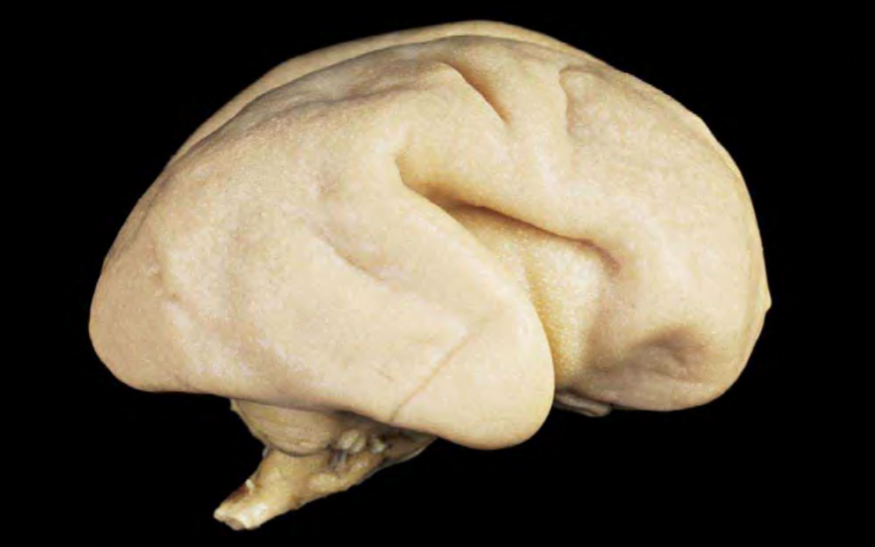
NEW BORN BRAIN – SUPPORT & SURVIVAL
Migrating neurons are helped along by glial cells. They support and nourish the neurons on their journeys. Some help regulate the neurons’ metabolism, and others coat the nerve cells’ axons with myelin, a fatty substance that provides electrical insulation and thus controls the speed of communication along neural networks.
Although the brain of a fetus at about eight months after conception weighs only a pound, or about a third of an adult’s, it contains twice as many neurons. Chemical signals called trophic factors influence how individual neurons connect to each other, but the survival of those connections depends on repeated communication across the synapses.
The brain cannot possibly sustain biochemical reactions across all of its neural connections, and so the weakest connections begin to die, through a process known as pruning. In the last stages of fetal development in the womb, about half of all neurons die. The loss is normal; it eliminates many of the connections that are weak or improper for efficient brain function, leaving behind the strongest and fittest neurons.
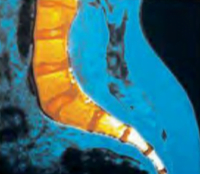
FIRST DESCRIBED 4,000 years ago, spina bifida is a malformation of the fetal spinal column that has been linked to a diet deficient in folate, a B vitamin, in pregnant women.
From the Latin for “spine split in two,” the birth defect occurs in 1 to 2 births per 1,000. One or more vertebrae, particularly in the small of the back, don’t grow the bony projections called vertebral arches that point away from the center of the body. Often a cyst bulges outward from the spine, encompassing spinal tissues, cerebrospinal fluid and even parts of the cord itself. Large cysts likely signal severe neurological impairment; a portion of the body’s central nervous system, designed to be safely protected from the outside world behind walls of tissue and bone, lies exposed. When the spinal cord is so compromised as to lose function, the infant may suffer paralysis of the legs and bladder, as well as bowel incontinence.
As a preventative measure, since 1998 all bread, pasta, and flour produced In America contains supplemental amounts of folate. The vitamin, found in green, leafy vegetables, helps the body grow new cells, but how its lack can trigger the disorder remains unclear. Genetics playa role, as the highest incidence rates occur among the citizens of Ireland and Wales as well as their immigrant descendants.
Surgery often can close openings over the exposed portion of a spine and reconstruct misshapen vertebrae, but many impairments remain for a lifetime.
Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.