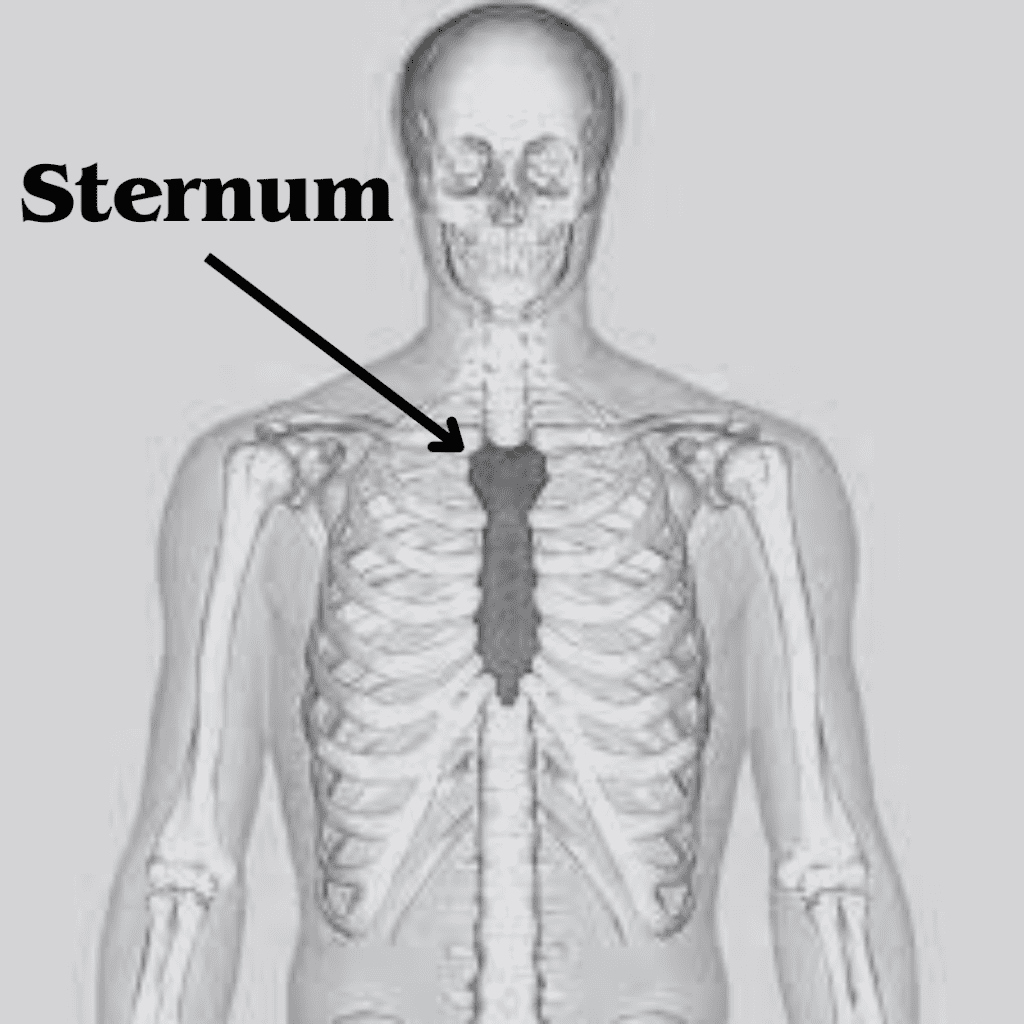
Sternum or breastbone
The sternum, commonly referred to as the breastbone, is a flat, elongated bone found in the central part of the thoracic skeleton. It plays a crucial role in the human body by serving as a key structural component of the rib cage. Anatomically, the sternum is located anteriorly to the heart and lungs, providing a protective shield for these vital organs while also functioning as an anchor point for several ribs. The sternum consists of three main parts: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process, each contributing to its overall function and structural integrity.
The importance of the sternum extends beyond mere structural support. As a pivotal element of the skeletal system, it facilitates attachments for several muscles involved in respiration. Specifically, the manubrium supports attachments for muscles such as the pectoralis major and the sternocleidomastoid, which are essential in the mechanics of breathing. Additionally, the articulation of the sternum with the first seven pairs of ribs illustrates its role in the respiratory system, allowing for the expansion of the thoracic cavity during inhalation.
In understanding the significance of the sternum, it is essential to acknowledge its clinical relevance as well. Injuries or conditions affecting the sternum can have detrimental effects on respiratory function and thoracic stability. For instance, sternal fractures often result from blunt trauma and may compromise surrounding organs, highlighting the need for awareness of the sternum’s functions in both health and disease. By recognizing the anatomical and functional importance of this bone, we can better appreciate its role within the human body and its implications for clinical practice.
Anatomy of the Sternum
The sternum, commonly referred to as the breastbone, serves a pivotal role in the human skeletal system. It is comprised of three primary segments: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process, each possessing distinct anatomical features and functions. The manubrium is the upper segment of the sternum, characterized by a broad, triangular shape. It articulates with the clavicles laterally at the sternoclavicular joints, forming a vital connection between the axial skeleton and the upper limbs. Additionally, the manubrium connects to the first pair of ribs through costal cartilage, providing stability and support to the ribcage.
The body of the sternum, following the manubrium, represents the longest part of the sternum and is notable for its elongated rectangular form. It comprises segments that articulate with the second to seventh pairs of ribs, allowing for an attachment that enhances the thoracic cage’s structural integrity. This area is critical for protecting vital organs such as the heart and lungs while also serving as an anchor point for respiratory muscles. Its secure articulations via cartilage contribute to the flexibility of the ribcage, facilitating the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity during respiration.
The xiphoid process, the smallest and most inferior portion of the sternum, is initially cartilaginous before ossifying with age. Although it may appear somewhat insignificant in size, the xiphoid process serves as an important landmark for medical professionals. It is a point of attachment for various muscles, including the diaphragm and rectus abdominis. The anatomical position of the xiphoid process also marks the location of the lower boundary of the thoracic cavity, further underscoring its clinical significance. Understanding the anatomy of the sternum and its components is essential for grasping its overall function and relevance within the greater context of human anatomy.
Functions of the Sternum
The sternum, or breastbone, plays a crucial role in the human body, serving multiple functions essential for overall health and well-being. One of its primary roles is protective; the sternum safeguards vital organs located within the thoracic cavity, including the heart and lungs. By forming a part of the thoracic cage, it helps to shield these organs from potential trauma caused by external forces, thereby contributing to cardiovascular and respiratory health.
Moreover, the sternum is integral to the stability of the skeletal system. It acts as an anchor point for the ribs through cartilage, aiding in the formation of the ribcage. This connection provides structural support, allowing the ribcage to maintain its integrity while accommodating the movements necessary for breathing. The stability offered by the sternum and ribcage is particularly significant, as it allows for the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity during respiration, ensuring adequate airflow into the lungs.
Additionally, the sternum plays a role in facilitating efficient respiration. When inhaling, the ribs, which are connected to the sternum, elevate as the muscles expand the thoracic cavity. This expansion decreases pressure within the lungs, prompting air to flow in. Conversely, during exhalation, the sternum aids in the return of the ribs to their resting position, allowing air to be expelled. Thus, the sternum not only supports the skeletal structure but also actively contributes to the respiratory process.
In summary, the sternum serves multiple essential functions in the human body, from protecting vital organs to stabilizing the skeleton and aiding in respiration. Its clinical significance is evident, underscoring the necessity of a healthy sternum for overall physiological function.

Development and Growth of the Sternum
The sternum, commonly referred to as the breastbone, undergoes significant development and growth that is integral to the formation of the chest structure. Initially, during the embryonic stage, the sternum starts as a cartilaginous structure, emerging from the mesoderm. This cartilaginous form is crucial for the early development of the thoracic skeleton and provides flexibility for the growing fetus.
As gestation progresses, the process of ossification—the conversion of cartilage to bone—commences. Bone development in the sternum typically begins around the sixth week of fetal life. Here, ossification centers appear, and by the end of the first trimester, the individual sternal segments begin to show substantial calcification. The sternum consists of three primary components: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process, each of which ossifies at different intervals during development.
During childhood, the sternum continues to grow and remodel, with complete ossification usually occurring in late adolescence or early adulthood. The fusion of the individual segments of the sternum, particularly the manubrium and body, is a critical event, as these segments merge to create a robust structure that provides support and protection to the thoracic organs, including the heart and lungs. Variations in sternal development can occur, including differences in the number of sternal segments or abnormal fusion patterns. These variations may be congenital and typically do not have a functional impact, although they can be relevant in surgical considerations or chest trauma assessment.
Understanding the developmental timeline of the sternum enhances appreciation for its anatomical significance and functional role throughout various life stages. It is essential for both healthcare professionals and students to recognize the processes involved in sternal growth and the potential implications of any developmental anomalies.
Common Sternum Injuries and Conditions
The sternum, also known as the breastbone, is a vital component of the chest that can be affected by various injuries and conditions. Understanding these common sternum-related issues is essential for effective diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
One prevalent injury is a sternal fracture, often resulting from trauma such as car accidents or falls. Symptoms typically include localized pain at the site of the injury, especially during movement or when taking deep breaths. Diagnosis is usually confirmed through imaging studies, such as X-rays or CT scans. Treatment often involves pain management, rest, and monitoring, as most sternal fractures heal on their own over time.
Another condition affecting the sternum is costochondritis, characterized by inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum. This condition is frequently seen in individuals with repetitive trauma or physical strain, and it can also occur following viral infections. Patients commonly report sharp pain in the chest area, which may worsen with certain movements or when palpating the affected area. Diagnosis is typically based on physical examination and patient history, as imaging studies may not reveal significant findings. Treatment generally involves anti-inflammatory medications and rest, with physical therapy sometimes recommended for persistent symptoms.
Lastly, tumors, although rarer, can also affect the sternum. These include both benign growths and malignant tumors such as sarcomas. Symptoms may vary based on the tumor’s nature and location but can include persistent pain, swelling, and fatigue. Diagnostic evaluation often entails imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans and sometimes biopsy to determine the tumor’s characteristics. Treatment options depend on the type and stage of the tumor, ranging from surgical removal to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
In conclusion, understanding the common injuries and conditions associated with the sternum can aid in early diagnosis and effective management, ensuring better health outcomes for affected individuals.
Sternum in Medical Procedures
The sternum, also known as the breastbone, plays a vital role in various medical procedures due to its central location within the ribcage and its protection of vital organs. One of the most significant procedures involving the sternum is sternotomy, which is a surgical technique that entails the opening of the sternum to gain access to the thoracic cavity. This procedure is commonly indicated in cardiac surgeries, such as coronary artery bypass grafting, heart valve repair or replacement, and procedures related to lung surgery.
Sternotomy is performed under general anesthesia, where a surgeon makes a vertical incision down the middle of the chest, followed by a systematic division of the sternum, allowing for surgical access. Once the necessary interventions within the chest cavity are completed, the sternum is typically closed with stainless steel wires that stabilize the bone as it heals. Patients can expect a hospital stay of several days post-surgery, during which they will be monitored for any complications. Recovery generally involves pain management and gradual strengthening to ensure proper healing of the chest wall.
In addition to sternotomy, the sternum is also pertinent in procedures such as the insertion of pacemakers and stents. Pacemaker implantation involves placing a small device under the skin that helps regulate heart rhythms. This can often be done through a minimally invasive procedure, bypassing the need for sternotomy. Stent placement, commonly performed during cardiac catheterization, involves inserting a small mesh tube to keep narrowed arteries open, facilitating increased blood flow and reducing the risk of angina or heart attacks.
Patients undergoing these procedures should be well-informed about the indicators, potential risks, and expected recovery timelines associated with interventions involving the sternum. Proper preoperative assessment and postoperative care are crucial for successful outcomes in all sternum-related medical procedures.

Sternum in Radiology and Imaging
The sternum, a vital part of the human thoracic skeleton, is often evaluated through various imaging techniques in clinical practice. Radiological assessments are essential for diagnosing trauma, infections, tumors, and other pathological conditions affecting the sternum. Among the primary modalities utilized are X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), each offering unique insights into sternum health.
X-rays are typically the first-line imaging technique used to evaluate the sternum. They provide a preliminary assessment of sternal fractures or dislocations, particularly in patients who have sustained chest trauma. When analyzed, X-rays can reveal obvious structural abnormalities, including fractures or changes consistent with conditions such as osteosarcoma, which can affect the sternum. However, X-rays have limitations in assessing soft tissue involvement or detecting more subtle bone lesions.
CT scans offer a more detailed view of the sternum and surrounding structures. This imaging modality is particularly useful in assessing complex fractures, evaluating the extent of any associated soft tissue injuries, and identifying the presence of metastasis or primary bone lesions. In pre-operative planning, CT imaging helps determine the best surgical approaches by providing an accurate assessment of the bony anatomy and any existing pathologies.
On the other hand, MRI is especially beneficial in evaluating sternal conditions that may not be well visualized on X-rays or CTs, such as inflammatory processes or marrow infiltration due to various systemic diseases, including hematological disorders. MRI’s superior soft tissue contrast can help elucidate the relationships between the sternum and adjacent soft tissues, making it a valuable tool in certain clinical scenarios.
In conclusion, radiological imaging plays a critical role in assessing the sternum, with each modality offering specific advantages for diagnosis and pre-operative planning. Understanding these techniques aids healthcare professionals in delivering precise and effective patient care.
Sternum Health and Maintenance
Maintaining sternal health is crucial for overall thoracic well-being, as the sternum plays a pivotal role in protecting vital organs and providing structural stability to the chest cavity. A comprehensive approach that includes proper nutrition, regular exercise, and safety measures can significantly enhance the strength of the thoracic region while minimizing the risk of injuries.
Nutrition is fundamental for maintaining optimal sternal health. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone strength, as these nutrients support the structure of the sternum and surrounding ribs. Foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified cereals can help maintain adequate calcium levels. Furthermore, incorporating omega-3 fatty acids from fish or flaxseed can assist in reducing inflammation in the body, which may indirectly support the sternum and surrounding areas.
In addition to proper nutrition, regular exercise is vital for strengthening the thoracic muscles that support the sternum. Engaging in activities that promote upper body strength, such as push-ups, resistance training, and aerobic exercises, can enhance muscular support around the sternum. Stretching exercises, particularly those focused on the shoulders and chest, can also improve flexibility and posture, which is essential for avoiding undue stress on the sternum.
Moreover, implementing safety measures during physical activities can prevent injuries to the sternum. When participating in contact sports or activities with a risk of trauma, wearing appropriate protective gear, such as chest guards, is critical. Additionally, being mindful of one’s movements and avoiding high-impact activities without proper training can significantly reduce the likelihood of sternal damage.
By focusing on these key aspects of nutrition, exercise, and safety, individuals can effectively maintain their sternal health, thereby promoting overall thoracic well-being. Strengthening the thoracic region not only protects the sternum but also contributes to better respiratory and cardiovascular functions. Taking proactive steps will allow individuals to foster lasting sternum health throughout their lives.
FAQs: the Sternum or breastbone
The sternum, commonly known as the breastbone, is a vital structure in the human body that plays an essential role in protecting vital organs and providing attachment for ribs and muscles. Here are some frequently asked questions regarding the sternum, with a focus on pain management, recovery, and general anatomy.
What causes sternum pain?
Sternum pain can arise from various conditions, including trauma, costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum), and esophageal problems. Additionally, pain may result from muscle strain or fractures. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the exact cause of sternum pain, as some conditions may require specific interventions.
How is sternum pain managed?
Management of sternum pain typically involves a combination of rest, ice application, and over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). For more severe cases, a doctor may recommend physical therapy or prescribe stronger medications. It is important to follow medical advice and avoid activities that may exacerbate the pain.
What is the recovery timeline after sternum surgery?
Recovery times can vary depending on the specific procedure performed on the sternum, such as sternotomy for heart surgery or sternum fracture repair. Generally, patients may require several weeks to months for complete recovery, during which they should adhere to their healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding activity levels and rehabilitation exercises.
Are there any anatomical variations of the sternum?
Yes, variations in the anatomy of the sternum can occur. These differences may include variations in size, shape, or the presence of supernumerary sternal elements. While most variations do not pose significant health risks, they can be relevant in surgical procedures and diagnostic imaging.
Understanding these common concerns about the sternum can assist individuals in recognizing the significance of sternum health and seeking prompt medical advice when necessary. Always consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns regarding sternum-related issues.

Discover more from HUMANITYUAPD
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

