Understanding Labyrinthitis: 7 Shocking Facts & Cure
Understanding Labyrinthitis
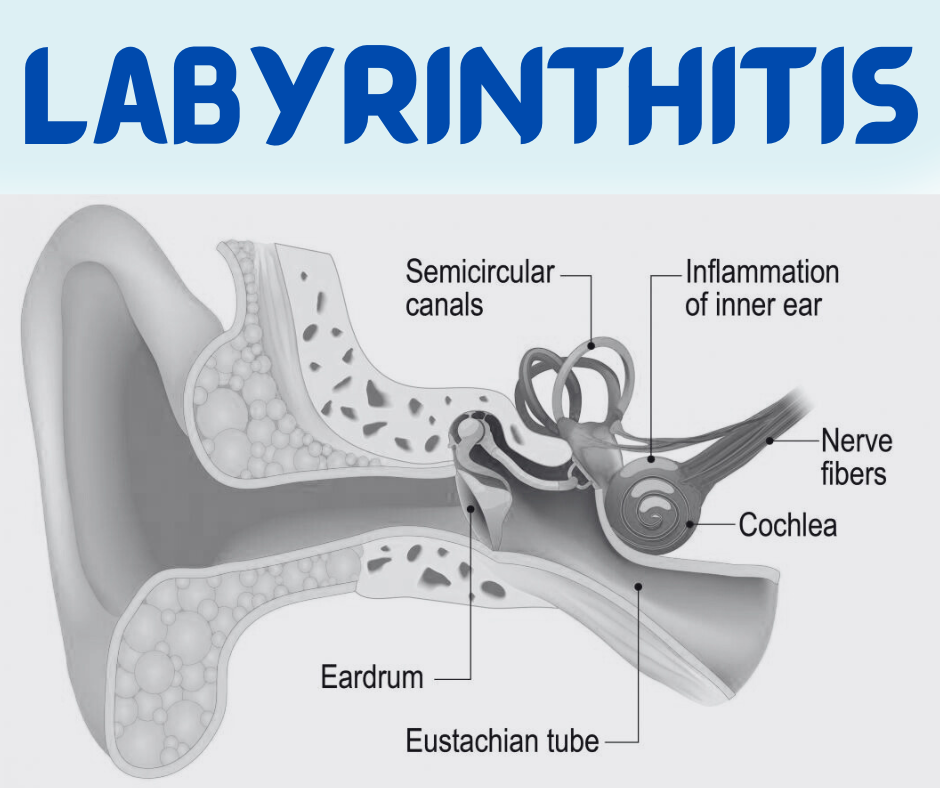
Labyrinthitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the labyrinth, a vital component of the inner ear responsible for maintaining balance and facilitating auditory functions. This intricate structure comprises the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals, which work collectively to process sound and spatial orientation. When the labyrinth becomes inflamed, individuals may experience a range of symptoms that can significantly hinder their daily activities.
The inflammation often results from infections—viral or bacterial—that can arise following illnesses such as upper respiratory infections or the flu. It can also occur as a consequence of exposure to certain medications or allergens. The body’s immune response to these pathogens can inadvertently lead to the swelling and dysfunction of the inner ear structures, causing disruptions in the transmission of auditory and vestibular signals to the brain.
Individuals suffering from labyrinthitis typically report symptoms such as vertigo, which is a spinning sensation that can lead to dizziness and a profound sense of instability. This can make even simple tasks, such as walking or standing, extremely challenging. Additionally, hearing impairment may manifest, ranging from partial hearing loss to complete deafness in the affected ear. Such symptoms can directly impact an individual’s quality of life, leading to difficulties in performing everyday activities and affecting social interactions.
Given the intricate connection between the inner ear and the brain, labyrinthitis can also result in associated neurological symptoms like nausea and tinnitus, further complicating the clinical picture. Understanding labyrinthitis and its implications is crucial in recognizing the necessity for timely diagnosis and effective management to alleviate symptoms and restore quality of life. The awareness of this inner ear disorder serves as a vital step in mitigating its impacts on individuals affected by this condition.
Causes of Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis is an inner ear disorder characterized by the inflammation of the labyrinth, a complex structure responsible for maintaining balance and hearing. One of the primary causes of labyrinthitis is viral infections, particularly those caused by common viruses such as the flu or the common cold. These viral infections can lead to the inflammation of the inner ear, triggering the symptoms associated with labyrinthitis.
Bacterial infections, while less common, can also lead to labyrinthitis. These infections may occur when bacteria invade the inner ear following an upper respiratory infection or when fluid becomes trapped in the middle ear. Conditions such as otitis media, which is an infection of the middle ear, can complicate matters and increase the risk of developing labyrinthitis. Hence, early treatment of ear infections is essential in mitigating the risk of progressing to labyrinthitis.
Another contributing factor to labyrinthitis is Meniere’s disease, a disorder characterized by episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss. Individuals who suffer from this condition may experience recurrent bouts of labyrinthitis due to the excess fluid buildup in the inner ear, resulting in further irritation and inflammation. Furthermore, autoimmune responses may also play a role in the development of labyrinthitis. The immune system can mistakenly attack the inner ear structures, leading to inflammation and subsequent symptoms of the disorder.
Lastly, physical trauma, such as a head injury or barotrauma (rapid changes in pressure), can lead to labyrinthitis by damaging the delicate structures of the inner ear. This emphasizes the importance of protecting the head during activities that may pose a risk of injury. Understanding the various causes of labyrinthitis is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment, enabling healthcare professionals to implement appropriate interventions and manage the condition effectively.
Symptoms of Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis is characterized by various symptoms arising from inflammation of the inner ear structures, particularly the labyrinth. The most prevalent symptoms include dizziness and vertigo, which are often debilitating. Dizziness can manifest as a sense of lightheadedness, while vertigo typically presents as a false sensation of spinning or movement, affecting a person’s balance and stability.
Patients may also experience hearing loss, which can range from mild to severe. This auditory impairment can occur in one or both ears, complicating daily activities and social interactions. The degree of hearing loss may fluctuate, sometimes improving as the inflammation subsides. Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, is another common symptom associated with labyrinthitis. This condition may add to the distress experienced by patients, as it can interfere with concentration and sleep.
Balance disturbances are significant symptoms of labyrinthitis, stemming from the inner ear’s role in maintaining equilibrium. These disturbances can lead to unsteadiness, increasing the risk of falls and injuries. Some individuals may find that their symptoms worsen with sudden movements or changes in head position, further complicating their ability to perform routine tasks safely.
The severity of labyrinthitis symptoms can vary considerably among individuals. Some may encounter mild cases that are manageable, while others may endure severe debilitating symptoms that require medical intervention. Understanding these symptoms is critical for those affected, as early recognition and appropriate treatment can significantly improve overall outcomes. Those experiencing symptoms of labyrinthitis should seek medical advice for tailored management strategies.

Diagnosis of Labyrinthitis
The diagnosis of labyrinthitis is a multi-faceted process that begins with a thorough patient interview. During this initial assessment, healthcare professionals typically inquire about the patient’s medical history, any recent infections, and the specific symptoms experienced. Symptoms such as vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, or balance issues can all point toward labyrinthitis, but they may also overlap with other vestibular disorders, necessitating further investigation.
Following the patient interview, a series of physical examinations are conducted to assess the patient’s balance and hearing capabilities. The healthcare provider may perform several tests, including the Romberg test, which evaluates balance and proprioception. Observations during movement, as well as responses to certain maneuvers, can provide vital clues about the inner ear’s function and its involvement in the labyrinthitis.
In addition to the initial clinical assessments, healthcare providers often recommend various diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of labyrinthitis and rule out other conditions that may mimic its symptoms. Audiometric testing, which assesses hearing ability, is a common procedure following preliminary evaluation. This test gauges how well sound travels through the ear and may reveal any hearing loss associated with labyrinthitis. Moreover, imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be used to visualize the inner ear structures. These imaging techniques help identify any anatomical abnormalities or other issues affecting the vestibular system.
By combining patient interviews, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can establish an accurate diagnosis of labyrinthitis. This thorough and systematic approach is essential in ensuring suitable treatment plans are developed, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
Treatment Options for Labyrinthitis
The management of labyrinthitis typically involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the severity of the condition and its underlying causes. Treatment strategies often begin with pharmacological interventions aimed at alleviating symptoms, promoting recovery, and addressing inflammation. Medications such as corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inner ear swelling and inflammation. Additionally, antihistamines can be beneficial for managing nausea and vertigo associated with labyrinthitis. Antihistamines work by blocking histamine receptors, thus providing relief from the uncomfortable symptoms that can significantly impact daily functioning.
In cases where labyrinthitis is attributed to a viral infection, management often focuses on supportive care since antibiotics are ineffective against viruses. Physical therapy is another essential component of treatment, particularly vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT), which helps patients regain balance and coordination. This specialized therapy includes exercises designed to retrain the brain’s response to balance signals, enabling individuals to adapt to the changes in their vestibular system.
Alongside medications and therapy, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in the recovery process. Patients are often advised to avoid sudden movements and activities that could exacerbate their symptoms, such as driving or operating heavy machinery. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy diet can also enhance overall well-being during recovery. Stress management techniques and ensuring adequate rest are essential, as fatigue can intensify symptoms.
A personalized treatment plan is vital, as labyrinthitis can arise from various causes, including infections, allergies, or autoimmune disorders. Collaboration with healthcare professionals can pave the way for effective management, ensuring that each aspect of the patient’s health is considered. By integrating medications, therapy, and lifestyle changes, individuals can find relief from the debilitating effects of labyrinthitis and work towards full recovery.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Strategies
For individuals experiencing labyrinthitis, various home remedies and self-care strategies can offer symptom relief and promote recovery. The primary aim is to create a supportive environment for healing while managing discomfort associated with this inner ear condition.
First and foremost, staying hydrated is essential. Adequate fluid intake helps maintain inner ear function, which is crucial given the role of fluid balance in this area. Drinking plenty of water, herbal teas, and clear broths can support hydration and overall well-being. It is advisable to limit caffeine and alcohol consumption, as these substances can exacerbate symptoms by affecting hydration and balance.
Rest is another critical component of self-care during episodes of labyrinthitis. Quality sleep and rest periods allow the body to heal and reduce fatigue that often accompanies this condition. Creating a calm and quiet environment, possibly dimming lights and reducing noise, can enhance the restorative effects of sleep.
Dietary considerations also play a significant role in managing symptoms. Incorporating nutrient-dense foods rich in vitamins and minerals may help support the immune system. Foods high in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can contribute positively to overall health. Some individuals may find that adopting a low-sodium diet helps alleviate feelings of fullness and pressure in the ears, which are common discomforts of labyrinthitis.
Lastly, stress management techniques can provide significant relief from symptoms. Practices such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and gentle yoga encourage relaxation, which may help reduce the severity of dizziness and anxiety associated with labyrinthitis. Implementing these self-care strategies can empower individuals to better navigate the challenges posed by labyrinthitis and potentially hasten recovery.

Living with Labyrinthitis: Coping Mechanisms
Labyrinthitis, an inner ear disorder that can impact balance and hearing, presents several challenges for those affected. Managing symptoms effectively is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. One of the primary strategies for individuals coping with labyrinthitis is to adopt a symptom management routine. This may include taking prescribed medications, utilizing over-the-counter treatments for dizziness, and engaging in physical therapy aimed at improving balance and coordination.
Another important aspect of navigating life with labyrinthitis is making adjustments to daily activities. Individuals may find it beneficial to establish a structured routine that accommodates periods of rest followed by light activities. Creating a calm environment can also help minimize stress and anxiety, which may exacerbate symptoms. For instance, reducing exposure to bright lights and loud noises can make a significant difference in comfort levels. Those experiencing vertigo should focus on staying hydrated and avoiding sudden movements, which can trigger dizziness.
Support networks play a vital role in managing labyrinthitis. Engaging with healthcare professionals who specialize in ear disorders can provide individuals with personalized strategies to cope with their condition. Additionally, participating in community groups or online forums can help individuals connect with others experiencing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and learning coping mechanisms from others can foster a sense of camaraderie and support.
Finally, practicing mindfulness techniques such as meditation or gentle yoga can aid in stress reduction, which is beneficial for overall well-being. Prioritizing relaxation, building a supportive network, and implementing practical coping strategies can improve the everyday lives of those living with labyrinthitis, allowing them to navigate their condition with confidence and resilience.
Potential Complications of Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis, an inner ear disorder characterized by inflammation of the labyrinth, can lead to several complications if left untreated or if the condition is severe. One of the primary risks associated with labyrinthitis is hearing loss. This may result from damage to the hair cells within the cochlea, which are crucial for sound detection. In some cases, this hearing impairment can become permanent, significantly affecting the individual’s ability to communicate effectively and engage in social situations.
Another potential complication of labyrinthitis is ongoing balance issues. The labyrinth plays a vital role in maintaining equilibrium, and its inflammation can disrupt the brain’s ability to interpret balance signals. Patients may experience vertigo, dizziness, and an unsteady gait, which can hinder their daily activities and increase the risk of falls. This problem can be particularly concerning for the elderly, who may already be susceptible to injuries related to balance loss.
Moreover, the impact of labyrinthitis-related complications on quality of life cannot be overstated. Individuals may find it challenging to perform everyday tasks, leading to reduced independence and possible social isolation. Constant dizziness or the fear of losing balance can contribute to anxiety and depression, further exacerbating the emotional toll of the condition. Those affected may also feel a decreased ability to concentrate, affecting both personal and professional spheres of their lives.
In conclusion, recognizing and treating labyrinthitis promptly is crucial in minimizing the risk of complications such as hearing loss and persistent balance issues. Awareness of these potential long-term effects underscores the importance of seeking medical advice if labyrinthitis symptoms arise.
FAQs : Understanding Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis, an inner ear disorder, often raises numerous questions for those affected or concerned. Understanding this condition can aid in better management and relief from symptoms. Below, we address some frequently asked questions regarding labyrinthitis.
What are the common causes of labyrinthitis?
Labyrinthitis typically results from viral infections, such as those accompanying a cold or flu. It can also develop due to bacterial infections following an ear infection or as a complication of diseases such as meningitis. In some instances, it may arise after head injuries or physical trauma impacting the inner ear.
How can labyrinthitis be distinguished from other ear disorders?
Labyrinthitis symptoms overlap with other ear-related conditions like vestibular neuritis or Meniere’s disease. However, labyrinthitis is characterized by both auditory and balance disturbances, including hearing loss, vertigo, and imbalance. Consulting a healthcare professional can facilitate accurate diagnosis through physical examinations and diagnostic tests.
What are the treatment options available for labyrinthitis?
Treatment for labyrinthitis often focuses on alleviating symptoms. Depending on the underlying cause, antiviral or antibiotic medications may be prescribed. Corticosteroids might be utilized to reduce inflammation, while antihistamines and anti-nausea medications can help manage specific symptoms. Physical therapy may also be beneficial in restoring balance.
Is labyrinthitis preventable?
While it may not be entirely preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk. Practicing good hygiene, such as thorough handwashing, can minimize exposure to viral infections. Additionally, seeking prompt treatment for ear infections can help avert complications that may lead to labyrinthitis.
What is the long-term prognosis for those diagnosed with labyrinthitis?
Most individuals experience a full recovery from labyrinthitis, especially when properly treated. However, persistent dizziness or balance issues may affect some individuals. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor recovery and manage any ongoing symptoms.
Can stress or anxiety trigger labyrinthitis?
While stress and anxiety do not directly cause labyrinthitis, they can worsen its symptoms. Stress may exacerbate dizziness and balance issues by increasing tension in the body and affecting the nervous system. Additionally, anxiety can heighten the perception of symptoms, making them feel more intense. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and proper sleep may help alleviate discomfort associated with labyrinthitis.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

