lead to the nipple.
The milk duct system can be compared to a tree, with the alveoli as the leaves, the smaller ducts as branches, and the larger ducts as the trunk. The nipple, analogous to the tip of a tree branch, is where milk is expelled from the body.
The Function of Milk Ducts
The primary function of milk ducts in the human body is to facilitate the production, storage, and transport of breast milk. These ducts are a crucial part of the female mammary system and are responsible for the following key functions:
- Milk Production: Milk ducts play a central role in milk production. Within the breast tissue, there are small, hollow sacs called alveoli, which are lined with milk-producing cells. When a woman is pregnant, hormonal changes, particularly the rise in prolactin, stimulate the alveoli to produce milk. This milk is initially secreted into the alveoli.
- Milk Storage: Once milk is produced in the alveoli, it is held in these small sacs temporarily. The alveoli act as storage units, allowing milk to accumulate before being transported to the nipple for eventual expulsion. This storage system ensures that a baby can access a consistent and readily available source of milk when breastfeeding.
- Milk Transportation: The milk-producing alveoli are connected to one another through a network of ducts. These ducts branch and merge as they extend through the breast tissue. They gradually converge into larger ducts, which ultimately lead to the nipple. These ducts are responsible for transporting milk from the alveoli to the exterior of the breast.
- Milk Release: When a baby begins to breastfeed and sucks at the nipple, the stimulation triggers the release of another hormone, oxytocin. Oxytocin causes the muscles surrounding the milk ducts to contract. This contraction propels the milk from the alveoli into the ducts and out through the nipple, making it available for the infant to consume. The release of milk is a highly coordinated process, ensuring that the baby gets the nourishment needed during breastfeeding.
- Adaptation to Demand: The milk duct system is adaptable and responsive to the demands of the infant. As a baby grows and requires more milk, the mother’s body can increase milk production by stimulating the alveoli to produce more milk. This process ensures that the baby’s nutritional needs are met at various stages of development.
Significance in Motherhood
The significance of milk ducts in motherhood is multifaceted, as they play a crucial role in the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the mother-child relationship. Here are some of the key ways in which milk ducts and breastfeeding are significant in the context of motherhood:
- Nutritional Benefits: Milk ducts enable mothers to provide their infants with the most natural and nutritionally balanced source of food – breast milk. Breast milk contains essential nutrients, antibodies, and hormones, perfectly designed to meet the baby’s nutritional needs, promote healthy growth, and provide protection against infections and diseases.
- Bonding: Breastfeeding is a deeply intimate and bonding experience between a mother and her child. The act of breastfeeding involves close physical contact and eye-to-eye interaction, fostering a strong emotional connection. This physical closeness and skin-to-skin contact promote a sense of security and emotional attachment.
- Emotional Well-being: Breastfeeding triggers the release of oxytocin, often called the “love hormone” or “bonding hormone.” Oxytocin not only helps with milk ejection but also enhances feelings of love, trust, and emotional connection between the mother and child. This emotional bond is a fundamental aspect of motherhood.
- Maternal Health: The process of breastfeeding has significant benefits for the mother’s health. It can help with post-pregnancy weight loss, as it burns calories, and it may reduce the risk of certain cancers, such as breast and ovarian cancer. Additionally, it aids in uterine contraction, helping the mother’s body return to its pre-pregnancy state.
- Psychological Well-being: Successfully breastfeeding can boost a mother’s self-esteem and confidence. Knowing that she can provide her child with the nourishment they need can be empowering and emotionally fulfilling. The sense of accomplishment and connection to her child can contribute to positive psychological well-being.
- Convenience: Breastfeeding can be more convenient than formula feeding, as it requires no preparation, sterilization of bottles, or carrying around formula. The mother’s milk is always ready and at the right temperature.
- Cost-Efficient: Breastfeeding is cost-efficient as it eliminates the need to purchase formula, bottles, and other feeding accessories. This can help ease the financial burden on mothers and families.
- Environmental Impact: Breastfeeding has a lower environmental impact compared to formula feeding. It reduces the need for manufacturing, packaging, and transportation of formula and feeding equipment, which can be resource-intensive.
Conclusion
Milk ducts and breastfeeding hold profound significance in motherhood, extending well beyond their biological functions. They are essential in providing the ideal source of nutrition for infants while fostering a strong emotional bond between mother and child. The benefits of breastfeeding also extend to maternal health, psychological well-being, and even environmental sustainability. As we appreciate the intricate marvel of milk ducts, we gain a deeper understanding of the extraordinary journey of motherhood, where nature’s design and a mother’s love intersect to nourish and nurture the next generation.
Disclaimer
This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns or questions about breastfeeding, milk ducts, or any related health issues, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or lactation consultant for guidance and support. The information provided here is based on general knowledge and may not apply to every individual’s unique circumstances.
Stay updated—subscribe now for informed empowerment!
Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

