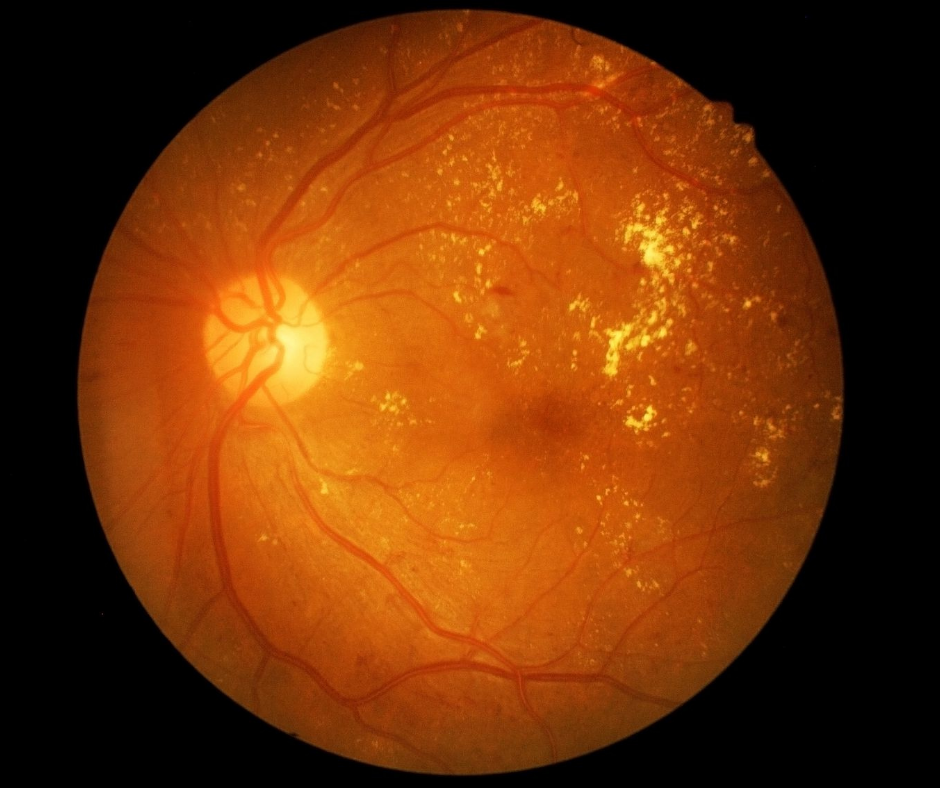
Understanding Retinopathy
Retinopathy is a medical condition characterized by damage to the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue located at the back of the eye. Essential for vision, the retina converts light into neural signals that are then interpreted by the brain. When the retina is compromised, it can lead to a range of visual impairments and potentially severe vision loss if not properly managed.
This eye disorder is of particular concern due to its prevalence among certain populations. Millions of individuals worldwide are affected, with diabetic retinopathy and hypertensive retinopathy being the most commonly diagnosed forms. Diabetic retinopathy, for instance, is a major health issue, especially among people with long-standing diabetes. This condition occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to swelling, leakage, and in severe cases, retinal detachment.
Hypertensive retinopathy, on the other hand, stems from high blood pressure, which can exert stress on the retina’s vasculature, leading to similar outcomes such as swelling, hemorrhages, and potential vision loss. Understanding retinopathy’s impact is crucial, as early detection and intervention can mitigate its progression and preserve vision.
Other types of retinopathy include retinopathy of prematurity, which affects premature infants, and central serous retinopathy, where fluid accumulates under the retina, often linked to stress or steroid use. Each type has unique causes and manifestations, but they all share the commonality of impairing the retina’s function.
Awareness and education about retinopathy are vital for prevention and management. Healthcare professionals emphasize the importance of regular eye check-ups, especially for individuals at risk, to detect early signs and provide timely treatment. As such, a comprehensive understanding of retinopathy will aid in reducing its burden on public health.
Causes and Risk Factors
Retinopathy, particularly diabetic retinopathy, develops due to a range of causes and risk factors that can be broadly categorized into medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and genetic predispositions. Understanding these elements is crucial in both preventing and managing the condition effectively.
Among the primary medical conditions contributing to retinopathy, diabetes stands out as the most prevalent. Persistent high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to leakage or blockage, which impairs vision. Additionally, hypertension, or high blood pressure, exacerbates this condition by putting further strain on these blood vessels, accelerating the process of retinal deterioration.
Lifestyle factors equally play a significant role in the development of retinopathy. Smoking, for instance, contributes to the narrowing of blood vessels and reduces blood flow, thus increasing the risk of retinopathy. Similarly, poor dietary habits, particularly diets high in fats and sugars but low in essential nutrients, can exacerbate existing medical conditions like diabetes and hypertension, which in turn affects retinal health.
Genetic predispositions also influence the likelihood of developing retinopathy. A family history of retinal diseases or systemic conditions that affect the eyes can significantly increase one’s susceptibility. Though genetic factors cannot be modified, being aware of such predispositions can prompt earlier and more frequent screening, leading to timely intervention.
Moreover, other less common factors such as autoimmune diseases and certain medications might also contribute to the onset of retinopathy. Autoimmune conditions can cause inflammation that damages retinal blood vessels, while some medications might have side effects that negatively impact retinal health.
By recognizing and addressing these diverse causes and risk factors, individuals can adopt more effective strategies to mitigate the risk of developing retinopathy. Regular medical check-ups, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle are essential in preserving retinal health and preventing severe complications associated with this visual impairment.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Retinopathy, a condition frequently linked to diabetes, entails damage to the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can manifest in a number of symptoms, making it crucial to recognize both the early and advanced warning signs. Identifying these symptoms promptly can significantly influence the management and prognosis of the condition.
In its initial stages, retinopathy might not present any noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience subtle changes in their vision. One of the earliest indicators is blurry vision, which occurs when the damaged blood vessels leak fluid into the retina, leading to swelling and obscured sight. Another common early sign is the appearance of floaters. These are small, shadowy shapes that drift across your field of vision and can be indicative of bleeding from new, abnormal blood vessels that form as the disease progresses.
As retinopathy advances, the symptoms become more pronounced and can significantly impact daily life. Dark spots or patches in the visual field, known as scotomas, may become apparent. These are areas where vision is entirely obscured, often caused by areas of the retina missing critical nutrients due to impaired blood flow. Sudden vision loss is a severe symptom that warrants immediate medical attention. This can result from a large bleed in the eye or a sudden detachment of the retina, both of which are serious complications that require urgent intervention.
Given the progressive nature of retinopathy, early detection is paramount. Regular eye examinations are critical, particularly for individuals with risk factors such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or a family history of the condition. These exams can help identify retinopathy before significant symptoms develop, allowing for timely treatment and better management.
Understanding and recognizing the symptoms of retinopathy is a vital step towards preserving vision and maintaining eye health. Regular check-ups and being vigilant about changes in vision can aid in the early identification and treatment of this debilitating condition.

Diagnosis and Screening
Retinopathy encompasses a range of deteriorating conditions that affect the retina, often necessitating prompt and precise diagnosis to prevent severe vision impairment or blindness. Accurate identification of retinopathy starts with various diagnostic procedures tailored to detect the specific variations and stages of this condition.
The diagnostic journey typically begins with a comprehensive eye examination. This includes assessments like visual acuity tests and dilated eye exams, where eye drops are used to widen the pupil, allowing for a closer inspection of the retina’s condition. One of the fundamental techniques employed is fundus photography, a method that captures detailed images of the retina. These images are invaluable for detecting signs of retinopathy, such as abnormal blood vessels, hemorrhages, or retinal swelling.
Another critical diagnostic tool is fluorescein angiography. During this procedure, a fluorescent dye is injected into the bloodstream, which then illuminates the blood vessels in the eye. A special camera captures the enhanced images, providing deeper insight into the blood flow and identifying any blockages or leakages indicative of retinopathy. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is also frequently utilized. This non-invasive imaging test generates high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina, revealing its thickness and any abnormal swelling or fluid accumulation.
Regular screenings are crucial for early detection and management of retinopathy, especially for individuals in high-risk categories such as diabetics or those with a history of hypertension. The significant benefit of these routine eye exams is the potential for identifying retinopathy in its early stages, often before noticeable symptoms arise. Such preemptive detection can significantly mitigate the progression of the disease.
Patients can expect a multi-step diagnostic journey tailored to their specific risk factors and symptoms. This journey not only involves thorough initial assessments but also ongoing monitoring to adapt to any changes in their condition. Adherence to these screening protocols empowers patients and healthcare providers to manage retinopathy more effectively, ultimately aiming to preserve vision and enhance quality of life.
Treatment Options
Retinopathy, a disease that affects the retina, can manifest through various stages, necessitating diverse treatment approaches to address its progression and mitigate its effects. Medical interventions remain the cornerstone of managing this condition, with laser surgery, injectable medications, and vitrectomy standing out prominently. Laser surgery is generally recommended for individuals with proliferative diabetic retinopathy and macular edema. This treatment aims to seal leaking retinal blood vessels and inhibit the growth of abnormal blood vessels, thereby preventing vision loss. However, its risks include potential but rare complications such as limited peripheral or night vision.
Injections of anti-VEGF drugs offer another viable option, particularly effective in reducing swelling and improving vision in those with macular edema. The treatment involves administering medication directly into the eye, usually through a series of injections over a set period. While effective, these injections carry risks like increased eye pressure and, in rare cases, infection or retinal detachment.
For severe retinopathy that does not respond to other treatments, a vitrectomy may be necessary. This surgical procedure removes the vitreous gel and scar tissue from the retina, often leading to significant vision improvement. Like all surgeries, it comes with risks such as bleeding, infection, and possible recurrence of retinal issues.
Lifestyle changes and preventive measures also play a critical role in managing retinopathy. A robust plan includes maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol through diet, exercise, and medication. These steps can slow the disease’s progression and enhance overall treatment outcomes. Additionally, regular eye exams are indispensable in monitoring the condition and facilitating timely intervention.
Ongoing management and follow-up care are essential components of a comprehensive retinopathy treatment plan. Regular check-ups enable healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments. This ongoing care helps in early detection of any changes or complications, ensuring that the patient’s vision is preserved to the greatest extent possible.
Living with retinopathy can present numerous daily challenges, but with mindful strategies and adjustments, individuals can manage their condition effectively and maintain a good quality of life. One of the most critical aspects of managing retinopathy is following a tailored diet. Consuming a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins C and E can help protect retinal cells from further damage. Foods like leafy greens, fish, and citrus fruits are particularly beneficial. Additionally, it is advisable to monitor and control blood sugar levels meticulously, especially for those with diabetic retinopathy, as fluctuating glucose levels can exacerbate retinal damage.
Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines is another key strategy. Physical activity helps improve overall cardiovascular health, which in turn optimizes blood flow to the retina. Activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga are excellent choices as they are generally low-impact and can be adjusted to suit individual fitness levels. It’s important, however, to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it aligns with personal health conditions and limitations.
Beyond diet and exercise, adopting practical adjustments to daily activities can significantly improve quality of life for those living with retinopathy. Utilizing visual aids like magnifying glasses, screen readers, and specialized apps can make tasks such as reading and navigating technology more manageable. Ensuring proper lighting in living spaces and using contrasting colors can also enhance visual perception and reduce strain.
Support groups and counseling play a vital role in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of living with retinopathy. Connecting with others who understand the challenges can provide invaluable emotional support and practical advice. Professional counseling can assist in coping with vision loss, helping individuals to develop effective strategies for adaptation and fostering a positive outlook.
Overall, managing retinopathy requires a holistic approach that includes dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, adaptive strategies for daily living, and emotional support systems. With the right measures in place, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition.

Prevention and Healthy Practices
Preventing retinopathy requires a proactive approach centered around maintaining overall health and regular monitoring. Key preventive measures include regular medical check-ups and managing underlying health conditions, particularly diabetes and hypertension. Chronic conditions such as these are major risk factors for developing retinopathy, making it crucial to keep them under tight control through consistent medical supervision and adherence to prescribed treatments.
A balanced diet is fundamental to preventing retinopathy. Aim to consume a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods rich in antioxidants, like leafy greens, berries, and nuts, play a significant role in protecting eye health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish such as salmon and mackerel, have been associated with a reduced risk of eye diseases. Limiting the intake of sugars and processed foods helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels, which is particularly essential for those with diabetes.
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of retinopathy prevention. Exercise improves overall cardiovascular health, helps manage weight, and contributes to better blood sugar control. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health guidelines.
Avoiding smoking is imperative, as smoking has been linked to increased risks of various eye conditions, including retinopathy. Smoking cessation not only benefits general health but also significantly reduces the likelihood of developing retinopathy.
Regular eye exams are crucial in the early detection and management of retinopathy. Eye exams can help identify early signs of retinal damage before significant vision loss occurs. Individuals, especially those with diabetes or high blood pressure, should have comprehensive dilated eye exams annually or as recommended by their healthcare provider.
In essence, integrating these healthy practices into daily routine not only helps in preventing retinopathy but also promotes overall wellness, thereby enhancing the quality of life.
FAQ : Understanding Retinopathy
What is retinopathy?
Retinopathy is a medical term used to describe conditions that affect the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye. These conditions often result from underlying health issues such as diabetes (diabetic retinopathy) or hypertension (hypertensive retinopathy). Early detection and treatment are critical to prevent progression to more severe stages.
How does retinopathy progress?
Retinopathy typically progresses in stages, starting with mild symptoms that can escalate if left untreated. Initial stages may present minimal to no symptoms, but as the condition advances, it might lead to blurred vision, dark spots, or complete vision loss. Regular eye examinations are essential to monitor and manage the condition effectively.
How can retinopathy impact daily life?
The impact of retinopathy on daily life can vary depending on its severity. Mild cases may not affect vision significantly, allowing individuals to continue their usual activities. However, advanced retinopathy can cause vision impairment, making everyday tasks like reading, driving, and recognizing faces challenging. It’s essential to follow medical advice to mitigate these impacts and maintain quality of life.
What treatments are available for retinopathy?
Treatment options for retinopathy depend on the type and severity of the condition. Common treatments include laser surgery, intravitreal injections, and vitrectomy. Early intervention can halt or slow down progression, so timely consultation with an ophthalmologist is crucial. Depending on the underlying cause, managing systemic conditions like diabetes or hypertension is also vital.
What should I expect during regular check-ups?
During regular check-ups for retinopathy, your ophthalmologist will perform various eye tests to assess the condition of your retina. These may include a dilated eye exam, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and fluorescein angiography. These tests help in monitoring disease progression and evaluating the effectiveness of treatments.
Are there any common myths about retinopathy?
Several myths surround retinopathy, such as the belief that it only affects the elderly or those with diabetes. While these groups are at higher risk, retinopathy can affect individuals of all ages and various health conditions. Another common misconception is that vision loss from retinopathy is irreversible. Early detection and prompt treatment can often preserve or even restore some degree of vision.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

