Traumatic Sternal Bulge: 7 Shocking Causes & Fixes
Understanding Traumatic Sternal Bulge
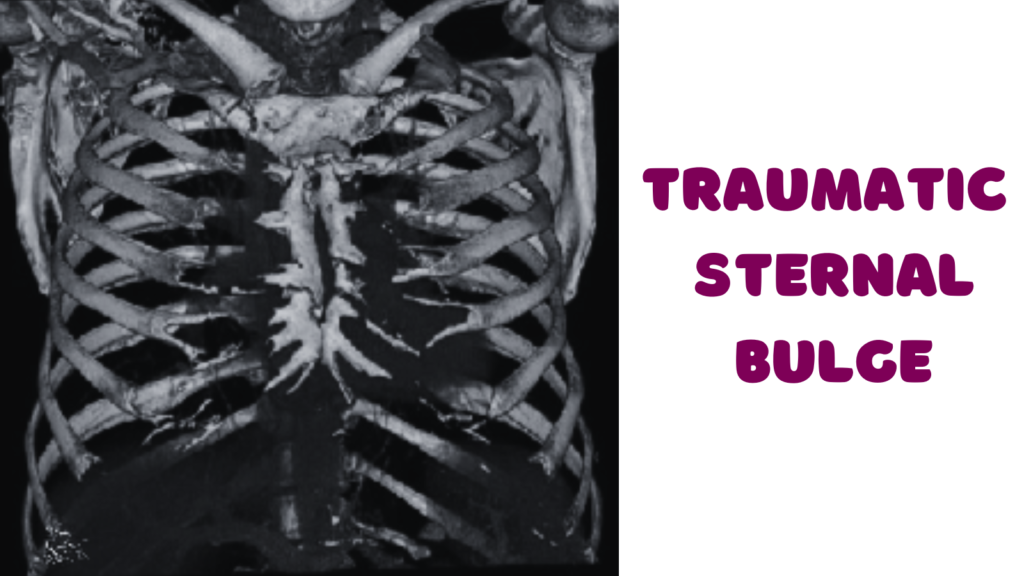
A traumatic sternal bulge is a noteworthy medical condition characterized by an abnormal protrusion of the sternum, which is often the result of traumatic injury. This condition is significant in the realm of thoracic injuries and can be indicative of underlying damage to the chest wall or mediastinum. The occurrence of a sternal bulge can arise from various incidents, such as vehicular accidents, sports-related injuries, or falls, all of which can result in blunt force trauma to the chest area.
Understanding this condition is crucial for both medical professionals and patients, as a traumatic sternal bulge may result in complications that extend beyond the superficial deformity. Trauma to the sternum can lead to serious consequences, including damage to the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels. Awareness of the signs and risks associated with this condition is essential for early diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Victims of chest trauma presenting with a sternal bulge must be evaluated promptly as the implications of such injuries are profound. The condition not only poses aesthetic concerns but may also indicate internal injuries that require surgical intervention. The importance of medical attention cannot be overstated, given the anatomical complexity of the chest region and the potential for life-threatening complications. Furthermore, a thorough understanding of the causes, symptoms, and necessary treatments for traumatic sternal bulge will empower patients and caregivers to make informed decisions regarding care and management.
Anatomy of the Sternum and Surrounding Structures
The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, is a key component of the human ribcage, playing a vital role in the protection of critical organs. Located at the anterior midline of the thoracic cavity, it serves as an attachment point for the ribs and various muscles. The sternum is divided into three main parts: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The manubrium articulates with the clavicles and the first pair of ribs, whereas the body connects to the true ribs through costal cartilage. This configuration provides both stability and flexibility to the thoracic cage, ensuring that respiratory movements can occur without obstruction.
Surrounding the sternum are the costal cartilages, which connect the sternum to the ribs. These cartilages play a crucial role by allowing for the expansion and contraction of the ribcage during respiration. The ribs, numbering twelve pairs, also protect vital organs, including the heart and lungs, which are situated medial to the thoracic wall. The close proximity of the sternum to the heart makes understanding its structure particularly important, especially in instances of trauma that may lead to a sternal bulge.
A traumatic sternal bulge can not only indicate structural changes in the sternum itself but may also exert pressure on surrounding structures, including the heart and major blood vessels. This can lead to complications such as impaired cardiac function or restricted blood flow. Therefore, a thorough comprehension of the anatomy involved is essential, as it helps to elucidate the potential implications of a sternal bulge on adjacent organs and systems within the thoracic cavity. Such an understanding is fundamental for healthcare professionals when diagnosing and treating patients experiencing issues related to the sternum.
Causes of Traumatic Sternal Bulge
Traumatic sternal bulge is often the result of direct trauma to the chest area, leading to injuries that compromise the structural integrity of the sternum. One of the most common causes is motor vehicle accidents, where the impact forces can exert significant pressure on the chest, resulting in fractures or dislocations of the sternum. Such incidents not only lead to physical damage but can also involve a range of secondary injuries, exacerbating the condition.
Another frequent cause of traumatic sternal bulge is sports-related injuries. Athletes, especially those involved in contact sports like football or rugby, face increased risks due to the high-energy impacts associated with gameplay. Falls, whether from a height or during physical activities, also contribute largely to the incidence of this condition. For example, an individual may sustain a direct hit to the chest during a fall, leading to a localized bulge as a result of bone fracture or soft tissue damage.
Moreover, there are certain risk factors that can predispose individuals to experience traumatic sternal bulge. Age is an important consideration; older adults tend to have a higher risk due to increased fragility of bone structures. Additionally, individuals with pre-existing conditions, such as osteoporosis, may be more susceptible to sternal injuries from relatively minor traumas. Body composition plays a role as well; individuals with prominent chests or pre-existing deformities may find that even standard injuries produce severe consequences, such as a traumatic sternal bulge.
Understanding the various causes of traumatic sternal bulge is crucial for effective prevention and treatment planning. Identifying these risk factors can significantly aid in mitigating potential injuries and developing strategies to protect vulnerable populations from chest trauma.

Signs and Symptoms of Traumatic Sternal Bulge
A traumatic sternal bulge is characterized by a range of physical and systemic symptoms that patients may experience following an injury to the sternum. The most prominent physical manifestation is a visible bulging of the sternum, which can be particularly alarming for both the patient and medical professionals. This bulging occurs as a result of trauma that may involve fractures or distortions in the sternal structure.
In addition to the visible displacement of the sternum, tenderness in the affected area is commonly observed. Patients may report localized pain when pressure is applied, which often intensifies with movement or deep breaths. This tenderness is indicative of underlying inflammation or damage to the bone and surrounding soft tissues.
Systemically, individuals with a traumatic sternal bulge may experience symptoms such as chest pain, which can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating ache. The pain may radiate to other areas, such as the shoulders, back, or arms, mimicking other serious conditions like myocardial infarction. Additionally, difficulty breathing can ensue, particularly if the bulging causes compression of nearby structures such as the lungs or great vessels. Patients often describe this sensation as feeling short of breath or as if they are “gasping for air.”
Other potential symptoms may include bruising or swelling around the sternum, which further highlights the extent of the injury. Some individuals might experience dizziness or lightheadedness, especially if the pain is severe and affects their ability to take deep breaths. In severe cases, additional complications such as pneumothorax may develop, necessitating immediate medical attention. Hence, prompt recognition of these signs and symptoms is essential for effective management and intervention in cases of traumatic sternal bulge.
Diagnosis of Traumatic Sternal Bulge
Diagnosing a traumatic sternal bulge involves a thorough evaluation that combines clinical assessments and advanced imaging techniques. The initial step typically includes a comprehensive physical examination where the healthcare provider assesses the chest area for any visible protrusions, tenderness, and range of motion. This evaluation not only identifies the presence of a sternal bulge but also helps assess the overall integrity of the chest structure.
Imaging plays a crucial role in accurately diagnosing a traumatic sternal bulge. X-rays are often the first imaging modality utilized, allowing clinicians to visualize any bone deformities or fractures. While X-rays provide a basic overview, they may not reveal the extent of soft tissue injury or associated complications. For a more detailed examination, computed tomography (CT) scans are employed. CT imaging provides cross-sectional views of the thorax, permitting healthcare professionals to assess the sternal bulge’s characteristics, determine the presence of any underlying injuries, and evaluate surrounding structures, including the lungs and cardiovascular system.
In certain cases, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be indicated, especially when soft tissue involvement is suspected. MRI is particularly useful in identifying potential muscle or cartilage injuries that might accompany a sternal bulge, offering a non-invasive assessment without the risks associated with ionizing radiation.
It is imperative to conduct a differential diagnosis to rule out other medical conditions that could mimic the symptoms of a sternal bulge, such as costochondritis, hernias, or infections. This differential analysis ensures that appropriate treatment strategies are implemented based on the underlying causes of the bulge. Overall, a combination of clinical evaluation and advanced imaging techniques facilitates an accurate diagnosis of a traumatic sternal bulge, paving the way for effective management and treatment.
Treatment Options for Traumatic Sternal Bulge
Treatment for traumatic sternal bulge primarily hinges on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced by the patient. For mild cases, conservative measures are often recommended. This includes rest and the application of ice to the affected area to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Pain management may involve the use of over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or prescribed medications that help in enhancing comfort during the recovery process.
Physical therapy can also play a crucial role in recovery from a traumatic sternal bulge. A tailored rehabilitation program focuses on improving strength and flexibility in the chest area, which can help mitigate discomfort and promote healing. In many instances, these non-invasive methods yield favorable results, allowing patients to regain their normal activities without the need for surgical intervention. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of these conservative approaches hinges on the patient’s adherence and the extent of the initial injury.
However, in more severe cases where conservative therapy fails to provide relief or if the bulge poses a risk of complications, surgical options may be necessary. Surgical intervention can involve approaches such as internal stabilization of the sternum or addressing any underlying damage to nearby structures. While these procedures can significantly alleviate symptoms and restore function, they are not without risks. Patients need to weigh the potential benefits against possible complications, such as infection or extended recovery time.
Moreover, post-operative management is vital for successful recovery. This typically includes a structured rehabilitation plan that ensures gradual return to activities while providing additional support to the healing process. Ultimately, the choice of treatment for traumatic sternal bulge should be made collaboratively between the patient and their healthcare provider, taking into consideration individual circumstances and preferences.

Complications of Traumatic Sternal Bulge
The management of traumatic sternal bulge is critical, as untreated or improperly addressed cases can lead to various complications. One of the most significant concerns associated with a sternal bulge is the potential for respiratory difficulties. Patients may experience compromised lung function due to altered thoracic mechanics, particularly when the bulge limits the expansion of the chest wall. This can lead to reduced oxygenation and increased work of breathing, raising the risk for respiratory infections or even failure if left unmonitored.
Moreover, traumatic sternal bulges can also impact the cardiovascular system. Displacement or pressure on underlying structures may lead to cardiac complications, including arrhythmias or reduced cardiac output. These risks are magnified in cases where the bulge results from severe trauma, where the heart and surrounding blood vessels may be directly affected. Additionally, the physical stress caused by the body adjusting to the bulge can contribute to cardiovascular strain.
Chronic pain syndrome is another potential consequence of a neglected traumatic sternal bulge. Patients may develop ongoing discomfort due to nerve irritation or structural changes within the chest wall. This persistent pain can severely impact the quality of life, leading to limitations in daily activities and contributing to psychological stress. Consequently, an interdisciplinary approach that includes pain management and psychological support may be beneficial.
Given the range of potential complications associated with untreated traumatic sternal bulges, continuous monitoring and follow-up care are essential. Regular evaluations can help in identifying and addressing any evolving issues, thereby improving outcomes for patients. Ensuring that healthcare providers remain vigilant in monitoring such cases is crucial to mitigate the risk of severe complications.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery from a traumatic sternal bulge involves a comprehensive rehabilitation process designed to promote healing and restore function. The intervention begins once the initial medical treatment has been administered, and the emphasis is placed on physical therapy. A personalized physical therapy program typically focuses on rebuilding strength, enhancing mobility, and alleviating pain. Physical therapists may introduce a range of exercises that target the thoracic region, with gentle stretches and strengthening workouts being fundamental components of the program.
Additionally, activity modification plays a crucial role in recovery. Patients are often advised to avoid high-impact activities or any movements that may exacerbate the sternal area. This can include refraining from heavy lifting or high-intensity sports until the physician or therapist deems it safe to resume such activities. During this modification period, monitoring the body’s signals is essential; any signs of discomfort or pain should prompt a reevaluation of the activity levels undertaken.
As patients progress, the rehabilitation protocol may gradually incorporate more challenging exercises that simulate real-life activities and sports-specific movements. Employing techniques such as progressive resistance training can further assist in achieving a successful return to normal life. Notably, the duration of the rehabilitation program can vary significantly from person to person, influenced by factors such as the severity of the bulge, concurrent health conditions, and adherence to the therapeutic regimen.
In conclusion, a structured rehabilitation plan following a traumatic sternal bulge is instrumental in fostering a full recovery. It encompasses physical therapy, sensible activity modifications, and a strategic approach to reintroducing sports and daily tasks, ultimately aiming to restore the patient’s quality of life and physical capabilities.
FAQs About Traumatic Sternal Bulge
Understanding a traumatic sternal bulge can often raise numerous questions among patients and caregivers. This section aims to address some of the most frequently asked questions regarding this condition.
What is a traumatic sternal bulge?
A traumatic sternal bulge is a protrusion that occurs on the sternum, often resulting from trauma or injury to the chest area. This can be due to blunt force, such as in car accidents, sports injuries, or falls. The bulge appears as a visible lump and can indicate underlying structural damage or instability within the sternum.
What are the common symptoms associated with this condition?
Symptoms of a traumatic sternal bulge may include localized pain, discomfort during movement, and visible deformities of the chest wall. In some cases, individuals may experience difficulty breathing or an increased heart rate, necessitating immediate medical evaluation.
How long does recovery typically take?
Recovery timelines for traumatic sternal bulges can vary based on the severity of the injury. Minor cases may resolve within a few weeks with proper management and rest, while more severe injuries might require surgical intervention and prolonged healing, often spanning several months. Physical therapy may also play a critical role in the recovery process to regain strength and mobility.
What are the long-term effects of a traumatic sternal bulge?
Long-term effects depend largely on the treatment received and the severity of the initial trauma. Potential complications can include persistent pain or discomfort and changes in the chest shape. In some instances, patients may develop complications related to lung function if the injury significantly impacted surrounding structures.
When should someone seek medical attention?
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if the bulge is associated with severe pain, difficulty breathing, or any signs of internal bleeding, such as coughing up blood. Early intervention can help mitigate complications and lead to a more favorable outcome.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

