7 Warning Signs of Tietze Syndrome You Must Know
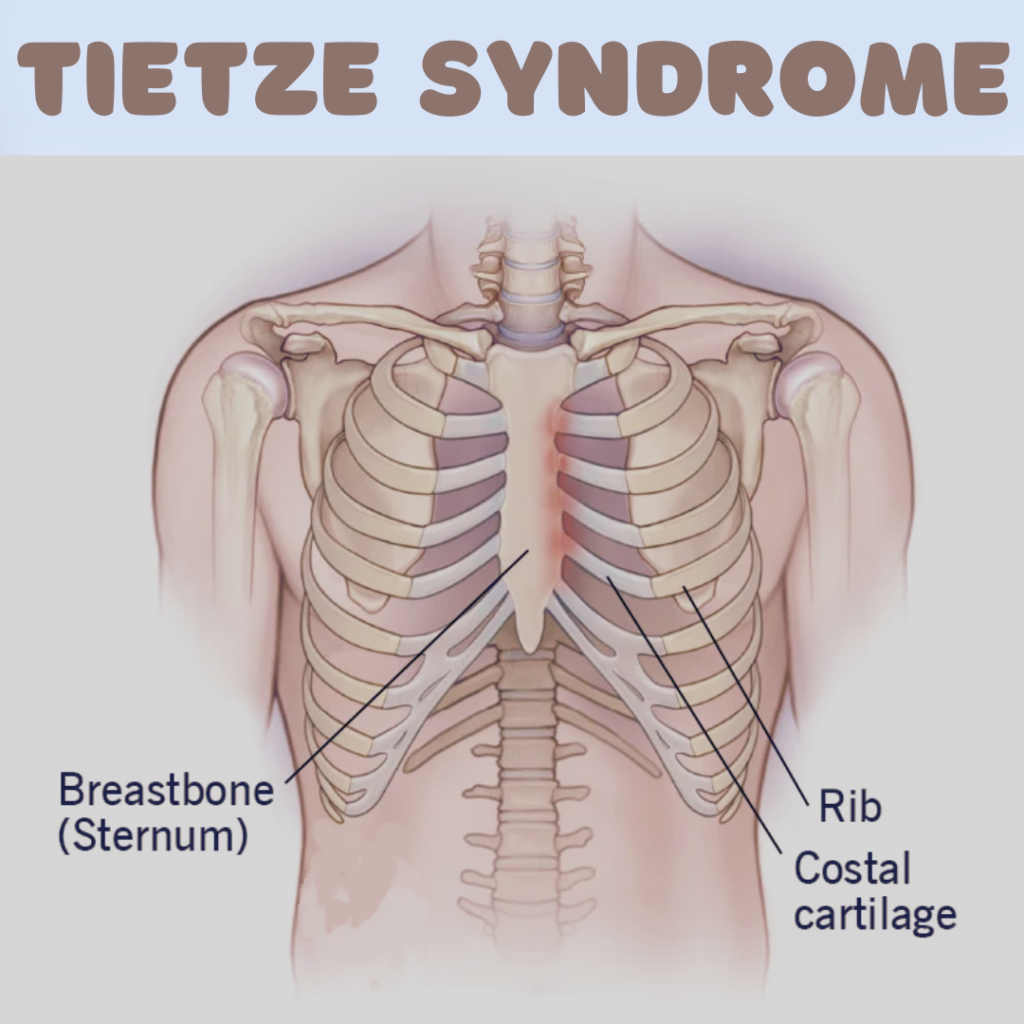
What is Tietze Syndrome?
Tietze Syndrome is defined as a benign inflammation of the cartilage that connects a rib to the sternum, specifically the costal cartilage. This condition is characterized by localized swelling, pain, and tenderness in the affected area, typically occurring in the upper part of the chest. While it may present symptoms similar to other conditions, such as costochondritis, it is important to note that Tietze Syndrome is distinguished by the presence of swelling in the costal cartilage, which is not seen in costochondritis. The inflammation can lead to discomfort, especially with activities that involve upper body movement or deep breathing.
The onset of Tietze Syndrome can occur at any age, but it is most commonly reported in adolescents and young adults. The exact cause of this condition is still unclear; however, some researchers suggest that repetitive trauma, physical strain, or viral infections may play a role in its development. It can sometimes be mistaken for cardiac issues due to the location of the pain, which often prompts patients to seek medical attention to rule out more serious conditions. Symptoms typically include sharp or aching pain in the chest, which may worsen with physical activities like lifting or twisting, as well as tenderness in the inflamed area when pressed.
The history of Tietze Syndrome dates back to its first description in the early 20th century by the physician Alexander Tietze, who outlined the characteristics and symptoms of the condition. Since then, medical understanding has evolved, but many aspects of this syndrome, including its diagnosis and treatment, remain an area of ongoing research. Understanding Tietze Syndrome is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management, thus allowing patients to find relief from their symptoms while differentiating it from similar inflammatory conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors
Tietze syndrome is characterized by chest pain due to inflammation of the costal cartilage, and while the exact causes remain elusive, several factors may contribute to its onset. One prominent cause is physical trauma, which can result from a variety of activities such as sports, heavy lifting, or accidents. Injuries that directly impact the chest area may lead to the inflammation typical of Tietze syndrome.
Repetitive activities also play a significant role in the development of this condition. Individuals who frequently engage in movements that involve the upper body—especially those that strain the chest, such as certain exercises or manual labor—may increase their risk of developing the syndrome. The repetitive stress placed on the costal cartilage can contribute to inflammation and pain. Moreover, occupations that necessitate sustained pressure on the chest may enhance susceptibility to Tietze syndrome.
An additional area of interest in understanding Tietze syndrome involves genetic predispositions. Some researchers propose that certain individuals may be genetically predisposed to inflammation, which could lead to the development of this syndrome. Family history of connective tissue disorders may suggest a link between genetics and the incidence of Tietze syndrome, warranting further study.
Current scientific theories also attribute inflammation as a potential underlying mechanism contributing to the pain associated with Tietze syndrome. Inflammatory processes may trigger the pain response in affected individuals, resulting in discomfort that can mimic other thoracic conditions. While the precise pathway remains unclear, the interplay between physical, repetitive, and genetic factors is crucial in understanding the risk of developing Tietze syndrome.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Tietze Syndrome is a condition that presents with a distinct set of symptoms primarily characterized by localized chest pain and swelling. The pain is typically unilateral and may manifest as a sharp or aching sensation, often exacerbated by activities such as deep breathing, coughing, or even physical exertion. Patients may notice tenderness in the costochondral junctions, where the ribs connect to the sternum, leading to discomfort that can be alarming and resembles more serious conditions like a heart attack. Additionally, swelling that occurs in the affected areas can be evident and may persist for extended periods.
In arriving at a diagnosis of Tietze Syndrome, healthcare professionals employ a systematic approach. The initial step involves a thorough physical examination where the clinician assesses the patient’s medical history and any related symptoms. The significance of this examination cannot be overstated, as it helps in ruling out other potential causes of chest pain, such as rib fractures, muscle strain, or cardiac issues. Clinicians often perform palpation of the affected area to determine the point of tenderness, which can further aid in the diagnostic process.
In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans may be ordered to exclude other conditions that can cause chest pain and swelling. These imaging techniques are particularly valuable in distinguishing Tietze Syndrome from costochondritis, which shares overlapping symptoms but may not present with swelling. Distinguishing between these conditions is crucial, as treatment options may vary based on the underlying issue. Once a definitive diagnosis of Tietze Syndrome is made, a tailored management plan can be developed, ensuring the patient receives appropriate care to alleviate their symptoms.

Treatment Options for Tietze Syndrome
Tietze Syndrome, characterized by localized chest pain and swelling at the costochondral junction, often requires a multi-faceted approach to treatment. Effective management typically begins with conservative strategies aimed at alleviating discomfort and promoting healing. Pain relief medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are commonly recommended to reduce inflammation and manage pain. Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen or naproxen may be effective in mitigating symptoms, while prescription medications can be considered in more severe cases.
In addition to pharmacological interventions, holistic therapies can provide significant relief for many individuals. Techniques such as acupuncture and massage therapy have been explored for their potential benefits in reducing pain and improving overall well-being. These complementary therapies should be approached as adjuncts to standard treatments, potentially enhancing the overall management of Tietze Syndrome.
Physical therapy is another cornerstone of treatment for Tietze Syndrome, focusing on strengthening the chest and upper body muscles. A skilled physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program aimed at improving flexibility, reducing tension, and addressing any underlying muscle imbalances. Techniques such as stretching, strengthening exercises, and postural training may be utilized to alleviate symptoms effectively and foster long-term recovery.
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, more invasive procedures may be considered. Corticosteroid injections can be utilized to directly reduce inflammation at the affected costochondral junction, offering more immediate relief for patients. Surgical interventions are rarely necessary but could be evaluated in chronic cases where other treatments have proved unsuccessful. Each treatment plan should be individualized, considering the patient’s medical history, the severity of symptoms, and personal preferences.
In conclusion, managing Tietze Syndrome effectively requires a combination of conservative management strategies, holistic approaches, and, if necessary, invasive treatments. A comprehensive understanding of these options can empower patients to make informed decisions and approach their recovery with confidence.
Living with Tietze Syndrome: Coping Strategies
Adapting to life with Tietze Syndrome, a condition characterized by inflammation of the costal cartilage, requires individuals to consider various lifestyle modifications that prioritize both physical and mental well-being. One of the fundamental strategies is to modify activity levels. Patients are encouraged to engage in low-impact exercises such as swimming or walking, which promote physical health without exacerbating pain. These adaptations not only help in managing symptoms but also prevent further irritation of the affected area.
In addition to modifying activity levels, ergonomic adjustments can have a significant impact on daily living. Individuals should assess their workspaces and home environments to ensure that they are conducive to comfort. For instance, using chairs with proper back support, maintaining a posture that alleviates pressure on the chest and ribcage, and utilizing desks at an appropriate height can all contribute to reducing discomfort. Such small changes in one’s surroundings can dramatically enhance the quality of life for those coping with Tietze Syndrome.
Mental health support is an often-overlooked component of managing chronic conditions like Tietze Syndrome. Engaging with a mental health professional can provide invaluable strategies for coping with the emotional toll that chronic pain can impose. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness practices are particularly beneficial in helping individuals deal with stress and anxiety related to their symptoms. Furthermore, support groups, whether in-person or online, can foster a sense of community and offer emotional support through shared experiences.
Overall, by implementing these coping strategies—ranging from physical adaptations to mental health care—individuals can manage Tietze Syndrome more effectively. A proactive approach not only mitigates symptoms but also enhances overall well-being, allowing individuals to lead fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis.
Recent Research and Perspectives on Tietze Syndrome
Recent scientific discourse surrounding Tietze Syndrome has significantly advanced our understanding of this condition, which is characterized by localized chest pain and tenderness at the costochondral junction. A key area of investigation focuses on the underlying physiological mechanisms contributing to the syndrome. Recent studies have suggested that inflammation of the costal cartilage may play a primary role, reminiscent of findings in related conditions such as costochondritis. This inflammation appears to be facilitated by both mechanical stress and immune system responses, leading researchers to explore anti-inflammatory treatments as potential interventions.
Moreover, several ongoing studies aim to elucidate the etiology of Tietze Syndrome, investigating genetic predispositions as well as environmental factors that may trigger symptom onset. Researchers are employing advanced imaging techniques, including MRI and ultrasound, which have enhanced the visualization of inflammation at the sternal and costal cartilages. These enhanced imaging modalities are providing clearer insights into how the syndrome manifests and its progression over time.
In addition, some experimental treatments have emerged from recent clinical trials. For instance, localized corticosteroid injections have shown promise in reducing pain and inflammation associated with Tietze Syndrome. Furthermore, early reports on the use of physical therapy techniques, including ultrasound therapy and specific stretching exercises, suggest they may help alleviate symptoms and improve functionality in affected individuals. As the body of research grows, the potential for developing more personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and condition is becoming increasingly feasible.
With advancements in research and patient management strategies, healthcare professionals are better equipped to address Tietze Syndrome comprehensively. These developments also inspire hope for improved quality of life for those affected by the disorder. The future of Tietze Syndrome research looks promising as it continues to evolve, revealing new therapeutic pathways and enriched understandings of this intricate condition.

Common Misconceptions about Tietze Syndrome
Tietze Syndrome, although clinically recognized, is often surrounded by various misconceptions that can cause confusion for patients and their families. One prevalent myth is that Tietze Syndrome is a serious condition that signifies the presence of severe underlying health issues. In reality, while the pain associated with Tietze Syndrome can be intense, it is generally not considered life-threatening. The syndrome primarily manifests as localized inflammation in the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone, leading to discomfort that can usually be managed with conservative treatments such as rest, ice application, and over-the-counter pain medications.
Another common misconception is that Tietze Syndrome is a rare condition. While the exact prevalence is not definitively established, it is more frequently diagnosed than many people realize. The condition may be underreported due to its similarities with other conditions, such as costochondritis, which can lead to misdiagnosis. Awareness of Tietze Syndrome is crucial, as its true incidence might be obscured by the frequent overlap with other thoracic pain conditions.
Additionally, there is a prevailing concern regarding the relationship between Tietze Syndrome and cardiac issues. Many individuals experiencing chest pain often fear that it signals a heart problem. However, while it is essential to rule out any serious cardiac conditions, Tietze Syndrome is primarily musculoskeletal in nature. It is important for patients to consult healthcare professionals to receive proper evaluations and avoid unnecessary anxiety regarding potential heart-related complications.
By addressing these misconceptions surrounding Tietze Syndrome, patients can better understand their condition and seek appropriate care tailored to their needs. This understanding aids in reducing stigma, providing reassurance, and promoting informed discussions between patients and healthcare providers about this often-misunderstood syndrome.
FAQs about Tietze Syndrome
Tietze syndrome is a condition characterized by inflammation of the cartilage connecting a rib to the sternum. It often raises several questions among those affected and their families. Below are some frequently asked questions about Tietze syndrome, along with their answers based on current medical understanding.
What causes Tietze syndrome?
The exact cause of Tietze syndrome remains unclear. However, it is commonly associated with physical trauma or repetitive activities that strain the chest area. Any history of upper respiratory infections or excessive coughing may also contribute to the condition due to potential inflammation around the rib cage.
How likely is Tietze syndrome to recur?
Recurrence of Tietze syndrome is not uncommon. Some individuals may experience multiple episodes of inflammation over time. Factors such as physical activity, stress, or even changes in weather can influence the likelihood of recurrence. Engaging in moderate physical activity while ensuring proper body mechanics can minimize the risk of recurring symptoms.
Are there long-term effects associated with Tietze syndrome?
Most people with Tietze syndrome recover fully, usually within weeks to months, with appropriate treatment. Long-term effects are rare, but chronic pain or discomfort can occur in some cases. It’s essential to follow a comprehensive treatment plan that includes pain management and physical therapy to reduce the risk of persistent symptoms.
How does Tietze syndrome affect physical activities or sports?
While it may be painful initially, many individuals can return to physical activities and sports once their symptoms are managed. It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for tailored recommendations based on individual circumstances. Gentle exercises and stretches can be beneficial, but high-impact activities should be avoided until cleared by a medical professional.
In conclusion, Tietze syndrome, although concerning, can typically be managed effectively with the right approach. Understanding its nature and the associated factors can help individuals navigate their symptoms and rehabilitation successfully.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways about Tietze Syndrome
Tietze Syndrome is a relatively rare condition characterized by inflammation of the costochondral junctions, which can lead to chest pain and discomfort. It is crucial for both patients and the medical community to recognize and understand the symptoms associated with this syndrome to facilitate timely diagnosis and treatment. This condition often presents similarly to other serious disorders, such as myocardial infarction, which can result in unnecessary anxiety and medical interventions when misdiagnosed.
One significant aspect to note about Tietze Syndrome is its differentiation from costochondritis. While both conditions involve costal cartilage inflammation and can cause similar chest pain, Tietze Syndrome is specifically identified by the swelling of the affected area, an important distinction for proper management. Awareness of this difference can lead to more accurate diagnoses and avoid the risks of misdiagnosis.
Patients experiencing symptoms such as chest pain localized to the ribcage should consider consulting a healthcare provider. Since Tietze Syndrome typically resolves on its own, supportive treatments including rest, ice therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications can help alleviate symptoms. Therefore, it is essential to foster an understanding of such treatments and approaches to care. This awareness not only aids in effective symptom management but also provides reassurance to individuals who may be fearful of their condition.
In summary, gaining knowledge about Tietze Syndrome empowers patients to seek appropriate evaluations and treatment options when necessary. Understanding its symptoms, differentiation from related conditions, and management strategies is vital for both individuals experiencing discomfort and practitioners in providing optimal care. If you suspect you are experiencing signs of this syndrome, do not hesitate to reach out to a medical professional for guidance and support.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

