Introduction to Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a significant health concern affecting men globally. This type of cancer originates in the prostate gland, a small, walnut-shaped organ that produces seminal fluid. Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men, particularly those over the age of 50. It is crucial to be well-informed about prostate cancer due to its high prevalence and the potential impact on quality of life.
The purpose of this FAQ is to provide comprehensive answers to some of the most common questions and concerns related to prostate cancer. By addressing these queries, we aim to shed light on various aspects of the disease, including its symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. Understanding prostate cancer can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and seek timely medical advice if needed.
Awareness and education play a vital role in the early detection and successful management of prostate cancer. This FAQ serves as a resource to help you navigate through the complexities of the disease, offering reliable information and expert insights. Whether you are seeking basic knowledge or detailed explanations, this guide is designed to provide valuable support in your journey towards better understanding prostate cancer.
What is Prostate Cancer?
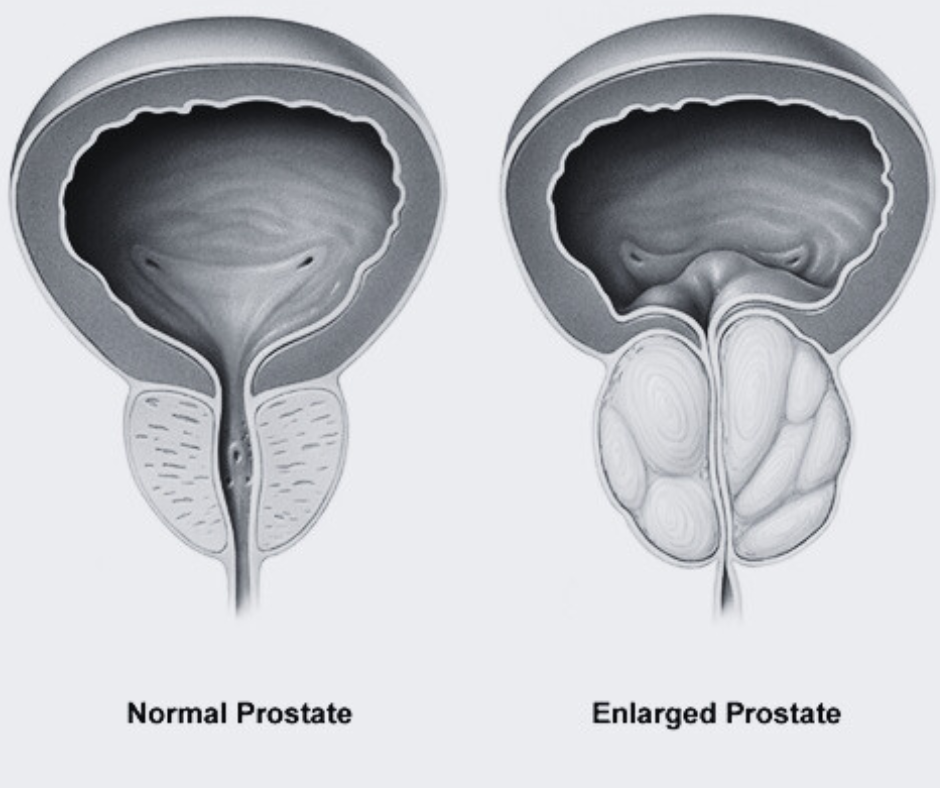
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped gland in males that produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. Located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum, the prostate plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. The development of prostate cancer begins when cells in the prostate gland start to grow uncontrollably. These abnormal growths, or tumors, can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
The basic biology of cancer involves the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells. This transformation typically occurs due to mutations in the DNA of cells. In the case of prostate cancer, these mutations lead to rapid cell division and growth of abnormal cells within the prostate gland. Unlike normal cells, which grow and divide in a controlled manner, cancer cells continue to grow and divide without the usual checks and balances. These malignant cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body through a process known as metastasis.
Prostate cancer often grows slowly and may initially remain confined to the prostate gland, where it might not cause serious harm. However, while some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly. Understanding the nature of prostate cancer, its development, and its impact on the male reproductive system is essential for early detection and effective treatment. Regular screening and awareness of symptoms can help in managing and reducing the risk associated with this common type of cancer among men.
What are the Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer?
Understanding the risk factors for prostate cancer is crucial for early detection and prevention. Various elements, both genetic and environmental, contribute to the likelihood of developing this condition. Below, we delve into the primary risk factors associated with prostate cancer.
Age: Age is a significant risk factor for prostate cancer. The probability of developing prostate cancer increases as men grow older, with most cases diagnosed in men aged 65 or older. This correlation underscores the importance of regular screenings for older men.
Family History: A family history of prostate cancer can considerably elevate a man’s risk. If a close relative, such as a father, brother, or son, has been diagnosed with prostate cancer, the likelihood of developing the disease doubles. This risk intensifies with the number of affected family members.
Race: Racial background also plays a role in prostate cancer risk. African American men are at a higher risk compared to men of other races. They tend to develop prostate cancer at younger ages and often have more aggressive forms of the disease. Conversely, Asian and Hispanic men have a lower risk.
Diet and Lifestyle: Diet and lifestyle choices can influence prostate cancer risk. A diet high in red meat and dairy products and low in fruits and vegetables has been linked to an increased risk. Additionally, obesity and a sedentary lifestyle are contributing factors. Engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight can help mitigate this risk.
Genetic Predispositions: Certain genetic mutations can predispose individuals to prostate cancer. Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are known to increase risk, as well as Lynch syndrome. Genetic counseling and testing may be advisable for those with a strong family history of these mutations.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors may also enhance prostate cancer risk. These include exposure to toxic chemicals, such as those found in some pesticides and industrial chemicals. Occupational hazards, such as working with cadmium or in the rubber industry, have also been linked to increased risk.
By recognizing these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps towards monitoring and potentially reducing their risk for prostate cancer. Regular screenings, particularly for those with higher risk factors, can facilitate early detection and more effective treatment.
What are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer, a significant health concern for men worldwide, often presents with a range of symptoms, though it is noteworthy that early-stage prostate cancer frequently has no noticeable symptoms. This asymptomatic nature can make early detection challenging, underscoring the importance of regular screenings for individuals at risk.
When symptoms do manifest, they commonly relate to urinary functions. One of the primary symptoms is difficulty urinating, which can include a weak or interrupted flow of urine, the need to urinate frequently, especially at night, and a feeling that the bladder has not completely emptied. These signs are often mistaken for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate, making medical consultation crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Another symptom that may arise is hematuria, or blood in the urine, which can be alarming and warrants immediate medical attention. This symptom can be indicative of advanced prostate cancer, as it may suggest the presence of tumors affecting the urinary tract.
Pelvic discomfort is also a symptom associated with prostate cancer. This can range from a general feeling of discomfort in the pelvic area to more specific pain in the hips, thighs, or lower back. This pain can be due to the cancer spreading to the bones, a common site for prostate cancer metastasis.
While these symptoms can be indicative of prostate cancer, they are not definitive and can overlap with other less serious conditions. Therefore, it is essential for individuals experiencing any of these symptoms to seek medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause. Early detection through regular screenings, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal exams (DRE), remains a critical strategy in managing and treating prostate cancer effectively.
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
Prostate cancer diagnosis involves multiple methods to ensure accuracy and thoroughness. One of the primary diagnostic tools is the PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) test. This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by both cancerous and noncancerous tissue in the prostate. Elevated PSA levels can indicate the presence of prostate cancer, although high levels can also be caused by other conditions such as prostatitis or an enlarged prostate.
In addition to the PSA test, a digital rectal exam (DRE) is commonly performed. During a DRE, a healthcare provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland for any irregularities or lumps. While this exam can be uncomfortable, it is a crucial step in identifying abnormalities that may suggest cancer.
When PSA levels are elevated or abnormalities are detected during a DRE, a prostate biopsy is often recommended. In this procedure, small samples of prostate tissue are removed and examined under a microscope to check for cancer cells. The biopsy can be guided by transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) or, more commonly in recent practices, MRI to improve accuracy.
Imaging tests also play a significant role in diagnosing prostate cancer. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of the prostate and surrounding tissues, helping in the detection of tumors and assessment of their extent. Computed Tomography (CT) scans, though less commonly used for initial diagnosis, can be valuable in evaluating whether cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Combining these diagnostic methods enhances the likelihood of an accurate diagnosis. Early detection through PSA tests, DREs, biopsies, and imaging scans is crucial for effective management and treatment of prostate cancer, providing a comprehensive approach to identifying this common yet serious disease.
What are the Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer treatment options vary depending on the stage and grade of the cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and personal preferences. Understanding these options is crucial for making informed decisions. The main treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and newer therapies such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
Surgery (Prostatectomy): One of the most common treatments for prostate cancer is a prostatectomy, which involves the surgical removal of the prostate gland. This can be performed using different techniques, including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or robotic-assisted surgery. The choice of method depends on factors such as the surgeon’s expertise and the patient’s specific condition.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. There are two main types: external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), which directs radiation from outside the body, and brachytherapy, which involves placing radioactive seeds inside the prostate. Both methods aim to destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Hormone Therapy: Also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), hormone therapy aims to reduce levels of male hormones (androgens) that can fuel cancer growth. This treatment can be achieved through medications or surgical procedures. It is often used in conjunction with other treatments, especially in advanced or recurrent cases.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. It is generally reserved for prostate cancer that has spread beyond the prostate or when other treatments have failed. Chemotherapy can help to shrink tumors and alleviate symptoms, although it often comes with significant side effects.
Newer Treatments: Recent advancements in medical research have led to the development of immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer, while targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These treatments offer new hope, especially for patients with advanced prostate cancer.
The choice of treatment is influenced by various factors, including the stage of cancer, the patient’s age, overall health, and personal preferences. Each treatment option has its benefits and potential risks, making it essential to discuss these thoroughly with healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Prostate cancer prognosis largely depends on the stage and grade of the cancer at the time of diagnosis. Generally, early detection significantly improves survival rates. According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year relative survival rate for localized prostate cancer is nearly 100%. For regional prostate cancer, where the disease has spread to nearby areas, the five-year survival rate remains high at around 99%. However, for distant or metastatic prostate cancer, where the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, the five-year survival rate drops to approximately 31%.
The stage of prostate cancer is determined by the size of the tumor, whether it has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body, and the Gleason score, which grades the aggressiveness of the cancer cells. Early-stage prostate cancer, such as Stage I or II, typically offers a better prognosis and more treatment options, including surgery, radiation therapy, and active surveillance. In contrast, advanced-stage prostate cancer, such as Stage III or IV, may require more intensive treatments, including hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and newer targeted therapies.
Advancements in medical research and treatment methodologies have markedly improved the prognosis for prostate cancer patients. Innovations such as robotic-assisted surgery, advanced imaging techniques, and precision medicine have enhanced the ability to detect and treat prostate cancer more effectively. Moreover, ongoing clinical trials continue to explore novel treatment options, providing hope for even better outcomes in the future.
Early detection remains crucial in improving the prognosis for prostate cancer. Regular screenings, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal exams (DRE), are vital in catching the disease at a more treatable stage. Men, particularly those with a family history of prostate cancer or other risk factors, should discuss screening options with their healthcare providers to tailor an appropriate approach to early detection.
Living with Prostate Cancer
Living with prostate cancer involves navigating a series of lifestyle changes and coping strategies aimed at improving quality of life. It’s crucial to understand that while treatment is a significant aspect, managing the day-to-day aspects of life is equally important. Effective management of side effects, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and prioritizing mental health are all integral components of living well with this condition.
Managing the side effects of prostate cancer treatment can be challenging, but several strategies can help. Common side effects include fatigue, urinary issues, and sexual dysfunction. To combat fatigue, it is essential to balance rest and activity, ensuring you get adequate sleep and engage in light exercises. For urinary issues, pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegel exercises, can strengthen the muscles and improve bladder control. Consulting with a healthcare provider for medical interventions can also be beneficial.
Maintaining a healthy diet is another critical aspect of living with prostate cancer. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and help manage treatment side effects. Foods high in antioxidants, such as berries and leafy greens, may provide additional benefits. Limiting the intake of red meat, processed foods, and high-fat dairy products is recommended. Consulting with a nutritionist can provide personalized dietary advice tailored to your specific needs.
Physical activity plays a vital role in managing prostate cancer. Regular exercise can help reduce treatment-related fatigue, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance mood. Activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga can be particularly beneficial. It is advisable to start with moderate exercises and gradually increase intensity based on individual capacity and medical advice.
The importance of mental health support cannot be overstated. Living with prostate cancer can be an emotional journey, and seeking support from mental health professionals, support groups, or counseling services can be immensely helpful. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can also alleviate stress and anxiety. Engaging in hobbies and maintaining social connections can further enhance emotional resilience.
By adopting these strategies, individuals living with prostate cancer can improve their overall well-being and navigate the challenges of their condition more effectively.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive FAQ about prostate cancer, we have covered a wide range of important topics, providing answers to common questions that many individuals have. We discussed the definition of prostate cancer, its stages, and the various treatment options available. Additionally, we explored the symptoms, risk factors, and preventive measures one can take to reduce the likelihood of developing prostate cancer.
The importance of regular screenings cannot be overstated. Early detection through screenings such as the PSA test and digital rectal exam (DRE) can significantly improve treatment outcomes. By being informed about the signs and symptoms of prostate cancer, individuals can seek medical advice promptly, which is crucial for effective management of the disease.
We also highlighted the role of lifestyle choices in managing prostate cancer risk. Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking are proactive steps that can contribute to overall prostate health. Understanding family history and discussing genetic predispositions with a healthcare provider can also help in formulating a personalized strategy for monitoring and prevention.
It is essential to consult healthcare professionals for tailored advice and support. Each individual’s situation is unique, and professional guidance can ensure that the most appropriate and effective measures are taken. Healthcare providers can offer insights into the latest advancements in prostate cancer research and treatment, providing a well-rounded approach to care.
Ultimately, staying informed and proactive about prostate health is vital. By leveraging the knowledge shared in this FAQ, individuals can make educated decisions about their health and well-being. Remember, early detection and informed choices are key to effectively managing prostate cancer and maintaining a high quality of life.
FAQs: Common Questions and Answers
1. What are the early signs of prostate cancer?
Early signs can include difficulty urinating, a weak urine stream, and frequent urination, especially at night. However, some men may not experience any symptoms in the early stages.
2. How is prostate cancer diagnosed?
Prostate cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. If these tests indicate potential issues, a biopsy may be performed.
3. What are the risk factors for prostate cancer?
Age, family history, race, and diet are significant risk factors. Men over 50, those with a family history of prostate cancer, African American men, and those with high-fat diets are at increased risk.
4. Can prostate cancer be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and regular screenings can help reduce the risk.
5. What are the treatment options for prostate cancer?
Treatment options vary based on the stage and may include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy.
6. What is active surveillance?
Active surveillance involves closely monitoring prostate cancer without immediate treatment, suitable for men with low-risk, slow-growing prostate cancer.
7. How does surgery treat prostate cancer?
Surgery, often a prostatectomy, involves removing the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. It is typically recommended for localized cancer.
8. What are the side effects of prostate cancer treatment?
Side effects can include urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, bowel problems, and fatigue, varying based on the treatment type.
9. How effective is radiation therapy for prostate cancer?
Radiation therapy can be highly effective, particularly for localized cancer, and may be used in conjunction with other treatments.
10. What is hormone therapy?
Hormone therapy reduces or blocks the body’s production of testosterone, which prostate cancer cells need to grow, slowing or stopping the cancer’s progression.
11. Can prostate cancer recur after treatment?
Yes, prostate cancer can recur. Regular follow-up appointments and PSA tests are crucial to monitor for recurrence.
12. How often should men get screened for prostate cancer?
Screening recommendations vary, but generally, men over 50 should discuss screening options with their healthcare provider. Those at higher risk may need to start earlier.
13. What is metastatic prostate cancer?
Metastatic prostate cancer is when cancer has spread beyond the prostate to other parts of the body, such as bones or lymph nodes.
14. How does diet impact prostate cancer risk?
A diet high in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats may lower the risk, while a diet high in red and processed meats, dairy, and unhealthy fats may increase the risk.
15. Is prostate cancer common?
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer among men, particularly affecting those over 50. Early detection and treatment are key to managing the disease effectively.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog post is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and recommendations regarding prostate cancer diagnosis, treatment, and management. Prostate cancer is a complex and individualized condition, and the appropriate course of action may vary from person to person.

