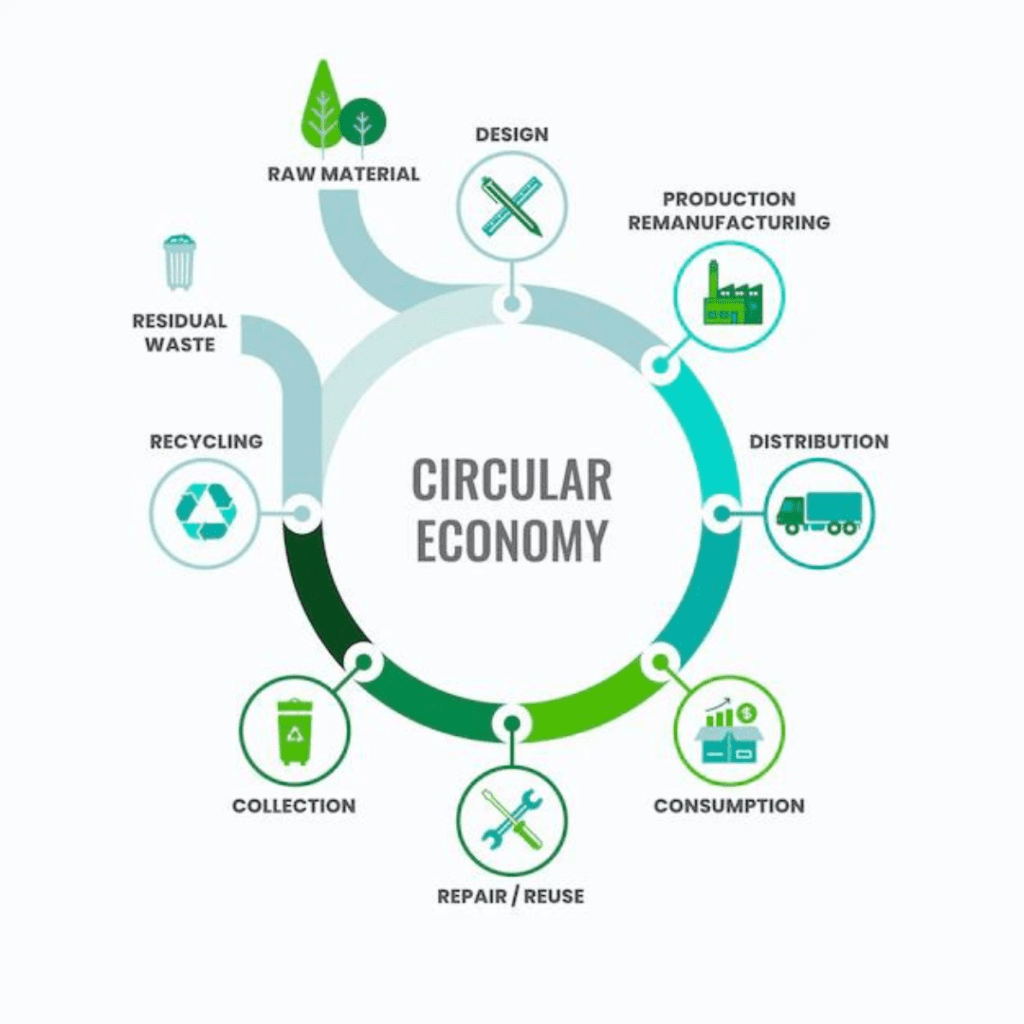
Embracing the Circular Economy: Co-creating a Sustainable and Prosperous Future
In recent years, the concept of the circular economy has gained significant traction as a transformative model for achieving sustainable development. As the detrimental effects of our linear “take-make-dispose” economic system become increasingly apparent, the circular economy offers a refreshing alternative that promotes resource efficiency, waste reduction, and long-term prosperity. In this blog post, we will explore the principles and benefits of the circular economy, highlighting how this innovative approach can pave the way towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Understanding the Circular Economy
At its core, the circular economy aims to redefine the traditional economic paradigm by decoupling growth from the consumption of finite resources. Unlike the linear model, where resources are extracted, manufactured into products, and ultimately discarded as waste, the circular economy strives to create a closed-loop system that maximizes the value and lifespan of products and materials.
Key Principles of the Circular Economy
Designing for longevity and durability
By prioritizing durability and repairability during the design phase, products can be built to last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacements and conserving valuable resources.
Embracing circular business models
Adopting innovative business models, such as product-as-a-service, sharing platforms, and leasing, encourages resource optimization, minimizes waste generation, and fosters a culture of reuse.
Promoting resource recovery and recycling
Efficient waste management systems enable the recovery of materials from products at the end of their life cycles. This recovered material can then be recycled or repurposed to create new products, minimizing the reliance on virgin resources.
Engaging stakeholders and fostering collaboration
Collaboration among governments, businesses, and consumers is crucial to driving the circular economy forward. By working together, we can address systemic challenges, share best practices, and create an enabling environment for sustainable innovation.
Benefits of the Circular Economy
Resource conservation and reduced waste
The circular economy minimizes resource extraction, reduces waste generation, and limits the environmental impact associated with resource depletion and waste disposal. This not only preserves natural resources but also reduces pollution and mitigates climate change.
Economic growth and job creation
Embracing the circular economy presents immense economic opportunities. Shifting towards circular business models and practices can stimulate innovation, drive job creation, and unlock new revenue streams. According to estimates by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the global circular economy could generate $4.5 trillion in economic benefits by 2030.
Enhanced resilience and risk mitigation
By diversifying supply chains, embracing renewable energy sources, and adopting circular practices, businesses can enhance their resilience to disruptions, such as resource scarcity, price volatility, and regulatory changes. The circular economy fosters a more robust and adaptable economic system.
Improved quality of life
The circular economy emphasizes the value of sustainable consumption and production, leading to the creation of products that are safer, healthier, and more efficient. It also promotes the sharing economy, enabling access to goods and services without the need for individual ownership.
Embracing the Circular Economy: Our Collective Responsibility
The transition to a circular economy is not solely the responsibility of governments or businesses—it requires collective action from all stakeholders. As individuals, we can contribute by adopting sustainable consumption habits, supporting companies that prioritize circular practices, and participating in local recycling and upcycling initiatives. Governments play a crucial role in creating supportive policy frameworks, providing incentives, and fostering collaboration between various sectors. Meanwhile, businesses can drive change by implementing circular business models, investing in research and development, and educating consumers about the benefits of circular products and services.
Partnerships for Circular Economy Success
Achieving a circular economy requires collaboration and partnerships at multiple levels. Governments, businesses, non-profit organizations, and individuals must work together to create a supportive ecosystem that fosters innovation, investment, and knowledge sharing. Here are some key areas where partnerships play a crucial role:
Cross-sector collaboration
Collaboration between different industries and sectors is vital for driving systemic change. For example, collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, and recyclers can facilitate the efficient recovery and recycling of materials. Partnerships between technology companies and waste management organizations can drive innovation in recycling processes. By bringing together stakeholders from various sectors, we can pool resources, expertise, and perspectives to develop holistic solutions.
Public-private partnerships
Governments can play a crucial role in facilitating the transition to a circular economy by creating policies, regulations, and incentives that support circular practices. Public-private partnerships can leverage the strengths and resources of both sectors to drive sustainable innovation. Governments can provide financial incentives, tax breaks, and grants to businesses that adopt circular business models or invest in research and development for circular solutions.
Research and development collaborations
Investing in research and development is essential for advancing circular economy practices. Collaborative research projects between academia, businesses, and research institutions can drive technological advancements, identify new materials, and develop innovative processes for resource recovery and recycling. By sharing knowledge, data, and best practices, these collaborations can accelerate the adoption of circular practices.
Consumer engagement
Educating and engaging consumers is key to the success of the circular economy. Partnerships between businesses, non-profit organizations, and consumer groups can raise awareness about the benefits of circular products and services, promote sustainable consumption behaviors, and provide information on recycling and waste management. By involving consumers in the transition, we can foster a culture of responsible consumption and create demand for circular products.
International cooperation
The circular economy is a global endeavor that requires international cooperation to address challenges such as cross-border trade of waste, harmonization of recycling standards, and sharing best practices. Collaborative initiatives between countries and international organizations can facilitate knowledge exchange, policy alignment, and capacity building. Sharing success stories and lessons learned can inspire other nations to embrace circular economy principles.
The Road Ahead: Overcoming Challenges
While the circular economy offers immense opportunities, there are also challenges to overcome. Some of the key challenges include:
Shifting mindsets and behaviors
Transitioning to a circular economy requires a shift in mindsets and behaviors at all levels of society. Breaking free from the traditional linear model and embracing circular practices may require changes in consumer preferences, business strategies, and policy frameworks. Education, awareness campaigns, and incentives can help drive this behavioral change.
Investment and financial mechanisms
Financing circular economy initiatives can be a challenge, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and start-ups. Innovative financial mechanisms, such as green bonds, impact investment funds, and public-private partnerships, can unlock capital for circular economy projects. Governments and financial institutions can play a crucial role in providing support and incentives for circular economy investments.
Infrastructure and supply chain challenges
The transition to a circular economy requires robust infrastructure for waste management, resource recovery, and recycling. Developing efficient collection systems, establishing recycling facilities, and creating circular supply chains can be complex and require significant investment. Partnerships between public and private entities can help address these infrastructure challenges.
Policy and regulatory frameworks
Governments need to create supportive policy and regulatory frameworks that incentivize circular practices and remove barriers to implementation. Policy coherence, harmonization, and long-term planning are crucial to provide businesses with the confidence and stability needed for sustainable investment.
Conclusion
The circular economy represents a fundamental shift in how we produce, consume, and manage resources. By aligning economic growth with environmental preservation, the circular economy offers a promising pathway towards a sustainable and prosperous future. Embracing this transformative model is not only an opportunity but also a responsibility we all share. Together, let us champion the principles of the circular economy and co-create a world that respects planetary boundaries, promotes inclusivity, and ensures a better quality of life for present and future generations.