Introduction to the Spleen
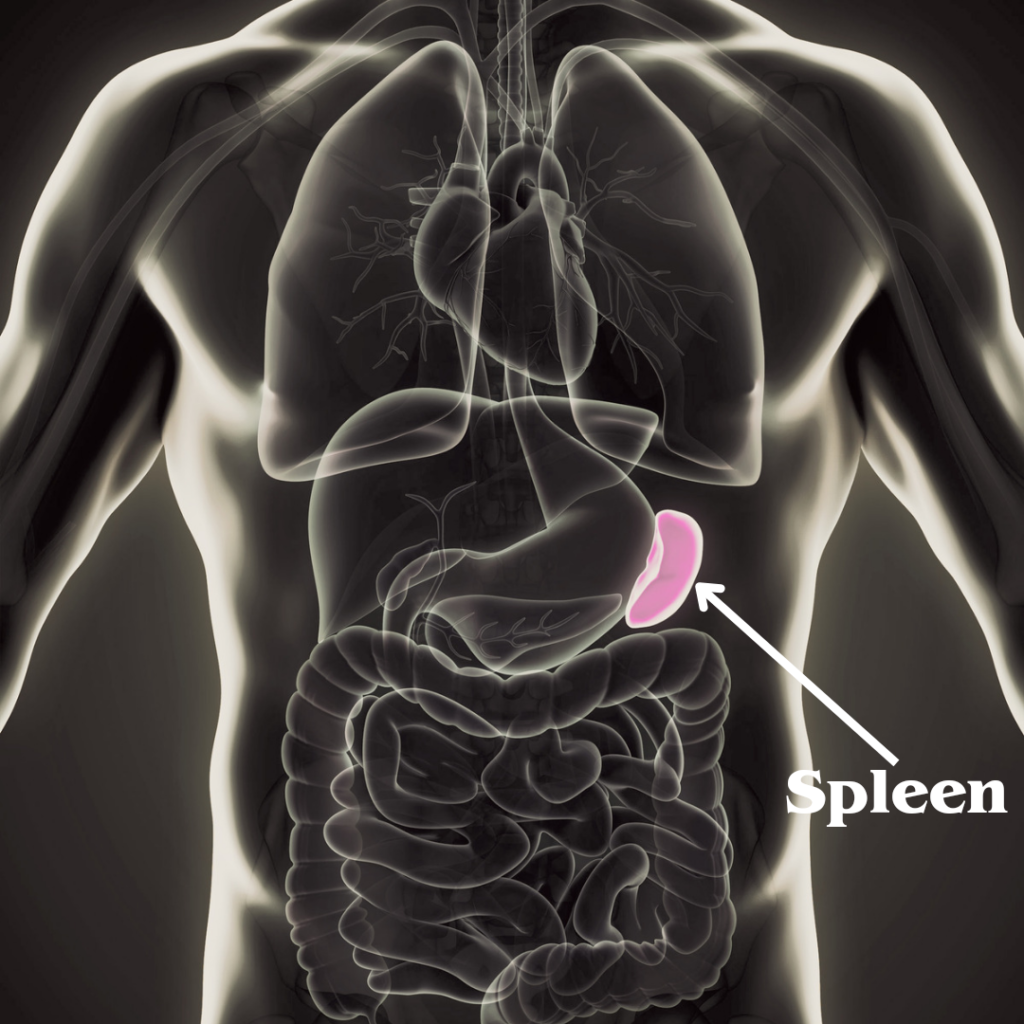
The spleen is a vital organ in the human body that frequently goes unnoticed despite its essential roles. Located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, just beneath the ribcage, the spleen is roughly the size of a fist and has a soft, spongy texture. Its strategic position allows it to effectively interact with both the circulatory and immune systems, thereby contributing significantly to overall health and well-being.
Anatomically, the spleen is part of the lymphatic system and is connected to the bloodstream via the splenic artery and vein. The organ is encapsulated by a protective outer layer called the capsule, which houses two distinct types of tissue: red pulp and white pulp. The red pulp is responsible for filtering and removing old or damaged red blood cells from the bloodstream, while the white pulp plays a critical role in the immune response by producing and storing white blood cells, particularly lymphocytes.
The spleen’s functions extend far beyond simple filtration. In addition to purifying the blood, the spleen acts as a reservoir for platelets, which are essential for blood clotting. Moreover, it helps recycle iron from hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. In the event of severe blood loss, the spleen can contract to release stored blood cells into circulation, thus aiding in maintaining blood volume and pressure.
On the immunological front, the spleen serves as a hub for immune activity. It identifies and removes pathogens such as bacteria and viruses from the blood, thus preventing infections. The organ’s ability to mount an immune response is crucial for the body’s defense mechanisms, making it indispensable for maintaining health.
Understanding the spleen’s multifaceted roles can provide valuable insights into its significance. This foundational knowledge sets the stage for more in-depth exploration of its functions and potential health issues in the subsequent sections of this blog post.
Anatomy of the Spleen
The spleen, located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, is a vital organ often overlooked in discussions of human anatomy. This fist-sized organ is nestled between the stomach and diaphragm, playing a pivotal role in the body’s immune system and blood filtration processes. The spleen’s shape is somewhat oval, resembling a large lymph node, and it can vary in size, typically measuring around 12 centimeters in length.
The spleen is composed of two primary types of tissue: red pulp and white pulp, each serving distinct yet complementary functions. The red pulp, making up roughly 75% of the spleen’s mass, is responsible for filtering the blood. It is rich in blood-filled cavities known as sinusoids, where old or damaged red blood cells are broken down and recycled. This part of the spleen also acts as a reservoir for blood, storing platelets and various immune cells that can be rapidly mobilized in response to bodily injury or infection.
In contrast, the white pulp is integral to the immune response. It consists of lymphoid tissue and is organized around central arterioles forming structures known as periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths (PALS). These sheaths are populated with T-lymphocytes, critical for the adaptive immune response. Adjacent to PALS are lymphoid follicles rich in B-lymphocytes, which produce antibodies to neutralize pathogens. Together, these elements of the white pulp enable the spleen to identify and respond swiftly to foreign invaders, filtering out bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens from the bloodstream.
The intricate interplay between red pulp and white pulp underpins the spleen’s dual role in both hematologic and immunologic functions. By understanding the anatomy of the spleen, we can appreciate the complex yet indispensable tasks this organ performs in maintaining overall health.
Functions of the Spleen
The spleen, a small organ located in the upper left abdomen, performs several crucial functions that are essential to maintaining a healthy body. Primarily, the spleen acts as a blood filter, removing old and damaged red blood cells from circulation. This filtration process is vital for maintaining the quality and efficiency of the blood supply.
In addition to filtering blood, the spleen also plays a role in recycling iron. As old red blood cells are broken down, the spleen recovers and recycles iron, which is then transported to the bone marrow to be used in the production of new red blood cells. This recycling process not only conserves valuable resources but also ensures the continuous production of healthy blood cells.
Another critical function of the spleen is the storage of white blood cells and platelets. White blood cells, or leukocytes, are essential components of the immune system, helping to detect and fight off infections. Platelets, on the other hand, are involved in blood clotting, which is crucial for stopping bleeding and initiating the healing process after injury. By storing these vital cells, the spleen acts as a reservoir, ready to release them when the body requires an immediate immune response or repair mechanism.
The spleen’s contribution to the immune system extends beyond storage. It is also involved in detecting pathogens and foreign particles in the blood. The spleen contains specialized white blood cells called macrophages and lymphocytes, which engulf and destroy bacteria, viruses, and other harmful entities. This immune surveillance ensures that infections are promptly identified and combated, helping to protect the body from disease.
Overall, the spleen’s multifaceted functions underscore its importance to overall health. From filtering and recycling blood components to storing and mobilizing immune cells, the spleen plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s internal balance and defending against infections.
Common Spleen Disorders
The spleen, though often overlooked, plays a crucial role in maintaining bodily health. However, like any organ, it can be susceptible to various disorders. Among the most prevalent spleen-related conditions are splenomegaly, spleen rupture, and infections such as mononucleosis.
Splenomegaly, or an enlarged spleen, is a condition where the spleen increases in size due to various underlying causes. These can range from infections and liver diseases to cancers and inflammatory diseases. Symptoms of splenomegaly often include pain or fullness in the upper left abdomen, fatigue, and a feeling of satiety after eating only a small amount. The causes of splenomegaly are diverse, encompassing conditions such as viral infections (e.g., mononucleosis), bacterial infections, and parasitic infections. Risk factors include chronic liver disease, certain types of anemia, and metabolic disorders. Treatment for splenomegaly typically focuses on addressing the underlying cause, which may involve antibiotics for infections or chemotherapy for cancers.
Spleen rupture is another significant condition that can arise due to trauma or, less commonly, spontaneous rupture associated with conditions like mononucleosis or certain cancers. The primary symptom is severe pain in the upper left abdomen, which may radiate to the left shoulder. Additional symptoms can include dizziness, lightheadedness, and signs of shock, such as rapid heart rate and fainting. Immediate medical attention is crucial, and treatment often involves surgery to repair or remove the spleen, depending on the severity of the rupture.
Infectious mononucleosis, commonly known as mono, is a viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). This condition can lead to spleen enlargement and other systemic symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. While mono is generally self-limiting, with symptoms resolving over time, patients are advised to avoid contact sports or heavy lifting to reduce the risk of spleen rupture. Supportive care, including rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate symptoms, is usually sufficient.
Understanding these common spleen disorders, their symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatments, is essential for recognizing when medical intervention may be necessary and ensuring the health and functionality of this vital organ.“`html
Diagnostic Procedures for Spleen Issues
Diagnosing spleen-related problems involves a multifaceted approach, combining physical examinations and advanced imaging tests. Physical examinations are often the first step. During these exams, a healthcare provider will palpate the abdomen to check for spleen enlargement, tenderness, or other abnormalities. However, palpations alone are not definitive; hence, imaging tests are essential to gain comprehensive insights into spleen health.
Ultrasound is a commonly used diagnostic tool due to its non-invasive nature and effectiveness. Using high-frequency sound waves, an ultrasound generates detailed images of the spleen. This test helps in identifying conditions such as splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), cysts, or tumors. Patients typically lie down during the procedure while a technician moves a transducer over the abdominal area. The process is generally quick and painless, with results available shortly after the examination.
For more detailed imaging, Computed Tomography (CT) scans and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are often employed. A CT scan uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the spleen, providing a more intricate view of its structure and any potential issues. An MRI, on the other hand, uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce highly detailed images, making it particularly useful for identifying soft tissue abnormalities. Both procedures require the patient to lie still inside the respective machines, and while a CT scan is relatively quick, an MRI might take longer to complete.
Doctors interpret the results of these imaging tests by looking for signs of disease or abnormalities. For instance, an enlarged spleen seen on an ultrasound or CT scan might prompt further tests to determine the underlying cause, such as blood tests or a biopsy. The accuracy of these imaging techniques allows healthcare providers to formulate an effective diagnosis and treatment plan, ensuring that any spleen-related issues are addressed promptly and appropriately.
Treatment Options for Spleen Disorders
Upon diagnosing a spleen disorder, medical professionals have a range of treatment options to consider. The choice of treatment depends on the specific condition, its severity, and the overall health of the patient. Common medical treatments include medications and lifestyle modifications, while more severe cases may necessitate surgical intervention, such as a splenectomy.
Medications are often the first line of treatment for spleen disorders. For instance, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat infections affecting the spleen. In cases of splenic inflammation or autoimmune disorders, corticosteroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs can be effective. Additionally, blood thinners might be used to manage conditions like splenic vein thrombosis.
Lifestyle changes can also play a crucial role in managing spleen disorders. Patients are often advised to adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while avoiding alcohol and processed foods. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight are also recommended to support overall spleen health. Stress reduction techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can further enhance the immune system’s functionality.
Surgical treatments, such as splenectomy, may be necessary for more serious spleen conditions. A splenectomy involves the surgical removal of the spleen and is typically recommended in cases of traumatic spleen injury, severe splenomegaly, or certain hematologic disorders. While splenectomy can be life-saving, it comes with risks, including an increased susceptibility to infections. Patients who undergo this procedure often require vaccinations and prophylactic antibiotics to mitigate these risks.
In some instances, less invasive procedures like partial splenectomy or splenic artery embolization may be considered. These techniques aim to preserve some splenic function while addressing the underlying issue. Each treatment option carries its own set of potential outcomes and risks, which should be thoroughly discussed with a healthcare provider to ensure the best possible care for the patient.
Living Without a Spleen
Living without a spleen, a condition known as asplenia, poses unique challenges and requires vigilant health management. The spleen plays a crucial role in the immune system by filtering blood and fighting certain types of bacteria. Its absence, often due to surgical removal (splenectomy) or medical conditions like trauma or certain blood disorders, can significantly impact the body’s ability to ward off infections.
One of the primary implications of living without a spleen is an increased susceptibility to infections, particularly those caused by encapsulated bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningitidis. Without the spleen’s filtering action, the risk of severe infections, including sepsis, becomes more pronounced. Therefore, individuals without a spleen must take extra precautions to protect their health.
Vaccinations are a critical preventative measure for individuals without a spleen. It is essential to receive vaccines against pneumococcal, meningococcal, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infections. Annual influenza vaccinations are also recommended, as complications from the flu can be more severe in asplenic individuals. Additionally, some patients may require booster doses to maintain immunity over time.
Preventative antibiotics may be prescribed as a prophylactic measure, especially for children and those with a history of severe infections. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding contact with sick individuals, is also crucial. Patients should be educated about recognizing early signs of infection, such as fever or chills, and seek prompt medical attention if these symptoms occur.
For those living without a spleen, wearing a medical alert bracelet can be a lifesaving measure in emergencies, alerting healthcare providers to their increased infection risk. Travel precautions, such as avoiding areas with high malaria risk and taking appropriate prophylaxis, are also advisable.
Overall, while living without a spleen necessitates adaptations and vigilance, individuals can lead healthy lives by adhering to recommended vaccinations, preventative measures, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the Spleen
Q: Is the spleen a necessary organ?
A: While the spleen plays a vital role in the body’s immune system and blood filtration, it is not considered essential for survival. Other organs, such as the liver and lymph nodes, can compensate for many of its functions if it is removed. However, the absence of the spleen can increase susceptibility to certain infections, necessitating extra precautionary measures.
Q: How can I recognize spleen problems?
A: Spleen issues can manifest in various ways. Common symptoms include pain or fullness in the left upper abdomen, which may spread to the left shoulder, fatigue, frequent infections, and anemia. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation. Early detection of spleen problems can significantly improve the outcome and management of any underlying conditions.
Q: What steps should I take if I suspect a spleen issue?
A: If you suspect a problem with your spleen, seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider may perform a physical examination and recommend imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan to assess the spleen’s condition. Blood tests may also be conducted to evaluate overall health and identify any infections or blood disorders. Based on the findings, your doctor will suggest appropriate treatment options, which could range from medication to, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Q: Can lifestyle changes impact spleen health?
A: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can support spleen health. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate hydration, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, staying up-to-date with vaccinations and practicing good hygiene can help reduce the risk of infections that could affect the spleen. While lifestyle changes alone cannot prevent all spleen issues, they contribute significantly to overall well-being and immune function.
Q: Are there specific conditions that affect the spleen?
A: Yes, several conditions can impact the spleen, including splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), splenic infarction (tissue death due to lack of blood flow), and various blood disorders such as leukemia and lymphoma. Infections like mononucleosis and malaria can also affect the spleen. Awareness and timely diagnosis of these conditions are crucial for effective management and treatment.

