Unveiling the Intricacies of Sternal Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
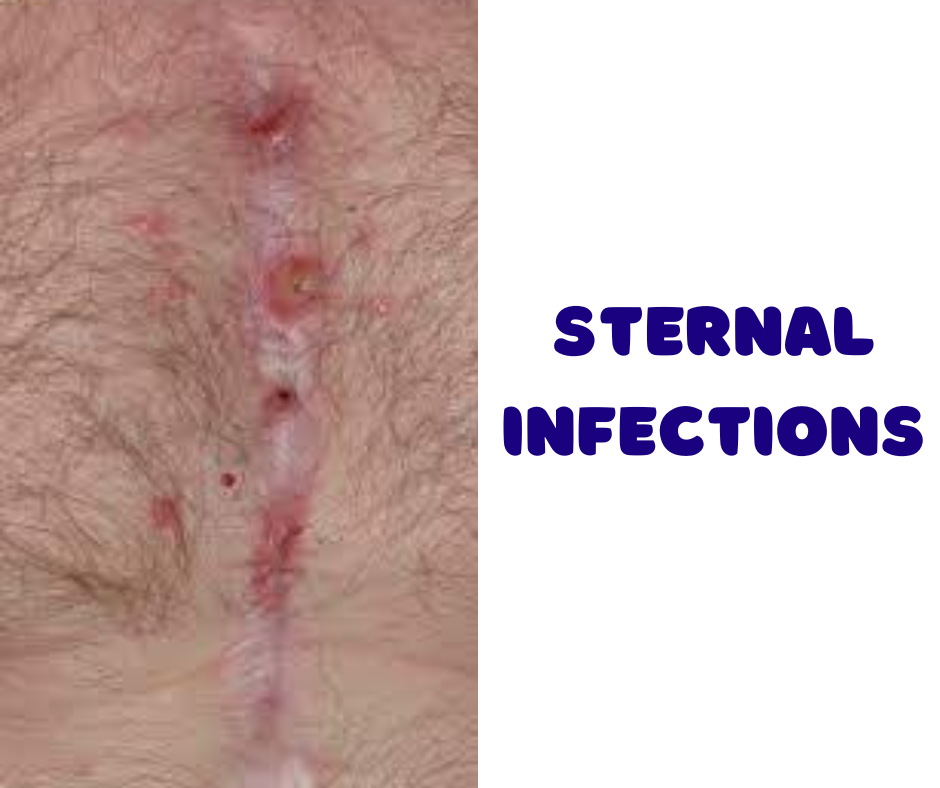
Sternal infections, though relatively uncommon, can pose serious risks to individuals’ health and require prompt attention and treatment. The sternum, or breastbone, plays a crucial role in protecting vital organs such as the heart and lungs. When infections occur in this area, they can lead to significant complications. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sternal infections to raise awareness and promote early detection.
Understanding Sternal Infections
Sternal infections, also known as sternal osteomyelitis or mediastinitis, typically result from bacterial or fungal invasion of the sternum. This can happen through various means, including surgical procedures, trauma, or the spread of infections from adjacent tissues. Post-surgical sternal infections are a common concern, particularly after cardiac surgeries or other procedures involving the chest.
Causes of Sternal Infections
Sternal infections can arise from various causes, and understanding these factors is crucial for both prevention and effective treatment. The primary causes of sternal infections include:
- Surgical Procedures:
- Cardiac Surgeries: Patients undergoing cardiac surgeries, particularly those involving sternotomy (an incision through the sternum), are at a heightened risk of sternal infections. Despite the implementation of sterile techniques, bacteria can enter during the surgical process, leading to infections.
- Orthopedic Surgeries: Procedures that involve the sternum or adjacent areas, such as spinal surgeries, can also increase the risk of sternal infections.
- Trauma:
- Direct trauma to the chest, resulting from accidents, falls, or impact, can cause fractures or damage to the sternum. Open wounds or compromised skin integrity following trauma create an entry point for bacteria, increasing the likelihood of infection.
- Spread from Adjacent Areas:
- Infections originating in nearby structures may extend to the sternum. For example, infections of the lungs, mediastinum (central thoracic cavity), or soft tissues surrounding the sternum can spread and cause sternal infections.
- Compromised Immune System:
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to underlying medical conditions (such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders) or immunosuppressive therapies, are more susceptible to infections, including those affecting the sternum.
- Inadequate Wound Care:
- Poor postoperative wound care, especially after cardiac or chest surgeries, can lead to infections. Inadequate hygiene practices and failure to detect early signs of infection contribute to the development of sternal infections.
- Pre-existing Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or peripheral vascular disease, can impair blood circulation and compromise the body’s ability to fight infections. Individuals with these conditions may be at a higher risk of sternal infections.
- Bacterial or Fungal Inoculation:
- During surgical procedures or as a result of trauma, bacteria or fungi can enter the sternum. Staphylococcus aureus is a common bacterium associated with sternal infections, but other pathogens may also be involved.
- Foreign Body Contamination:
- Presence of foreign bodies, such as surgical implants or devices, may increase the risk of infection. In some cases, infections may be linked to the introduction of foreign materials during surgical interventions.
Understanding the specific cause of a sternal infection is crucial for tailoring an appropriate treatment plan. Additionally, preventive measures, such as stringent sterile techniques during surgeries and careful wound care, play essential roles in minimizing the risk of sternal infections, particularly in high-risk individuals undergoing surgical procedures involving the chest cavity.
Common Symptoms
Sternal infections can manifest with a range of symptoms, and recognizing these signs is vital for early detection and intervention. The symptoms of sternal infections may vary in severity, and some individuals may exhibit only a subset of these indicators. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and Tenderness:
- Persistent pain in the sternal area is a hallmark symptom of sternal infections. The pain may be localized, dull, or throbbing, and it often worsens over time. Palpation of the sternum may reveal tenderness.
- Swelling and Redness:
- Inflammatory responses to the infection can lead to swelling and redness around the sternal region. The skin over the sternum may appear warm to the touch.
- Fever and Chills:
- Systemic symptoms such as fever and chills are common manifestations of an ongoing infection. The body’s immune response to the infection can result in an elevated temperature.
- Wound Issues (Post-Surgical Infections):
- For individuals who have undergone surgical procedures involving the sternum, complications with the surgical wound may arise. These can include redness, warmth, discharge, or delayed healing. Wound dehiscence (opening of the wound) may also occur.
- Difficulty Breathing:
- In severe cases, sternal infections may extend to affect the nearby structures, leading to respiratory symptoms. Individuals may experience difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, or chest pain during breathing.
- Fatigue and Weakness:
- The body’s response to infection can result in general malaise, fatigue, and weakness. Individuals may feel unusually tired and lacking in energy.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
- Chronic infections, including sternal infections, can lead to unintended weight loss. The body’s metabolic response to infection can contribute to a decrease in appetite and weight loss.
- Elevated Heart Rate:
- Infections can cause an increased heart rate (tachycardia) as the body tries to cope with the infectious process. Monitoring heart rate can provide additional insight into the severity of the infection.
It’s important to note that the symptoms of sternal infections can overlap with other medical conditions, making a thorough clinical evaluation crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
The treatment of sternal infections involves a comprehensive approach aimed at eradicating the infection, relieving symptoms, and promoting optimal healing. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection, the causative agent, and individual patient factors. Here are common treatment options for sternal infections:
- Antibiotics or Antifungal Medications:
- Bacterial Infections: Antibiotics are prescribed to target and eliminate bacterial infections. Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), is a common pathogen associated with sternal infections.
- Fungal Infections: Antifungal medications are utilized if the sternal infection is caused by fungi. These medications may include fluconazole or amphotericin B.
- Surgical Intervention:
- Drainage of Abscesses: If abscesses are present, surgical drainage may be necessary to remove the accumulated pus and infected material.
- Debridement: Surgical debridement involves the removal of infected or necrotic tissue, promoting wound healing and preventing the spread of infection.
- Hardware Removal: In cases where sternal infections occur post-surgery and involve implanted hardware, such as sternotomy wires or plates, removal of these materials may be necessary to eliminate the source of infection.
- Supportive Care:
- Pain Management: Adequate pain control is crucial for patient comfort. Pain medications, both oral and intravenous, may be prescribed.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential for preventing further complications. Regular dressing changes and monitoring for signs of infection are key components.
- Intravenous Fluids and Nutrition: Maintaining hydration and proper nutrition supports the body’s immune response and aids in recovery, especially in cases of prolonged illness.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT):
- In some cases, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be considered. This involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room, promoting healing by increasing the oxygen supply to tissues.
- Prophylactic Antibiotics:
- After the acute phase of treatment, individuals may be prescribed prophylactic antibiotics to prevent recurrence, particularly in those with risk factors or undergoing additional surgeries.
- Close Monitoring:
- Regular follow-up visits and monitoring of symptoms, laboratory markers, and imaging studies are crucial to assess treatment progress and detect any signs of recurrence.
- Management of Underlying Conditions:
- If the sternal infection is associated with underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or immunosuppression, managing these conditions is integral to preventing recurrence.
It’s important to note that the choice of treatment is individualized based on the patient’s specific circumstances. A multidisciplinary approach involving infectious disease specialists, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals is often employed to optimize patient care. Early detection and prompt initiation of treatment are critical for favorable outcomes in sternal infections.
Prevention Strategies
While not all sternal infections can be prevented, there are measures that can reduce the risk, including:
- Sterile Surgical Techniques:
- Healthcare professionals must adhere to strict sterile techniques during surgical procedures, particularly those involving sternotomy. This includes maintaining a sterile field, using sterile instruments and equipment, and following established protocols to minimize the risk of bacterial or fungal contamination.
- Preoperative Screening and Prophylactic Antibiotics:
- Identifying individuals at higher risk of infections and administering prophylactic antibiotics before certain high-risk surgical procedures can help prevent postoperative sternal infections.
- Optimizing Patient Health:
- Ensure that patients undergoing surgical interventions are in optimal health. Managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or immunosuppression, can enhance the body’s ability to resist infections.
- Adequate Wound Care:
- Implementing proper wound care practices is crucial in preventing postoperative sternal infections. This includes keeping the surgical site clean, monitoring for signs of infection, and promptly addressing any wound-related issues.
- Postoperative Monitoring:
- Regular and vigilant monitoring of postoperative patients is essential. Healthcare providers should closely observe patients for any signs of infection, such as increased pain, swelling, redness, or abnormal discharge from the surgical site.
- Patient Education:
- Providing patients with information on proper wound care, signs of infection, and when to seek medical attention empowers them to actively participate in their recovery and facilitates early detection of potential issues.
- Optimizing Nutrition:
- Adequate nutrition is essential for wound healing and overall immune function. Ensuring that patients receive proper nutrition before and after surgery can contribute to a faster and more robust recovery.
- Avoiding Contamination:
- Taking precautions to avoid contamination during and after surgery is crucial. This includes proper handling of surgical instruments, maintaining a sterile environment, and using aseptic techniques when managing wounds.
- Regular Follow-up:
- Establishing a schedule for regular follow-up appointments allows healthcare providers to monitor the patient’s progress, assess the healing of the surgical site, and detect any signs of infection or complications early on.
- Research and Quality Improvement:
- Ongoing research and quality improvement initiatives in surgical techniques, infection prevention protocols, and postoperative care contribute to the development of best practices and continuous improvement in patient outcomes.
Preventing sternal infections requires a collaborative effort involving healthcare providers, patients, and support staff. By implementing these preventive strategies, the risk of sternal infections can be significantly reduced, leading to better overall patient outcomes and recovery.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, treatment, and personalized medical recommendations. The content is based on general knowledge and may not reflect the most recent advancements in medical science. The author and publisher are not responsible for any potential consequences of the information presented in this blog post.
Stay updated—subscribe now for informed empowerment!

