Exploring the Fascinating Functions and Significance of Bone Marrow
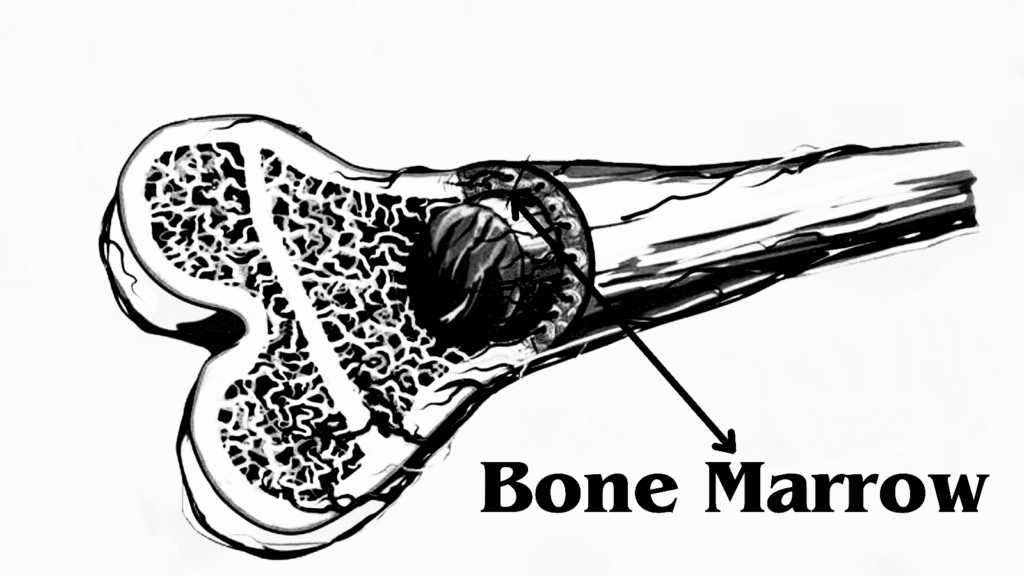
While many parts of our body often steal the spotlight, there’s one unsung hero that deserves our attention and appreciation: bone marrow. Nestled inside our bones, this remarkable tissue plays a pivotal role in our overall health. In this blog post, we’ll explore the fascinating world of bone marrow, its functions, and its significance in maintaining our well-being.
What Is Bone Marrow?
Bone marrow is the spongy, soft tissue found in the cavities of our bones, primarily the long bones like the femur, pelvis, and sternum. This vital tissue is essential for a variety of critical functions in the body, making it an indispensable part of our physiology.
Types of Bone Marrow
There are two main types of bone marrow: red marrow and yellow marrow.
- Red Marrow: This is the active, blood-producing marrow. It contains hematopoietic stem cells that give rise to red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red marrow is crucial for the body’s ability to carry oxygen, fight infections, and control bleeding.
- Yellow Marrow: As we age, red marrow gradually transforms into yellow marrow, which consists of primarily fat cells. While it no longer plays a role in blood cell production, it still has significance in storing fats and acting as a source of energy.
Functions of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a multitasking wonder, performing various essential functions in our body:
- Blood Cell Production: Red marrow is responsible for producing approximately 500 billion blood cells each day. Red blood cells transport oxygen, white blood cells defend against infections, and platelets help with blood clotting.
- Immune System Support: White blood cells generated in bone marrow are a critical component of our immune system. They patrol the body, identifying and neutralizing harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses.
- Blood Clotting: Platelets, also produced in bone marrow, play a crucial role in preventing excessive bleeding. When you cut yourself, platelets rush to the scene to form a clot and stop the bleeding.
- Storage of Nutrients: Yellow marrow stores fats, which can be converted into energy when needed by the body.
- Stem Cell Reservoir: Bone marrow contains hematopoietic stem cells, which have the unique ability to develop into various types of blood cells. These stem cells serve as a reservoir, ensuring a continuous supply of new blood cells throughout our lives.
Tips for Maintaining Bone Marrow Health
Now that we understand the importance of bone marrow, here are some practical tips to help you keep it healthy:
- Nutritious Diet: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially iron, vitamin B12, and folate, supports healthy blood cell production. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for overall health, including the function of bone marrow. Water helps transport nutrients and oxygen throughout the body, aiding in the production of blood cells.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity promotes circulation and helps maintain a healthy weight. Both of these factors are important for bone marrow function and overall health.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can harm bone marrow and increase the risk of conditions like leukemia. Quitting smoking and drinking in moderation are crucial steps in protecting your bone marrow.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively affect your immune system and overall health. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to support your bone marrow.
- Protect Against Radiation and Toxins: Limit exposure to harmful radiation, such as excessive X-rays or radiation therapy, and avoid exposure to toxic chemicals, which can damage bone marrow.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health, including your blood cell counts. Early detection of any issues can lead to more effective treatment.
- Bone Marrow Donation: Consider becoming a bone marrow donor if you are healthy and eligible. You may have the opportunity to save a life by providing bone marrow to someone in need.
Bone Marrow and Medical Breakthroughs
The importance of bone marrow extends beyond its everyday functions. In the world of medicine and research, bone marrow has been a source of incredible breakthroughs. Here are a few ways in which bone marrow has contributed to advancements in healthcare:
- Bone Marrow Transplants: Perhaps the most well-known application of bone marrow is in bone marrow transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplants. These procedures have revolutionized the treatment of various diseases, including leukemia, lymphoma, and certain genetic disorders. By replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells from a compatible donor, patients can have a chance at a new lease on life.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cells harvested from bone marrow have shown promise in treating a range of conditions, from heart disease to neurological disorders. Researchers are exploring how these versatile cells can be used to regenerate damaged tissues and organs, potentially opening doors to innovative treatments in regenerative medicine.
- Advancements in Blood Disorders: The study of bone marrow has led to a deeper understanding of blood disorders, such as anemia, myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and hemophilia. This knowledge has paved the way for improved diagnostic techniques and more targeted therapies for patients with these conditions.
- Cancer Research: Bone marrow research has provided critical insights into the development and progression of blood cancers, such as leukemia and multiple myeloma. Understanding the intricacies of bone marrow function has helped researchers devise more effective treatments and therapies for these diseases.
- Immune System Insights: The bone marrow’s role in immune system function has been a subject of extensive research. Insights into how immune cells are produced and regulated within the bone marrow have contributed to the development of immunotherapies and vaccines.
Bone Marrow and Ethical Considerations
While the potential of bone marrow in medicine and research is undoubtedly exciting, it also raises important ethical questions that must be addressed. Here are some key considerations:
- Donor Consent: Bone marrow transplants and stem cell therapies often require donors to provide their bone marrow or stem cells. Ensuring informed consent and the well-being of donors is crucial. Ethical guidelines must be in place to protect donors from coercion or harm.
- Equity in Access: Access to bone marrow transplants and cutting-edge treatments derived from bone marrow research can be limited by factors such as cost and geographic location. Ensuring equitable access to these life-saving therapies is an ethical imperative.
- Genetic Editing: As genetic editing technologies advance, there may be ethical dilemmas surrounding the modification of bone marrow stem cells to treat or prevent genetic disorders. Questions about the potential misuse of these technologies and their long-term consequences must be carefully considered.
- Research Ethics: Research involving bone marrow and stem cells should adhere to rigorous ethical standards, including obtaining informed consent from participants, minimizing risks, and ensuring transparency in reporting findings.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Bone marrow research should encompass diverse populations to ensure that treatments and therapies are effective for everyone. Lack of diversity in research can lead to health disparities and unequal access to benefits.
- Human-Animal Chimeras: Some experiments involve the creation of chimeras, organisms containing human and animal cells, for research purposes. Ethical concerns arise regarding the treatment and rights of these hybrid creatures.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects of certain bone marrow-related treatments and therapies are still unknown. Ethical considerations should include monitoring and addressing potential risks that may emerge over time.
The Future of Bone Marrow Research
As we look ahead, the future of bone marrow research promises to be both exciting and transformative. Scientists, healthcare professionals, and researchers continue to explore new avenues and technologies that leverage the incredible potential of bone marrow. Here are some key directions that the field is heading towards:
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in genomics and our understanding of bone marrow genetics are paving the way for personalized medicine. Tailoring treatments based on an individual’s genetic makeup and bone marrow characteristics can lead to more effective and less invasive therapies.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cells derived from bone marrow are at the forefront of regenerative medicine. Researchers are exploring their use in tissue engineering and organ regeneration, which could revolutionize the treatment of injuries and degenerative diseases.
- Immunotherapy: Harnessing the immune-modulating properties of bone marrow-derived cells holds immense potential for treating a wide range of conditions, including autoimmune diseases and cancer. Immunotherapies that enhance the body’s natural defenses are becoming increasingly important in healthcare.
- Gene Editing: CRISPR and other gene-editing technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to modify bone marrow stem cells to correct genetic defects or enhance their therapeutic potential. Ethical considerations surrounding these technologies will be crucial.
- Artificial Bone Marrow: Researchers are developing artificial bone marrow environments in the lab to better understand how the bone marrow microenvironment influences blood cell production and immune function. These models can accelerate drug discovery and improve our understanding of bone marrow disorders.
- Drug Development: Bone marrow research is driving the development of novel drugs and therapies. Targeted treatments that address specific bone marrow-related conditions are continually being explored.
- Disease Prevention: Insights from bone marrow research may lead to preventive strategies for diseases like leukemia, allowing for early intervention and improved outcomes.
- Global Collaboration: International collaboration and data sharing are critical for advancing bone marrow research. Researchers from different regions are working together to pool knowledge and resources to accelerate progress.
Conclusion
Bone marrow is truly a remarkable and unsung hero of the human body. Its multifaceted functions not only support our daily health but also hold the key to groundbreaking advancements in medicine and research. As we move forward, ethical considerations, diversity and inclusion, and global collaboration will be essential in harnessing the full potential of bone marrow for the benefit of all humanity. The future of bone marrow research is filled with promise, offering hope for more personalized, regenerative, and effective treatments that can transform healthcare and improve lives worldwide.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Stay updated—subscribe now for informed empowerment!

